Trophoblast
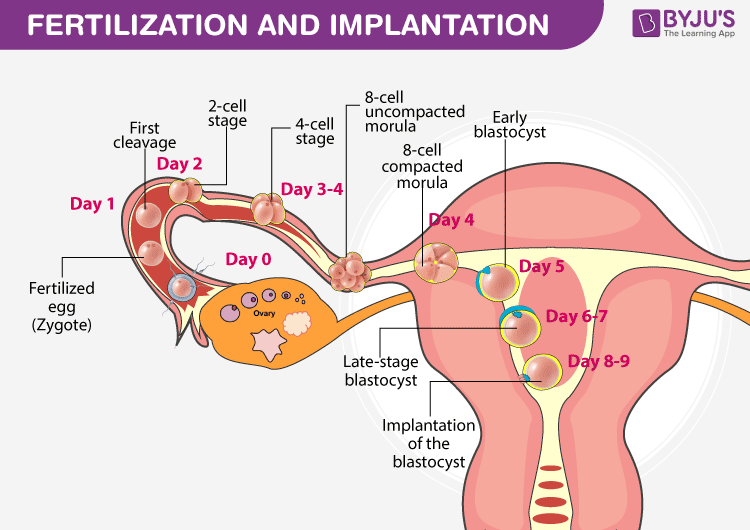
The male and female gamete fuses to form a zygote. The zygote undergoes mitotic division to form blastomeres. They further divide to form a blastocyst. As it develops, it further moves into the uterus. The blastomere cells in the blastocyst are arranged into an outer layer called the trophoblast. The inner cells of the trophoblast are termed inner cell mass. Later, the trophoblast gets attached to the endometrium of the uterus. It is the inner cell mass that gets differentiated as an embryo.
Functions of Trophoblast
- The trophoblast forms the outer layer of the blastocyst. Thus, their main role is to provide nutrition to the developing embryo.
- They also help in the embryo implantation process.
- Placenta – After implantation, chorionic villi (finger-like projections) on the trophoblast get surrounded by the maternal blood and uterine tissue. The uterine tissue and chorionic villi get integrated to form the placenta. Thus, the trophoblast aids in the formation of the placenta.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a blastocyst?
A blastocyst is a stage in embryo development. The zygote undergoes mitotic division as it moves towards the uterus. They form several daughter cells known as blastomeres. They continue to divide and form a blastocyst. The inner cell mass of the blastocyst eventually develops into an embryo.
What is the role of a placenta?
Placenta aids in oxygen and nutrient supply to the developing embryo. They also remove carbon dioxide and waste products from the embryo. All this happens via the umbilical cord, which is a connection between the placenta and the embryo.
Extended Reading: Placenta
What is a morula?
Morula is also a part of the embryo development process. The zygote divides to form a blastomere. An embryo with eight to six blastomeres is termed a morula. It is the morula that gets transformed into a blastocyst.
Also Read:Implantation
Keep exploring BYJU’S Biology for more exciting topics.
Comments