Table of Contents
Guttation
Guttation is the process of secretion of water droplets from the pores of some vascular plants like grass. Guttation is often confused with dew droplets that condense from the atmosphere onto the plant’s surface. The liquid of guttation comprises a variety of inorganic and organic compounds which mainly include potassium and sugars. A white crust remains on the leaf surface.

Mechanism of Guttation
Under the condition where the soil is flooded with rainwater and humidity is high in the atmosphere, the plant’s root system absorbs excess water. As a result, hydrostatic pressure develops in the roots that force the water upwards. Hence the water involving other soluble cell components is forced out of the xylem present in the Epithem tissue.
As a result, stomata which are filled with water are forced out by the root pressure. The liquid is forced out of the pores where the stomata offer no resistance. Transfer cells can also help in the retrieval of minerals from xylem elements and secrete them out along with water.
Guttation vs Transpiration
Here are some of the major differences between Guttation and Transpiration which makes them two distinct phenomena.
| Guttation | Transpiration | |
| 1 | Occurs during nighttime. | Occurs during daylight. |
| 2 | Water lost in guttation is rich in minerals. | The transpired water is pure. |
| 3 | Water is lost as a liquid. | Water is lost in the form of vapours. |
| 4 | The process takes place through hydathodes. | Stomata perform this process. |
| 5 | Guttation is an uncontrolled phenomenon. | Transpiration is a controlled and regulated phenomenon. |
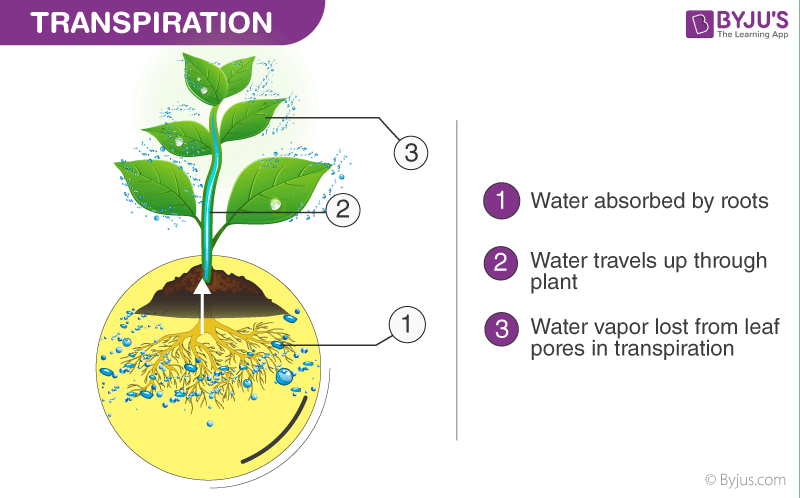
Transpiration in Plants
Transpiration does not occur during the night because the stomata are closed. When the soil has a high moisture content, the water enters the roots because the water potential of the roots is less than that in the soil. The water gets accumulated in the plant and creates a small root pressure. This root pressure forces the water to exude through the leaf tip, hydathodes or water glands, forming droplets. The guttation process is observed the most when transpiration is suppressed and relative humidity is maximum, as seen during the night.
Also Read: Difference between transpiration and guttation
To learn more about guttation, visit BYJU’S.

very nice