What are Copolymers?
A copolymer is a polymer that is made up of two or more monomer species. Many commercially important polymers are copolymers. Examples include polyethylene-vinyl acetate (PEVA), nitrile rubber, and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). The process in which a copolymer is formed from multiple species of monomers is known as copolymerization. It is often used to improve or modify certain properties of plastics.
A homopolymer is a polymer that is made up of only one type of monomer unit. The difference in the constitution of a copolymer and a homopolymer is illustrated below.
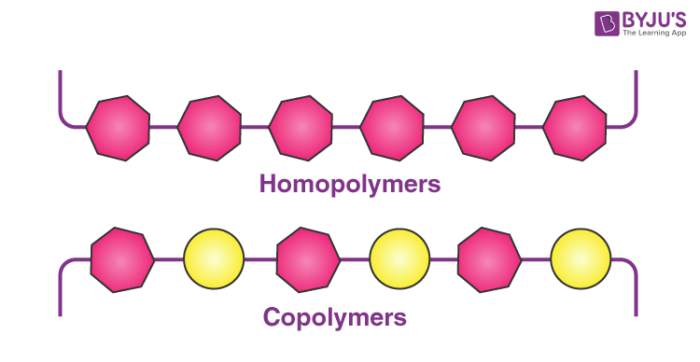
Copolymers are categorized based on their structures. Those containing a single chain are known as linear copolymers whereas those containing polymeric side chains are called branched copolymers.
Table of Contents
Classification of Copolymers
What are the Different Types of Linear Copolymers?
Linear copolymers can be further classified into several categories such as alternating and statistical copolymers. This classification is done based on the arrangement of the monomers on the main chain.
Block Copolymers
-
-
-
- When more than one homopolymer units are linked together via covalent bonds, the resulting single-chain macromolecule is called a block copolymer.
- A junction block is an intermediate unit at which the two homopolymer chains are linked.
- A diblock copolymer contains two homopolymer blocks whereas a triblock copolymer contains three distinct blocks of homopolymers.
- An example of such a polymer is acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, commonly referred to as SBS rubber.
- An illustration describing the structure of a block copolymer which is made up of the monomers ‘A’ and ‘B’ is provided below.

-
-
Statistical Copolymer
-
-
-
- Statistical copolymers are the polymers in which two or more monomers are arranged in a sequence that follows some statistical rule.
- Should the mole fraction of a monomer be equal to the probability of finding a residue of that monomer at any point in the chain, the entire polymer is then known as a random polymer.
- These polymers are generally synthesized via the free radical polymerization method.
- An example of a statistical polymer is the rubber made from the copolymers of styrene and butadiene.
- An illustration describing the structure of a statistical copolymer is provided below.

-
-
Alternating Copolymers
-
-
-
- Alternating copolymers contain a single main chain with alternating monomers.
- The formula of an alternating copolymer made up of monomers A and B can be generalized to (-A-B-)n.
- Nylon 6,6 is an example of an alternating copolymer, consisting of alternating units of hexamethylene diamine and adipic acid.
- An illustration describing the general structure of these polymers is provided below.

-
-
Periodic Copolymers
These polymers feature a repeating sequence in which the monomers are arranged in a single chain. An illustration of the structure of a periodic copolymer made up of monomers A and B is provided below.
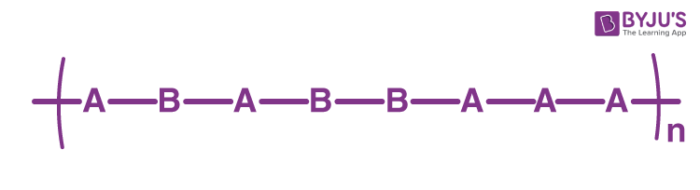
Gradient and Stereoblock Copolymers
The single-chain copolymers in which the composition of monomers gradually changes along the main chain are called gradient copolymers. If the tacticity of the monomers varies with different blocks or units in the polymer, the macromolecule is known as a stereoblock copolymer.
What is a Branched Copolymer?
As the name suggests, a branched copolymer is a polymer in which the monomers form a branched structure. Some important types of branched copolymers include star, comb, grafted, and brush copolymers.
A star copolymer contains several polymeric chains that are attached to the same central core.
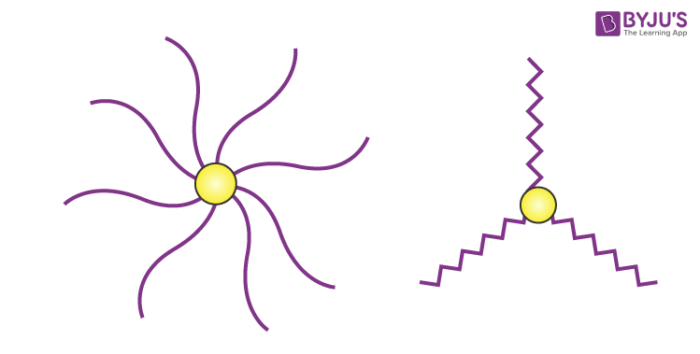
The structures of different types of star-shaped copolymers are illustrated above. They consist of a multifunctional centre to which three or more polymer chains are attached.
Graft Copolymers
Branched copolymers featuring differently structured main chains and side chains are known as graft copolymers. An illustration detailing the structure of a graft copolymer made up of monomers A and B is provided below.
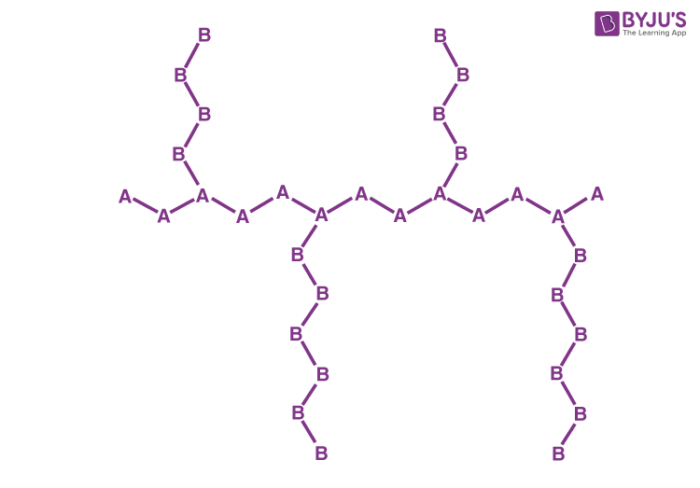
The main chain or the side chains of these polymers can be copolymers or homopolymers. High impact polystyrene is an important example of a graft copolymer. They can be synthesized from free radical polymerization.
To learn more about copolymerization and other important types of polymerization reactions, register with BYJU’S and download the mobile application on your smartphone.

A lot of thanks for this lovely study material.