“Oogenesis is the process of formation of female gametes.”
Oogenesis is the type of gametogenesis through which ova, also called the female gametes are formed and the produced female gamete is known as an ovum. In general terms, the female gametes are referred to as eggs, but the word egg can involve various stages of development, therefore, the significance of an egg varies based on the type of organisms.
For example, Once, after the birds lay eggs, the entire development of an egg until the transformation of the egg into the chick occurs within the eggs. Whereas, in the placental mammals, once the egg is fully developed and fertilized, it begins to divide and we no more call it as an egg. We need to recall that every ovum has to be haploid and consist of a single copy of every chromosome.
Also Read: Difference between spermatogenesis and oogenesis
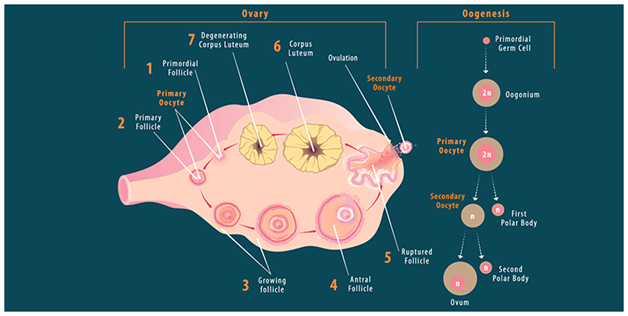
Oogenesis Diagram
Oogenesis is the differentiation of the ovum. Spermatogenesis and oogenesis are two different forms of gametogenesis. Gametogenesis in the male is known spermatogenesis and in the female is known oogenesis, which results in the formation of ova in the female. Oogenesis completely differs from spermatogenesis in several ways.
Let us have a detail view on oogenesis, its process, ovulation and fertilization.
Table of Contents
What is Oogenesis?
Oogenesis is the process of formation of female gametes. This process begins inside the fetus before birth. The steps in oogenesis up to the production of primary oocytes occur before birth. Primary oocytes do not divide further. They either become secondary oocytes or degenerate.
Oogenesis occurs in the outermost layers of the ovaries. Oogenesis starts with a germ cell called oogonium and undergoes mitosis to increase in number. The process of oogenesis takes place in the following three stages:
- Pre-natal
- Antral
- Pre-ovulatory
Also Read: Spermatogenesis
Process of Oogenesis
The process of oogenesis is completed in the following three stages:
Pre-natal Stage
The primary oocyte grows while being arrested in meiosis-I. The follicular cells proliferate and form a stratified cuboidal epithelium. Such cells are known as granulosa cells. These cells secrete glycoproteins to form zona pellucida around the primary oocyte.
Antral Stage
The fluid-filled area, present between granulosa cells, combines to form a central fluid-filled space called the antrum. These are known as secondary follicles. In every month cycle, these secondary follicles develop under the influence of follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone.
Pre-Ovulatory Stage
This stage is induced by LH surge, and meiosis-I completes here. Two haploid cells of unequal sizes are formed within the follicle. One of the daughter cells that receive less cytoplasm forms a polar body. This cell does not participate in ovum formation. The other daughter cell is known as the secondary oocyte. The two daughter cells undergo meiosis-II. The polar body replicates to form two polar bodies, while the secondary oocyte arrests in the metaphase stage of meiosis-II.
Ovulation
Development of oocyte takes place in ovaries. Every oocyte is neighboured by follicle cells to form a follicle.
As the menstrual cycle starts, primary oocytes initiate to grow bigger, and follicle cells rise in number, causing the follicle to grow larger too.
Normally, some nurturing oocytes degenerate and leave just one follicle to mature. Here, fraternal twins may be born, which are distinct genetically.
When a follicle attains maturity, the primary oocyte finishes its primary meiotic division and becomes secondary oocyte. Soon after, the follicle breaks and secondary oocyte is liberated in the fallopian tube even when the second meiotic division has not happened. This release of a secondary oocyte from ovaries is known as ovulation.
Also Read: Gametogenesis – Spermatogenesis and Oogenesis in Humans
Fertilization
Meiosis-II is completed on fertilization. This gives off a third polar body. If the fertilization does not occur, the oocyte degenerates 24 hours after ovulation while remaining arrested in meiosis-II cell division.
The major difference between oogenesis and spermatogenesis is that oogenesis begins in the fetus prior to birth.
Also Read: Fertilization And Implantation
To know more about what is oogenesis and the process of oogenesis, keep visiting BYJU’S website or download BYJU’S app for further reference.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Oogenesis?
Oogenesis is the process of formation of female gametes. It is the type of gametogenesis through which ova or the female gametes are formed, and this female gamete is known as an ovum
What are the stages of Oogenesis?
The process of oogenesis has three stages. They are as follows:
- Pre-natal Stage
- Antral Stage
- Pre-Ovulatory Stage
Explore more details about Oogenesis or other topics by registering at BYJU’S.

Comments