What is Photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is a biological process that uses light energy to synthesise organic compounds. Most green plants and some bacteria use this type of autotrophic nutrition. These organisms are called photoautotrophs. In the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll, the organisms convert carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates. Also, oxygen is released as a by-product. This process plays a vital role in maintaining the Earth’s oxygen content.
Extended Reading: Photosynthesis
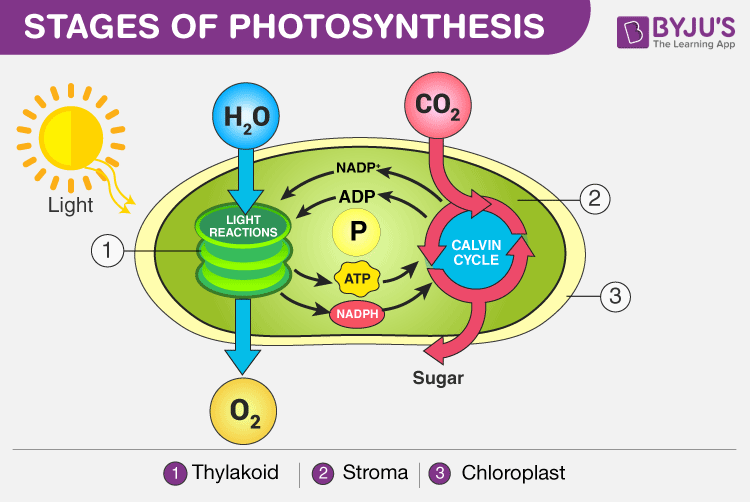
What is Chemosynthesis?
Here, the biological conversion of inorganic substances into organic compounds happens by utilizing chemical energy. Many underwater organisms and bacteria that thrive in the dark use chemosynthesis to produce food.
The chemical energy stored within the bonds of hydrogen sulfide and methane is used by the organisms to prepare their food. There is no sunlight or chlorophyll involved. Sulfur is the usual by-product.
Difference between Photosynthesis and Chemosynthesis
Both photosynthesis and chemosynthesis are autotrophic modes of nutrition. Let us see the differences between them.
Photosynthesis |
Chemosynthesis |
|
It is a process of converting water and carbon dioxide to glucose and oxygen in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll. |
It is a process by which bacteria produces carbohydrates, sulfur and water. |
|
The presence of sunlight is necessary. Hence, this process occurs only during the day. |
Sunlight is not required for chemosynthesis. Hence, it can occur both day and night. |
|
Chlorophyll is required for this process. |
Chlorophyll is not necessary for this process. |
|
Oxygen is formed as a by-product. |
Sulfur and water are formed as a by-product. |
|
Photoautotrophs – Green plants, cyanobacteria and green algae. |
Chemoautotrophs – Sulfur bacteria. Iron-oxidising bacteria and nitrogen-fixing bacteria. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between chemosynthetic and photosynthetic bacteria?
What are photoheterotrophs?
These are heterotrophic organisms that cannot synthesise carbohydrates from carbon dioxide. They rely on organic compounds from the environment. But they use light for their energy (ATP). Examples – Green non-sulfur bacteria, purple non-sulfur bacteria, etc.
What is the light-independent process of photosynthesis?
The photosynthesis process involves two stages. The light-dependent stage and light-independent stage. The light-independent stage is also known as Calvin’s cycle. This cycle is seen in most of the photosynthetic eukaryotes, and also in some photosynthetic bacteria.
Also Read: Light Reaction and Dark Reaction

Keep Exploring BYJU’S Biology for more exciting topics.
Comments