Octopuses are small, soft bodied molluscs that belong to the class cephalopoda. The class also contains other molluscs like squids and cuttlefish. They are eight-armed and are hence classified in the order Octopoda.
Octopuses grow quickly and are usually short lived, living up to 6 months or so. They reside in different regions of the ocean such as the seabed, coral reefs, pelagic waters, abyssal depths and intertidal zones.
Classification
|
Kingdom |
Animalia |
|
Phylum |
Mollusca |
|
Class |
Cephalopoda |
|
Order |
Octopoda |
|
Genus |
Octopus |
Octopus – Diagram
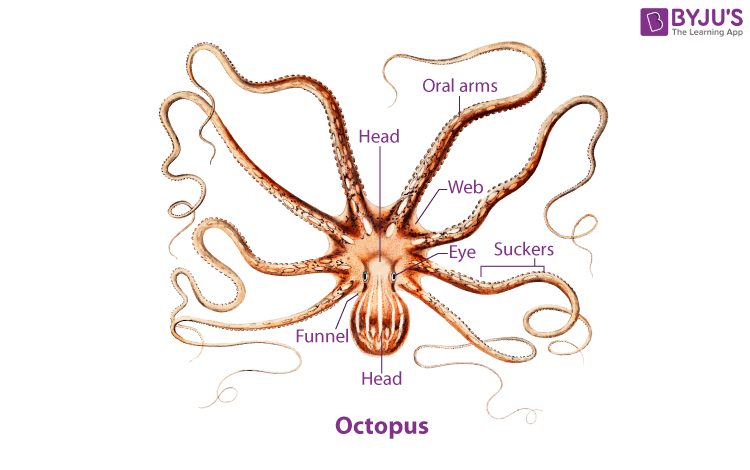
Morphology
- Octopuses have a bilaterally symmetrical body with two eyes and a two-part beaked mouth.
- They are of different sizes, the smallest one O. arborescens being as small as 5cm while the largest species can grow up to 5.4 metres tall.
- They have a saccular body with big complex eyes and large contractile arms that can grow up to 9 metres long.
- Each of the eight arms has two rows of fleshy suckers that have a strong holding power.
- The arms are joined at the base that is known as skirt. At the centre of the skirt lies the mouth.
- The mouth has sharp, file-like structures called the radula that helps in tearing away the flesh and also drilling shells.
- The mantle is a bulbous and hollow structure that is fused at the back of the head and contains all the vital organs such as gills.
- The mantle is connected to the exterior with a funnel-like structure called the syphon.
- The mantle helps in respiration by drawing up water which passes through the gills and is finally expelled by the syphon.
- Their soft body can be squeezed easily that allows them to pass even through small gaps.
- They swim by jetting water from the syphon and trailing their appendages behind their body.
- It secretes an inky substance to protect itself from predators. The inky substance is mostly paralysing in nature and affects the sensory system of the attacker.
- This inky substance is stored in an ink sac that is located below the digestive gland. The gland is situated near to the funnel, this allows easy shooting of the ink to scare away the predator.
- They feed on crabs, fishes, planktons and other crustaceans found in the water.
- The circulatory system of the organism is of closed type and it has three hearts.
- It has a complex nervous system with the highest brain to body mass ratio of all invertebrates.
Reproduction
- Octopuses exist as different sexes, males and females.
- The males have a specialised arm-like structure called hectocotylus that helps in inserting sperm pockets into the female’s mantle cavity.
- The most common species O.vulgaris mates during the winter season and lays eggs under rocks or rock crevices.
- The egg takes about four to eight weeks to hatch. Till then, the female octopus guards the eggs and cleans them regularly by agitating water.
Visit BYJU’S Biology for more information.
Also Read:
Comments