What are the p-Block Elements?
P block elements are those in which the last electron enters any of the three p-orbitals of their respective shells. Since a p-subshell has three degenerate p-orbitals each of which can accommodate two electrons, therefore in all there are six groups of p-block elements.
P block elements are shiny and usually a good conductor of electricity and heat as they have a tendency to lose an electron. You will find some amazing properties of elements in a P-block element like gallium. It’s a metal that can melt in the palm of your hand. Silicon is also one of the most important metalloids of the p-block group as it is an important component of glass.
In this section, we will study the elements of P-block and their properties.
Table of Content
- Related Topics
- Do you know where P-block elements are in the Periodic Table?
- Recommended Videos
- Characteristics of p-Block Elements
- Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Related Topics
P block elements consist of
- Group 13 Elements: Boron family
- Group 14 Elements: Carbon family
- Group 15 Elements: Nitrogen family
- Group 16 Elements: Oxygen family
- Group 17 Elements: Fluorine family
- Group 18 Elements: Neon family
Do you know where P-block elements are in the Periodic Table?
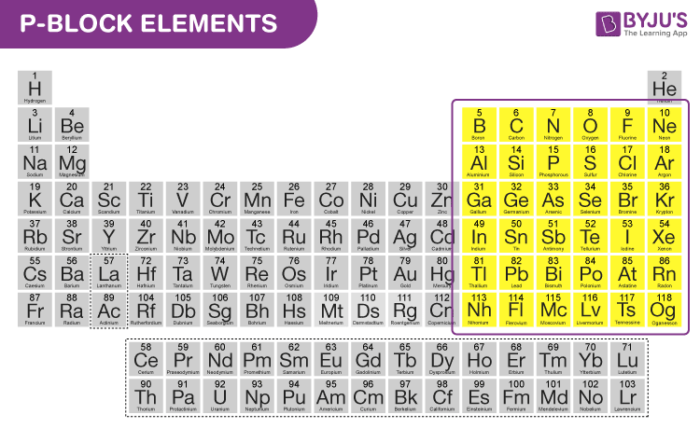
P block elements are nothing but the element in which the last electron enters the outermost p-subshell. P block starts from the 13th group and goes till the 18th group in the periodic table.
You must have seen that coal is used in villages to cook food. It is nothing but a P-block element i.e. carbon. Diamonds used for making beautiful ornaments are also made up of carbon. Aluminium foil made up of aluminium is also made up of the p block element.
Recommended Videos
P-block Concept Booster – PYQs Practice

p-Block Revision in One-shot

Related Videos
P-Block Elements

P-Block Elements-Top 7 Questions

P-Block Elements-Top 15 Questions

P Block Elements MCQs

p-Block Elements – Important Topics
p-Block Elements – Important Questions
Characteristics of p-Block Elements
- The general electronic configuration of p-block elements is ns2np1-6(except He). Whereas the inner core electronic configuration may differ. Just because of this difference in the inner core, there are changes in both physical and chemical properties of the elements.
- The oxidation state of elements in p – block is maximum when it is equal to a total number of valence electrons i.e. the sum of S and P electrons. One of the most interesting facts about the p-block elements is that it contains both non-metals and metalloids.
The first member of the p block elements differs from other elements in two major respects:
- First is the size and each and every property which depends upon the size.
- The second difference applies only to the p-block element, which arises from the effects of d-orbitals in the valence shell of heavier elements.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is the P block element?
The p-block is the region of the periodic table that includes columns IIIA to column VIIIA and does not include helium. There are 35 p-block elements, all of which are in p orbital with valence electrons. The p-block elements are a group of very diverse elements with a wide range of properties.
Why are they called P block elements?
The elements s-block and p-block are so-called because their valence electrons are either in an orbital s or p. These are often called Standard Components, in order to differentiate them from the sequence of transformation and internal transformation.
What are the 17 non-metals?
Non-metals are on the extreme right side of the periodic table, except for hydrogen, found in the upper left corner. The 17 non-metal elements are: Hydrogen, Helium, Carbon, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Fluorine, Neon, Phosphorus, Sulphur, Chlorine, Argon, Selenium, Bromine, Krypton, Iodine, Xenon, and Radon.
What are the properties of non-metals?
Usually non-metal is brittle when it is solid and typically has low thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity. Chemically, non-metals tend to have relatively high energy from ionization, contact with electrons, and electronegativity. As they react with other elements and chemical compounds, they receive or exchange the electrons.
What is the general electronic configuration of P block elements?
The general electronic external configuration for p block components is ns2np(1−6). (n−1)d(1−10)ns(0−2) is the general electronic outer configuration of d block components. The general electronic outer F block element configuration is (n−2)f(0−14)(n−1)d(0−1)ns2.

What is Catenation and which elements greatly show this property?
The property of an element that gives it the ability to form covalent bonds with other atoms of same element (resulting in the formation of a chain of atoms) is called catenation. Carbon exhibits the property of catenation to a great extent. For example, carbon atoms can combine to each other to form long chains, branched chains and closed rings.