We get to hear the terms like oxidation and reduction a lot in CBSE class 12th Chemistry and to be precise, oxidation means gaining oxygen in a chemical reaction We will be looking at oxidation and reduction from two different points of view.
The chemical reactions which involve the transfer of electrons from one chemical substance to another. These electron-transfer reactions are termed as oxidation-reduction reactions or redox reactions. These reactions are accompanied by energy changes in the form of heat, light, and electricity etc. The oxidation and reduction reaction also involve the addition of oxygen or hydrogen to different substances.

Table of Content
- What is oxidation?
- What is reduction?
- Recommended videos
- Classical Idea of oxidation and reduction reactions
- Oxidation and reduction in terms of electron transfer
- Common Redox reactions
- How to balance the Redox reaction?
- Oxidation vs Reduction
- Summary
- FAQs
What is Oxidation?
According to Classical or earlier concept oxidation is a process which involves the addition of oxygen or any electronegative element or the removal of hydrogen or any electropositive element.
According to electronic concept oxidation is defined as the process in which an atom or ion loses one or more electrons.
What is Reduction?
According to Classical or earlier concept reduction is a process which involves the addition of hydrogen or any electropositive element or the removal of oxygen or any electronegative element.
According to electronic concept reduction is defined as the process in which an atom or ion gains one or more electrons.
Recommended Videos
Oxidation & Reduction – Concept + Quiz

Learn Redox Reactions with Examples in 30 Mins

Classical Idea of Oxidation and Reduction reactions:
Oxidation reactions involve:
1. Addition of oxygen:
C + O2 → CO2 (oxidation of carbon)
2. Addition of electronegative element:
Fe + S → FeS (oxidation of Iron)
3. Removal of hydrogen:
H2S + Br2 → 2 HBr + S (oxidation of sulphide)
4. Removal of electropositive elements:
2 KI + H2O2 → I2 + 2 KOH (oxidation of iodide)
Oxidising agent is a substance which brings about oxidation. In the above examples O2, S, Cl2, Br2, and H2O2 are oxidising agents.
Reduction reactions involve:
1. Addition of hydrogen:
N2 + 3 H2 → 2NH3 ( reduction of nitrogen)
2. Addition of electropositive element:
SnCl2 + 2HgCl2 → SnCl4 + Hg2Cl2 ( reduction of mercuric chloride)
3. Removal of oxygen
ZnO + C → Zn + CO (reduction of zinc oxide)
4. Removal of electronegative element
2FeCl3 + H2 → 2FeCl2 + 2HCl (reduction of ferric chloride)
Reducing agent is a substance which brings about reduction. In the above examples H2, HgCl2 and C are Reducing agents.
Note: A substance, which undergoes oxidation, acts as a reducing agent while a substance, which undergoes reduction, acts as an oxidising agent.
Oxidation and Reduction in terms of Electron Transfer
- This is the most commonly used definition of oxidation and reduction and most widely applicable.
- In this case, Oxidation is the loss of electrons and Reduction is the gain of electrons.
- A very clever mnemonic to remember this concept is oil rig.
OIL RIG
Oxidation is loss Reduction is gain
Oxidation and Reduction reactions are always interlinked. Because electrons are neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction, oxidation and reduction always occur in pairs, it is impossible to have one without the other. In the below reaction Magnesium gets oxidized by losing two electrons to oxygen which gets reduced by accepting two electrons from magnesium.
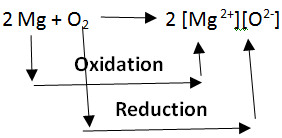
Since oxidation and reduction cannot occur individually, they as a whole are called ‘Redox Reactions’. The reactant that oxidizes the other reactants is called as the Oxidizing agent and reactant that reduces is called Reducing agent. There is quite some confusion about the aspect of whether oxidizing agents accept or give away electrons.
The following steps can help you figure it out.
- An oxidizing agent oxidizes the other reactants
- This must mean that the oxidizing agent is getting reduced
- Oxidation is the loss of electrons (OIL RIG)
- So an oxidizing agent must gain electrons
Common Redox Reactions
The three common redox reactions are discussed below:
1. Combustion reaction – It is a type of redox reaction which occurs between molecular oxygen and compound to form oxygen-containing products.
2C8H18+25O2 → 16CO2(g)+18H2O
2. Disproportionation reaction – It is a type of redox reaction where a single reactant is reduced and oxidized. It is also known as an auto-oxidation reaction.
3ClO−(aq) → ClO3−(aq)+2Cl−(aq)
3. Single replacement reaction – It is a type of redox reaction that involves two elements switching places within a compound. It is also known as a single displacement reaction.
Zn(s)+2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq)+H2(g)
How to Balance Redox Reaction?
Every chemical reaction must be balanced according to the “Law of conservation of mass”. The chemical equations which involve oxidation and reduction can also be balanced with the help of the following methods
- Oxidation number method.
- Ion electron method ( or half reaction method)
Oxidation number method:
The various steps involved in balancing a redox equation by oxidation method are discussed here through an example.
Example: Balance the chemical equation by the oxidation number method
CuO + NH3 → Cu + N2 + H2O
Solution:
Step-1 : Write the oxidation number of each atom in the skeleton equation
Step-2 : Identify the atoms which undergo change in oxidation number.

Step-3 : Calculate the increase and decrease in oxidation number w.r.t reactant atoms.

Step-4 : Equate the increase and decrease in oxidation number on the reactant side.

Step-5 : Balance the number of Cu and N atoms on both sides of the equation.
![]()
Step-6 : Now balance H and O atoms by hit and trial method.
![]()
Note:(i) In the reactions taking place in acidic medium, balance the O atom by adding the required number of H2O molecules to the side deficient in O atoms. Then balance the H atoms by adding H+ to the side deficient in H atoms.
(ii) In the basic medium, first balance the number of negative charges by adding the required number of OH– ions to the side deficient in the magnitude of the charges. Then add H2O molecules on the other side in order to balance the OH– ions added.
Ion electron method ( or half reaction method):
It is based on the Principle that the electrons lost during oxidation half reaction in a particular redox reactions is equal to the electrons gained in the reduction half reaction. The method is called half reaction method. The balancing is completed in the following steps:
Example: Balance the chemical equation by ion-electron method:
Cr2O72- + Fe2+ + H+ → Cr3+ + Fe3+ + H2O
Step-1 : Write the oxidation number of each atom in the skeleton equation:  Step-2 : Find out the species involved in the oxidation and reduction half reactions:
Step-2 : Find out the species involved in the oxidation and reduction half reactions:

Step-3 : Balancing oxidation half reaction:
As oxidation number increases 1, add one e– on the product side to balance change in O.N.
![]()
Step-4 : Balancing reduction half reaction:
The decrease in oxidation number per Cr atom is 3 and the total decrease in O.N for two Cr atoms is 6. Therefore, add 6e– on the reactant side. In order to balance O atoms add 7 H2O molecules on the product side then balance H atoms by adding 14 H+ on reactant side.
![]()
Step-5 : Adding the two half reactions:

Oxidation vs Reduction
When a reactant loses electrons during a reaction, it is called oxidation. When a reactant accumulates electrons during a reaction, it is called reduction. When metals react with acid, this is a common occurrence. When a reactant loses electrons during a reaction, it is called oxidation. When a reactant accumulates electrons during a reaction, it is called reduction. When metals react with acid, this is a common occurrence.
A reduction-oxidation or redox reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which reduction and oxidation occur at the same time. The reduced species receives electrons whereas the oxidised species loses them. An oxidation process does not need the presence of oxygen, despite its name.
Summary
Originally, the term oxidation was used to describe reactions where an element combines with oxygen. For example, the oxidation of magnesium involves the chemical reaction between magnesium metal and oxygen to form magnesium oxide.
The word reduction comes from the “to lead back” sense of the Latin stem. Thus, everything that leads back to magnesium metal in the previously mentioned chemical reaction implies reduction. An example of the reduction of magnesium oxide to magnesium metal is a reaction between magnesium oxide and carbon at 2000 degrees Celsius to form magnesium metal and carbon monoxide.
Due to the changes in oxidation states that occur without the independent transfer of electrons, many reactions in organic chemistry can be classified as redox reactions. For instance, the oxidation state of carbon atoms in the wood increases during the combustion of wood with molecular oxygen, and that of oxygen atoms decreases as carbon dioxide and water are produced. The oxygen atoms are reduced, formally receiving electrons, while the carbon atoms are oxidised, losing electrons. Therefore, oxygen is the oxidising agent and the reducing agent in this reaction is carbon.
Related Video
Mole Concept, Stoichiometry & Redox Reaction

Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is the difference between oxidation and reduction?
It loses electrons in a reaction in chemistry if a substance is oxidized. It gains electrons in a reaction if a substance is reduced. A reaction within which there is both oxidation and reduction is called a REDOX reaction.
Why are oxidation and reduction Important?
Oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions are significant because they are the main natural or biological and artificial energy sources on this planet. Oxidation of molecules usually releases large amounts of energy by removing hydrogen and replacing it with oxygen.
What is the oxidation-reduction process?
It oxidizes the material that gives electrons. It forms a chemical called rust when iron reacts with oxygen because it has been oxidized (the iron has lost some electrons) and the oxygen has been reduced (the oxygen has gained some electrons). The cause of reduction is oxidation.
What is called the oxidation state?
The oxidation state, also referred to as the amount of oxidation, defines a chemical compound’s degree of oxidation (loss of electrons) of an atom. Antoine Lavoisier first used the term oxidation to describe a substance’s reaction with oxygen.
What is an example of slow oxidation?
Iron rusting and wood-rotting are good examples of gradual oxidation.
What is meant by the oxidation-reduction reaction?
A chemical reaction where the oxidation number of an atom, ion, or molecule changes by losing or gaining an electron is called an oxidation-reduction reaction.
What is the major difference between oxidation and reduction?
Reduction is the gain of electrons whereas oxidation is the loss of electrons.
To learn more about oxidation and reduction, register with BYJU’S and download our app.
Read more:

I’m getting too beneficial with your information about science and mathematics
Very nice app