The majority of flowering plants reproduce sexually i.e., through seed formation. We know sexual reproduction is incomplete without fertilization. The male and female gametes have to meet for fertilization and further development. Have you ever wondered how plants ensure their continuity on earth despite their immobile nature? Let us answer the same by having a brief discussion on a process called pollination.
Pollination in Plants
Reproduction is the life process, which helps an organism procreate its own offspring. There are a lot of events involved in this. In plants, pollination is one among them.
Pollination Definition
“Pollination is defined as the pre-fertilization event or process, where pollen grains from anther are transferred to the stigma of a flower.”
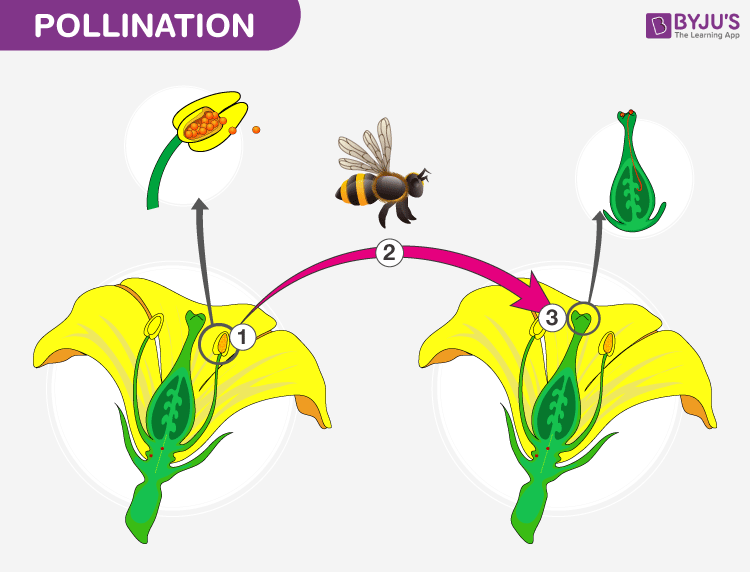
Plants are immobile. They can’t copulate with each other by themselves. They need a vector for this. Pollination is the process that helps to unite the male and female gametes and thus helps in fertilization. It can be broadly classified into two, cross-pollination and self-pollination and this is achieved with the help of a variety of vectors/agents. For successful pollinations, it must occur between the same species.
Explore more about Pollination
Types of Self-pollination and Cross-pollination
Pollinations can occur either within a flower or between flowers of the same plant or flowers of different plants. Depending on this, pollinations are of three types, namely:
Autogamy
It is a type of self-pollination where the transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma takes place within the same flower. Coordinated opening, maturation and exposure of the anther and stigma are necessary for autogamy. There are two conditions for autogamy to take place:
- Anther-stigma synchronization; when the pollen is released, stigma should be ready to receive it.
- The position of or distance between anther and stigma. Both should be close enough for pollination.
In chasmogamous flowers, anther and stigma are exposed. The exposed reproductive parts give a chance of cross-pollination in chasmogamous flowers. While in cleistogamous flowers anther and stigma are not exposed but lie close enough for transfer. Thus, the chances of cross-pollination in cleistogamous flowers are almost none. In addition, they barely require a pollinating agent.
Geitonogamy
Geitonogamy is the type of self-pollination where the transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma takes place between different flowers in the same plant. Though it seems like cross-pollination and takes place with the help of pollinators, both the gametes have the same plant as their origin.
Xenogamy
Xenogamy is the cross-pollination where the pollen grain transfer occurs across flowers of two different plants. In other words, the transfer of pollen from the anther of one plant to the stigma of another plant.
Each type of pollination has its own merits. Xenogamy leads to a new variety, whereas autogamy helps to preserve parental characters. Plants have various adaptations to accomplish this task. In addition, flowers depend on certain pollinating agents which can either be biotic or abiotic. These biotic and abiotic pollinating agents are collectively termed pollinators.
Pollinating Agents
Plants utilise both biotic and abiotic agents for pollination.
Biotic agents – Animals, insects, butterflies, etc. Pollination by insects is called entomophily and pollination by birds is called ornithophily. Pollination by vertebrates is known as zoophily.
Abiotic agents – Wind and water. Wind pollination is known as anemophily and pollination by water is called hydrophily.
Learn more about Pollination, its types, and other related topics at BYJU’S Biology
Recommended Video:

Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Pollination?
Pollination is a biological process in which the pollen grains are transferred from an anther (male part of a flower) to the stigma (female part of a flower). There are two types of pollination:
- Self-Pollination
- Cross-Pollination
What are the Pollinating Agents? Enlist agents for pollination.
How does Pollination occur in Plants?
Name the plants which undergo Self- pollination?
What Is Self-Pollination?
What are pollen grains?
What is Cross-Pollination?
Name the plants which undergo Cross pollinations?
Air pollination is mainly observed in?
Further Reading:

Thanks. I think BYJU’S learning program is a good choice for other people. We will be looking at this page