Mixtures are substances consisting of two or more types of matter. Mixtures are of two types – homogeneous mixture and heterogeneous mixture. In a heterogeneous mixture, the components are not uniformly distributed and there is no particle level homogeneity. For example, suspension.
On the other hand, the mixtures containing the same composition and uniform appearance throughout are stated as homogenous. For example, solutions. We can easily separate a heterogeneous mixture into the respective components of the mixture. Sieving, filtration, hand-picking, etc. are a few common separation techniques used for the heterogeneous mixture. In the case of a homogeneous mixture and sometimes a heterogeneous mixture, we need to use special separation techniques. Evaporation, centrifugation, chromatography, sublimation, separating funnel, etc. are special separation techniques.
Let’s see how to obtain different gases from the air.

Table of Contents
- Separation Techniques: Obtaining Gases from Air
- Step 1:Conversion of air into liquid air
- Step 2:Fractional Distillation
Separation Techniques: Obtaining Gases from Air
We know that air is a homogeneous mixture of gases. It consists of gases like nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, argon, etc. in different proportions. Since it is a homogeneous mixture, we need special separation techniques. Fractional distillation is the technique that is used for obtaining different components from the air.
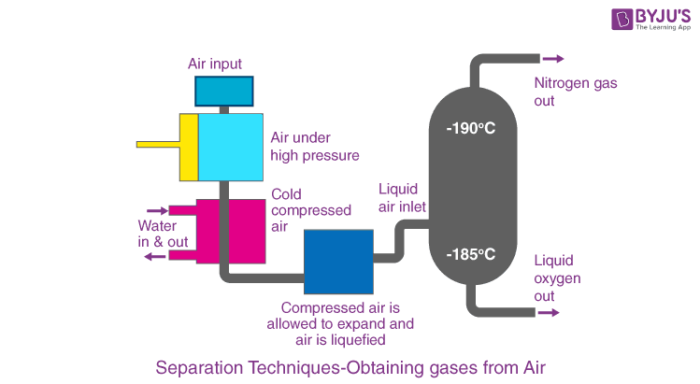
Fractional distillation is a separation method where the difference in boiling points of components is used to separate the liquid mixture into fractions through distillation. The process begins with the liquefaction of air. Let’s try to understand the process with the help of an illustration of the separation of nitrogen from the air.
In order to obtain nitrogen gas from the air, we need to remove the rest of the constituents of air. Before we start, the air is filtered to remove the dust particles and then liquefied.
Step 1:Conversion of air into liquid air
The air which is in gaseous form is converted into liquid air. This is done under high pressure. Under high pressure, the air is compressed and then cooled by reducing the temperature. This results in the formation of air in a liquid form.
Step 2:Fractional Distillation
The liquid air is then passed through the fractional distillation column. Here, the liquid air is allowed to warm up. The bottom of the fractionating column is warmer than the top. Each gas starts to separate at different temperatures according to its boiling point.
Nitrogen has a boiling point of -196 °C while oxygen has -183 °C. The nitrogen gas will start to escape through the outlet and is collected. And then the liquid oxygen will be collected in the fractionating column.
To understand the separation techniques with video lessons, download BYJU’S – The Learning App.

Comments