What are Phenolic Acids?
Phenolic acids, also known as phenol carboxylic acids, are aromatic acids that contain a phenolic ring and a carboxyl functional group.
Flavonoids and phenolic acids constitute one of the most widespread groups of plant phenolics. Because of their significance in plants and human health, a deeper understanding of flavonoid concentration and biological activities may suggest their potential as therapeutic agents, as well as predicting and monitoring the quality of medicinal herbs, would be useful.
Therefore, these compounds contain at least one aromatic ring, one hydroxyl group, and one carboxyl group. Salicylic acid is one of the simplest phenolic acids. The structure of a salicylic acid molecule is illustrated below.
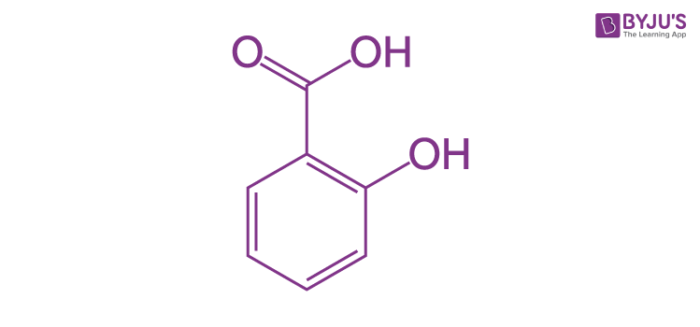
Other important naturally occurring phenolic acids include hydroxycinnamic acids and hydroxybenzoic acids. Hydroxycinnamic acids are derived from non-phenolic cinnamic acid molecules whereas hydroxybenzoic acids are derived from non-phenolic benzoic acid molecules.
Table of Contents
- Natural Occurrences of Phenolic Acids
- Examples of Phenolic Acids
- Phenolic Acid Uses
- Frequently Asked Questions
Natural Occurrences of Phenolic Acids
- Many dried fruits contain phenolic acids.
- Phenolic acids can also be found in horse grams.
- The Basidiomycetes species of mushroom is known to contain these organic compounds.
- These aromatic acids can also be found in soil humus.
- Human urine also contains some phenolic acids.
Examples of Phenolic Acids
Some examples of phenolic acids are listed below.
- Protocatechuic acid (PCA)
- p-hydroxybenzoic acid (PHBA)
- Vanillic acid
- Caffeic acid
- p-Coumaric acid
- Ferulic acid
- Syringic acid
- Sinapinic acid
Phenolic Acid Uses
- Phenolic compounds are among the phytochemicals present in cereals which promote health. Because of their antioxidant properties, phenolic compounds are receiving a lot of attention. The most common types of phenolic compounds found in whole grains are phenolic acids and flavonoids.
- Phenolic acids are the most abundant in cereals, and flavonoids also exist in grains. The total phenolic and flavonoid content of 20 genotypes of small grain cereals, including bread wheat, durum wheat, rye, hulless barley and hull-less oat, was analysed. These phytochemicals had the highest content in hull-less barley followed by hull-less oat, rye, durum wheat, and bread wheat.
- The role of gut microbiota in the biotransformation of phytochemicals, including phenolic acids, is widely accepted, causing the formation in the circulation of food-derived metabolites and excreted in the urine.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is phenolic acid used for?
Phenolic acids are readily absorbed through the walls of your intestinal tract, which can be beneficial to your health as they serve as antioxidants that avoid cellular damage due to free-radical oxidation reactions. If you eat them regularly, they may also promote anti-inflammatory conditions in your body.
What does phenol do to the body?
Concentrated phenol applied to the skin can cause serious skin damage. Short-term exposure to high levels of phenol in animals has caused respiratory tract irritation and twitching of the muscles. In animals, long-term exposure to high phenol levels causes damage to the heart, kidneys, liver and lungs.
What is phenol used for medically?
Phenol was used to disinfect the skin and ease itching. Phenol is also used in products such as Chloraseptic as an oral analgesic or anaesthetic to treat pharyngitis. In addition, phenol and its related compounds are used in the treatment of surgically grown toenails, a procedure called phenolization.
What is the difference between alcohol and phenol?
Alcohol is an organic compound where molecule is made up of one or more groups of hydroxyl which are further attached to a carbon atom. Phenol, on the other hand, is a compound containing a group of hydroxyls bound directly to an aromatic group of hydrocarbons.
To learn more about Phenolic acids and other important types of aromatic compounds, register with BYJU’S and download the mobile application on your smartphone.

Comments