Both hyperthyroidism and goiter are hormonal disorders caused by defects in the thyroid gland.
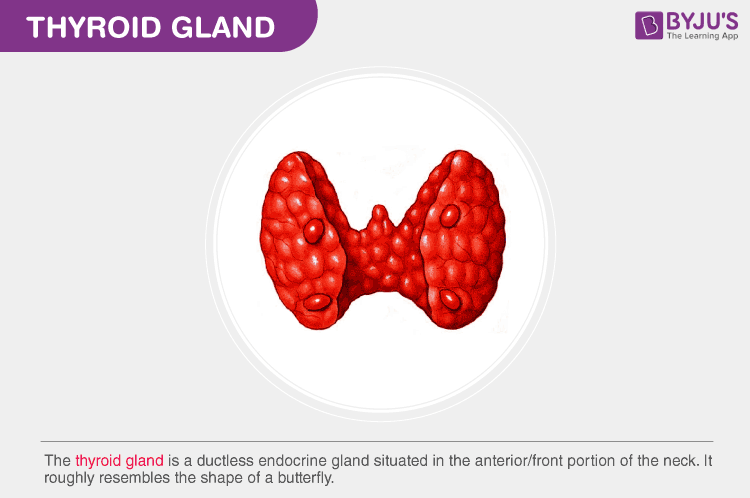
The thyroid gland is one of the largest and ductless glands of the endocrine glands, which is situated in the front portion of the neck and resembles the shape of a butterfly. This gland is responsible for the production of two main thyroid hormones called T3 (Triiodothyronine) and T4 (Thyroxine). The thyroid hormones are mainly involved in the regulation of many functions and aspects of the human body, such as regulation of :
- Bone density.
- Bodyweight.
- Energy levels.
- Body temperature.
- Growth of hair and nails.
Explore more: Endocrine glands and their Hormones
What is Hyperthyroidism?
This is a hormonal disorder caused by the excessive production of T3 and T4 hormones from the thyroid gland. This hormonal disorder is most commonly caused by an auto-immune disorder and females are at higher risks compared to males. Complications related to excessive production of thyroid hormones are excessive hair fall, less or frequent periods, infertility, osteoporosis, brittle bones, weakness, etc.
Explore more: Functions of thyroid hormones
What is Goiter?
The enlargement of the thyroid gland irrespective of its pathology is called goiter. The term goiter is mainly derived from the Latin word – Guttur, which refers to the throat. It can also be defined as the uneven growth of the thyroid gland. This is more common in females than males, especially after the age of 40 years, i.e., after menopause.
Explore more: Goiter
Let’s learn the differences between hyperthyroidism and goiter.
Hyperthyroidism and Goiter – Comparisons
| The hormonal disorder in which the thyroid gland is overactive and produces large quantities of the thyroid hormone. | This hormonal disorder results in an enlarged thyroid gland near the neck region. |
| The most common forms of hyperthyroidism include Graves disease, Plummer disease and toxic adenoma. | The most common forms of goiter include simple goiter and toxic goiter. |
There are various factors responsible for the cause of hyperthyroidism:
|
There are various factors responsible for the cause of goiter and it includes:
|
| Thyroid hormone level tests, blood tests and other tests for hyperthyroidism are based on individuals. | Thyroid hormone test, ultrasonography, MRI, Chest radiography, Isotope scan, thyroid ultrasound, etc. |
| Symptoms vary – Fatigue, weight loss, nervousness, excessive sweating, decreased concentration, irregular and scanty periods, rapid or irregular heart rate, thinning or smooth velvety skin and increased bowel movements. | Symptoms generally vary with age, sex, rate of growth, pain in the swelling area, duration, etc. The common symptoms include pain and difficulty while swallowing and breathing. |
| Medications include antithyroid drugs, Radioiodine and surgery in very rare cases. | Medication to control the hormonal level, Radioiodine and surgery in very rare cases. |
Also Refer: Differences Between Turner Syndrome and Klinefelter Syndrome.
This article concludes the introduction to hyperthyroidism and goiter and their differences. Stay tuned to BYJU’S Biology to learn more in detail about the different types of deficiency diseases, along with their causes, symptoms, and their treatments.
Comments