What is Ammonium Oxalate (C2H8N2O4)?
Ammonium Oxalate is an inorganic compound with chemical formula C2H8N2O4. It is also called as diammonium oxalate or diammonium salt.
Ammonium Oxalate is an oxalate salt with ammonium. Ammonium Oxalate is a strong dicarboxylic acid. This compound consists of ammonium ions and oxalate ions in a ratio of 2:1.
Table of Contents
- Structure of Ammonium Oxalate
- Properties of Ammonium Oxalate
- Uses of Ammonium Oxalate
- Health Hazards
- Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Under standard conditions, it is a colourless to white salt. It is odourless and non-volatile in nature. It mixes slowly with water. It occurs naturally in many vegetables and plants.
Structure of Ammonium Oxalate – C2H8N2O4
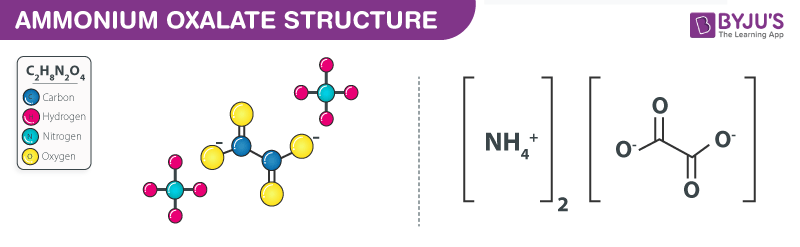
Structure of Ammonium Oxalate
Properties of Ammonium Oxalate – C2H8N2O4
| C2H8N2O4 | Ammonium Oxalate |
| Molecular Weight/ Molar Mass | 124.1 g/mol |
| Density | 1.5 g/cm3 at 65.3° F |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Melting Point | 70°C |
It is a colourless crystalline solid under standard conditions (as shown below) with a melting point of 374.5K in hydrated form and 463K in anhydrous form. It is soluble in water and alcohol but insoluble in ether.

Uses of Ammonium Oxalate
- It is found in the body of vertebrates which is produced by metabolism of ascorbic acid or glyoxylic acid.
- Ammonium oxalate exists in mineral form as Oxammite.
- It is used as a reducing agent.
- It is used as an analytical reagent.
- To preserve blood outside the body, it is used as an anticoagulant.
Health Hazards Associated with Ammonium Oxalate
- Ammonium oxalate dust upon ingestion or excessive inhalation causes systemic poisoning.
- Contact with eyes causes irritation. Contact with skin causes irritation of severe burns.
- Absorbed through skin. Contact with skin causes irritation and a physician should be contacted if anyone develops any signs or symptoms and suspects that they are caused by exposure to ammonium oxalate.
Learn more about the Structure, physical and chemical properties of C2H8N2O4 from the experts at BYJU’S. For the latest updates on ammonium oxalate register with BYJU’S now!
Other important links:
| Ammonia molecule | Oxalic acid |

Comments