A cell is the structural and functional unit of life. Every living organism existing on this planet is composed of either one or many cells. Living cells are composed of minute organelles, which are collectively called cell organelles. They are membrane-bound structures bounded by a layer of phospholipids found within a cell.
Explore more: Cells
Table of Contents
- What are Mitochondria?
- Structure and Functions Of Mitochondria
- Matrix
- Cristae
- Ribosomes
- Inner membrane
- Outer membrane
- Intermembrane Space
What are Mitochondria?
Mitochondria are known as the powerhouses of the cell. It is involved in different cellular activities like respiration, differentiation, cell signalling, cell senescence, controlling the cell cycle, cell growth and other metabolic activities of the cell. They are rod-shaped, a double membraned organelle found both in the plant as well as animal cells.
The term ‘mitochondrion’ is derived from a Greek word which refers to threadlike granules, and it was first described by German pathologist – Richard Altmann in 1890.
Mitochondria are a double-membrane-bound cell organelle found in most eukaryotic organisms. In all living cells, these cell organelles are found freely floating within the cytoplasm of the cell.
The diagram of Mitochondria is useful for both classes 10 and 12. It is one among the few topics having the highest weightage of marks and is majorly asked in the examinations.
Read More: Mitochondria
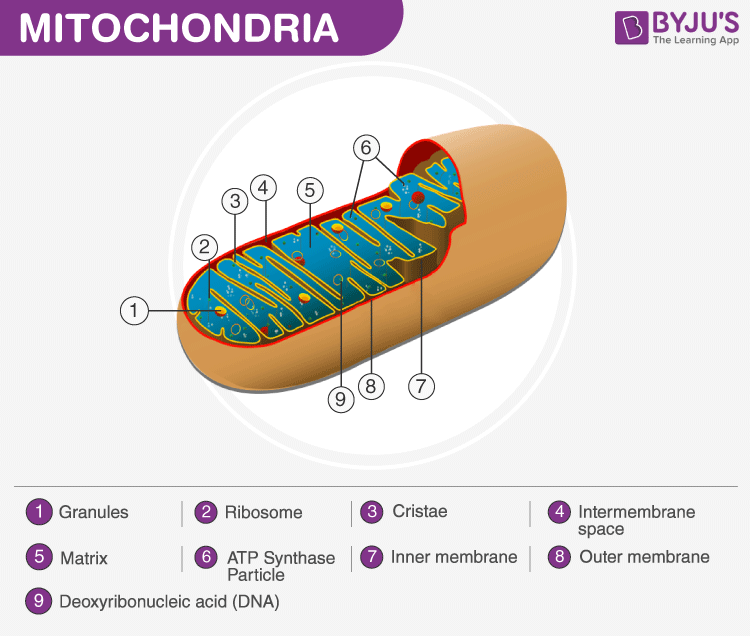
Structure and Functions Of Mitochondria
Matrix
It is a viscous or gel-like fluid containing a mixture of enzymes, ribosomes, inorganic ions, mitochondrial DNA, nucleotide cofactors, and organic molecules. It is involved in cellular respiration and the production of ATP molecules.
Cristae
The inner layer, surrounded by the folds of the mitochondrial matrix, is collectively referred to as Cristae. These inner membranes increase the surface area of the inner membrane and have different roles in cellular respiration, generation of ATP molecules- the energy currency of the cell and other chemical reactions.
Also Read: ATP-Energy Currency of the Cell
Ribosomes
The ribosomes found within the mitochondria are called the mitochondrial ribosome or mitoribosome. It is a protein complex which functions by translating mitochondrial mRNAs encoded in mtDNA.
Also Read: Ribosomes
Inner membrane
The inner mitochondrial membrane holds proteins and functions by permitting the entry of only the selected molecules. Therefore they are also called special membrane transporters.
Outer membrane
The outermost layer of the Mitochondria hold proteins called porins and form channels that allow the movement of proteins across the inner and outer membrane of mitochondria. It also holds a number of enzymes with a wide variety of functions.
Intermembrane Space
This is the area between the inner and outer membranes. It is subdivided into two distinct subcompartments: the intra-cristae space and the lumen. Both are separated by tubular structures measuring 10 to 40nm in diameter called the cristae junctions. The Intermembrane space is mainly involved with the transportation, modification of protein coordinates, apoptosis and also in the regulation of the respiratory chain complexes.
Also Read: Apoptosis
This was a brief introduction to the Diagram Of Mitochondria. For more information about Mitochondria, their structure, functions and other related topics, visit us at BYJU’S Biology.

Comments