What is Carbon monoxide?
Carbon monoxide is a colourless gas and is represented as CO.
It has one carbon atom which is covalently bonded to one oxygen atom. It is also known as Carbonic oxide or Carbon oxide. It is a toxic gas. It is odourless and has no taste. It is a poisonous gas that when inhaled causes asphyxiation and damage to the Central Nervous System. When it combines with haemoglobin it forms Carboxyhemoglobin. It is widely used as industrial fuel for various operations.
Table of Contents
- Properties of Carbon monoxide
- Carbon monoxide Structure
- CO Uses
- Recommended Video
- Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Properties of Carbon monoxide – CO
| CO | Carbon monoxide |
| Molecular Weight/ Molar Mass | 28.010 g/mol |
| Density | 789 kg/m3 |
| Boiling Point | −191.5 °C |
| Melting Point | −205.02 °C |
Carbon monoxide Structure
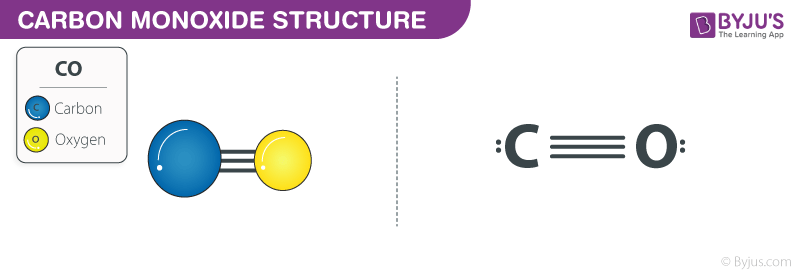
Carbon monoxide Structure – CO
CO Uses
- It is used in the production of methanol
- It is used in the packaging of fresh meat products such as fish, beef, etc
- It is used as a strong reducing agent
- It is used in infrared lasers
- It is used in beverages and food like jam and cola to acidify them
- It is used to remove rust from the surface to metals.
Recommended Video
Carbon Compounds

Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Why carbon monoxide is dangerous?
What appliances can cause carbon monoxide?
How does carbon monoxide affect the human body?
Can you recover from carbon monoxide poisoning?
How do you get rid of carbon monoxide?
Also Read:
| Citric Acid | Calcium Hydroxide |
| Carbonic Acid | Ethylene Glycol |
Learn more about the chemical behavior and importance of Carbon monoxide (CO) with the expert faculties at BYJU’S – India’s largest education company.

Comments