What is Potassium Nitrate (KNO3)?
KNO3 is a chemical compound with the chemical name Potassium Nitrate.
Potassium nitrate also called saltpetre or nitre is a white solid soluble in water formed by fractional crystallisation of sodium nitrate and potassium chloride solutions. It occurs naturally as nitre in rocks in India, South Africa and Brazil. When heated it decomposes to give the nitrite and oxygen. Unlike sodium nitrate it is non-deliquescent. Potassium nitrate is used in gunpowder, fertilisers and in the laboratory preparation of nitric acid.
Table of Contents
- Synthesis of Potassium Nitrate (KNO3)
- Properties of Potassium Nitrate – KNO3
- Potassium Nitrate structure (KNO3 Structure)
- Potassium Nitrate (KNO3 ) Uses
- Potassium Nitrate (KNO3 ) Health Hazards
- Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Potassium nitrate is the most common desensitising agent in over-the-counter dentifrices. At a concentration of 5%, potassium nitrate in conjunction with sodium or monofluorophosphate fluoride significantly reduces symptoms within 2 weeks of daily use. Potassium ions penetrate the length of the dentinal tubule and block the repolarization of the nerve ending.
Frequent and regular application of a potassium nitrate dentifrice is necessary to avoid recurrence of symptoms, maintain a high abundance of extracellular potassium ions, and maintain the interdental nerves in a hyperpolarized state. Potassium nitrate, often called saltpetre, occurs as an efflorescence in caverns and on soils in arid regions.
Synthesis of Potassium Nitrate (KNO3)
Potassium nitrate is a salt. It is prepared by neutralising acid. When potassium hydroxide neutralises nitric acid potassium nitrate is formed.
KOH + HNO3 → KNO3 + H2O
Neutralising nitric acid always makes “nitrate” salts. Other acids make other types of salts.
Potassium nitrate contains potassium (a soft, light, and silver metal), oxygen, and nitrogen (a colourless and odourless gas). It is an alkali metal nitrate because it is an ionic salt of potassium ions K+ ions and nitrate ions NO3−. It is solid white or sometimes white to dirty grey in colour. Potassium nitrate is soluble in hot water. This compound releases oxygen when heated or decomposed. It is a strong oxidising agent It is widely used in the removal of stumps, fireworks, fertilisers, etc. It is a major constituent of black powder and food preservation techniques.
Properties of Potassium Nitrate – KNO3
| KNO3 | Potassium Nitrate |
| Molecular Weight/ Molar Mass | 101.1032 g/mol |
| Density | 2.109 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 400 °C |
| Melting Point | 334 °C |
Potassium Nitrate structure (KNO3 Structure)
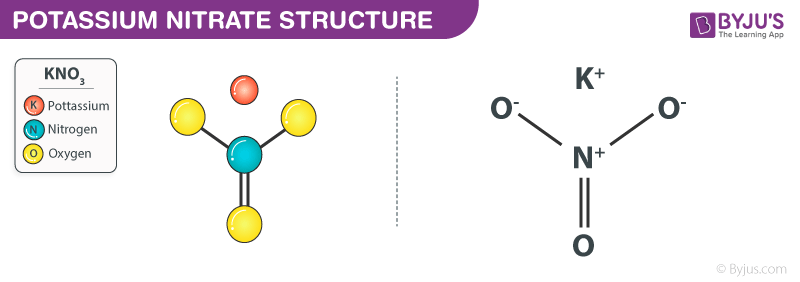
Potassium Nitrate Structure
Potassium Nitrate (KNO3 ) Uses
- It is used as a form of fertiliser as it contains all the macronutrients needed for the plants to grow.
- It is used as gunpowder in explosives such as bombs, grenades, etc.
- Used in the manufacturing and production of cigarettes.
- It is used extensively used in the preservation of hides
- It has medicinal applications such as a diuretic in medicine
- Used in toothpaste to make the teeth less sensitive to pain
- Used in the food industry to preserve meat against microbial agents
Nutritional Value of Potassium Nitrate
Potassium nitrate is effectively absorbed. The synergistic interaction of K+ and NO3– makes it easier for the plant to absorb both nutrients through its roots. Additionally, the negative charge of nitrate and the positive charge of potassium have an affinity for one another, which reduces the likelihood of soil particles being absorbed and prolongs the time that they are available to plants.
Potassium nitrate boosts a plant’s defence resistance against diseases. Short-chain carbohydrates and non-protein nitrogen buildup, which serves as a barrier against bacteria, fungi, nematodes, and viruses, are removed. Potassium nitrate enhances soil water absorption, encourages the commencement and ramification of the root system, and makes plants more drought-tolerant.
Potassium nitrate’s potassium content stops water loss. Because potassium controls the opening and shutting of the stomata, it helps plants use less water by reducing transpiration. Additionally, supplying plants with enough potassium boosts their ability to absorb water from the soil. The salt buildup is prevented by potassium nitrate. Potassium nitrates take the place of the need for more water to remove salts from the soil.
Potassium Nitrate (KNO3 ) Health Hazards
- Potential exposure – Potassium Nitrate is used in chemical analysis, as a food additive in fertilisers in medications as a vasodilator and as an antidote for cyanide poisoning.
- Short term exposure – Potassium nitrate can affect when breathed in. Contact can cause eye and skin burns. Breathing the dust or mist can irritate the nose, throat and lungs and may cause coughing with phlegm. Higher exposures can cause pulmonary edema, a medical emergency that can be delayed for several hours. This can cause death.
- Long term exposure – Repeated skin contact causes dermatitis, drying and cracking. May cause lung irritation, bronchitis may develop. There is limited evidence that potassium nitrite may damage the developing foetus.
- Medical surveillance – If symptoms develop or overexposure is suspected, the following may be useful, blood test for methemoglobin. Lung function tests. Consider chest X-ray after acute overexposure.
- Potassium nitrate is an inorganic salt which has a molecular KNO3 formula. This is a common form of nitrate which has been used for numerous uses as a component, including agricultural preservatives, fertilisers, tree stump removal, rocket propellants, and fireworks.
- Potassium nitrate is a common active ingredient that exerts an anti-sensitive effect in toothpaste. It offers enhanced protection against the painful sensitivity of the teeth to ice, sun, acids, sweets or touch.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Is potassium nitrate harmful to humans?
A number of health hazards can present in potassium nitrate. It can trigger breathing issues when inhaled, including coughing and shortness of breath. Contact with the skin or eye can lead to discomforts such as redness, itching, and pain.
What contains potassium nitrate?
Potassium nitrate is a nitric acid crystalline potassium salt. Many products in households, agriculture, and industry use potassium nitrate. There are examples of toothpaste, fertilisers, fireworks, pesticides and molten salt.
Is potassium nitrate safe in toothpaste?
There is often confusion between nitrates and nitrites. The FDA recognizes nitrates used in potassium nitrate as secure and efficient for use in anti-sensitive dental products. Additionally, temporary pain relief is provided by delicate toothpaste.
What are the dangers of potassium nitrate?
Contact can trigger irritation of the eyes and skin. Potassium nitrate respiration may irritate the nose and throat causing sneezing and coughing. High concentrations may interfere with the blood’s capacity to carry oxygen which causes headache, tiredness, dizziness, and blue skin and lips.
What is potassium nitrite used for?
In the production of heat transfer salts, potassium nitrite is used. Potassium nitrite as a food additive E249 is a sodium nitrite-like preservative and is approved for use in the EU, USA, Australia and New Zealand.
Is potassium nitrate harmful to humans?
Potassium nitrate when breathed in will impact you. * Touch can cause discomfort to the eyes and skin. * Potassium nitrate for breathing can irritate the nose and throat causing sneezing and coughing.”
Is potassium nitrate a carcinogen?
Nither IARC nor the EPA have listed carcinogenicity nitrates. There are however several potential mechanisms that can metabolise nitrates to N-nitroso compounds, some of which are carcinogenic.
What plants benefit from potassium?
Potassium grows good lawns by encouraging deep-rooted lush, robust stems. By supporting solid stems and well-developed flowers it benefits roses and other flowering plants. The farmers depend on potassium to grow good crops. Plants which are rich in carbohydrates like potatoes need potassium to develop tuber.
Learn more about the Structure, physical and chemical properties of KNO3 from the experts at BYJU’S.
Other related links:
| Oxidizing Agent | Potassium Permanganate |


Comments