Skeletal System
The skeletal system functions as the basic framework of a body and the entire body are built around the hard framework of Skeleton. It is the combination of all the bones and tissues associated with cartilages and joints. Almost all the rigid or solid parts of the body are the main components of the skeletal system. Joints play an important role in the skeletal system as it helps in permitting the different types of movements at different locations. If the skeleton were without joints, then there would be no sign of the movements in the human body.
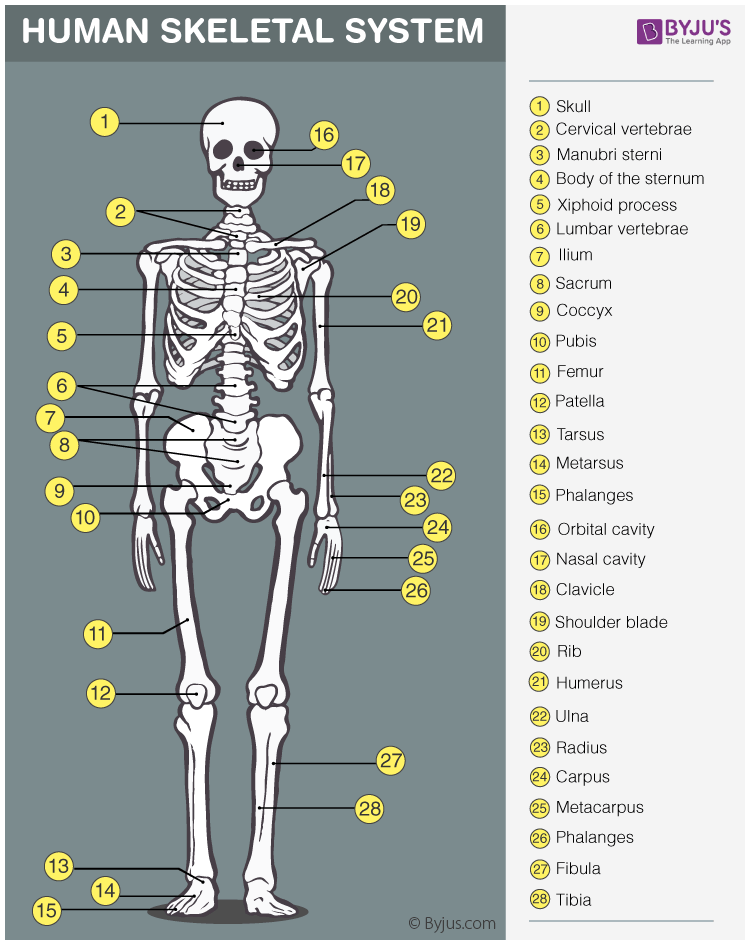
Skeletal System Anatomy
This skeletal system can be divided into the axial and appendicular systems. In an adult body, it is mainly composed of 206 individual bones which are organized into two main divisions:
- Axial skeleton
- Appendicular skeleton.
Axial skeleton
The axial skeleton runs along the body’s central axis, therefore it is called the central core of the human body. The axial skeleton is composed of 80 bones and it consists of:
- Skull Bone – It includes 8 cranial bones, 14 facial bones, 6 auditory ossicles, and the Hyoid Bone
- The bone of the Thoracic Cage – It includes 25 bones of the thorax- a breastbone and 24 ribs.
- The bone of the Vertebral column- It includes 24 vertebrae bones, the sacrum bone, and the coccyx bone.
Also check: Function of Parietal Bones
Appendicular skeleton
The appendicular skeleton is composed of 126 bones and it comprises of the-
- Pelvic girdle
- Upper Limbs
- Lower Limbs
- Shoulder Girdle or the Pectoral
Read more: Parts and Names of Human Skeleton
Skeletal System Physiology
The primary functions of the skeletal system include movement, support, protection production of blood cells, storage of minerals and endocrine regulation.
Support
The primary function of the skeletal system is to provide a solid framework to support and safeguard the human body and its organs. This helps in maintaining the overall shape of the human body.
Also check: Function of Short Bones
Protection
The skeletal system also helps to protect our internal organs and other delicate body organs, including the brain, heart, lungs and spinal cord by acting as a buffer. Our cranium (skull) protects our brain and eyes, the ribs protect our heart and lungs and our vertebrae (spine, backbones) protect our spinal cord.
Movement
Bones provide the basic structure for muscles to attach themselves onto so that our bodies are able to move. Tendons are tough inelastic bands that attach our muscle to that particular bone.
Also read: Femur Structure and Function
Storage
The bone matrix of the skeletal system is mainly involved in storing or preserving different types of essential minerals which are required to facilitate growth and repair of the body cells and tissues. The cell-matrix acts as our calcium bank by storing and releasing calcium ions into the blood cell when required.
Regulation of Endocrine glands
The bone cells present within the skeletal system plays an important role in releasing the synthesized hormones from the respective endocrine glands for the further requirement by the body for different metabolisms. Apart from these functions, the skeletal system also contributes to the regulation of blood sugar.
To learn more about the structure and functions of the skeletal system, visit BYJU’S.
Also check:

Comments