Agricultural diversification is one of the essential components of economic growth. It is the stage where traditional agriculture is transformed into a dynamic and commercial sector by shifting the traditional agricultural product mix to high standard products, which has a high potential in stimulating production rate. Here, agricultural diversification is supported by a change in technology or consumer demand, trade or government policy, and by transportation, irrigation, and other developments of infrastructure.
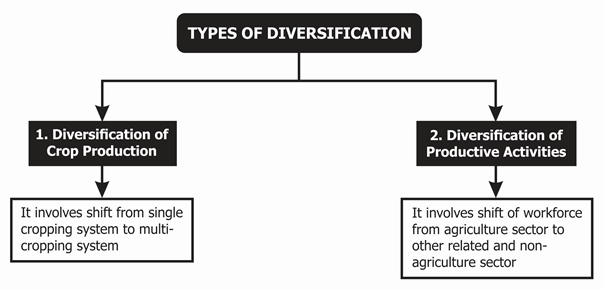
Two aspects of Diversification
- The change in the cropping pattern
- The transformation of the manpower from agricultural work to other associated activities like poultry, livestock, fisheries, etc., and also of the non-agriculture sector
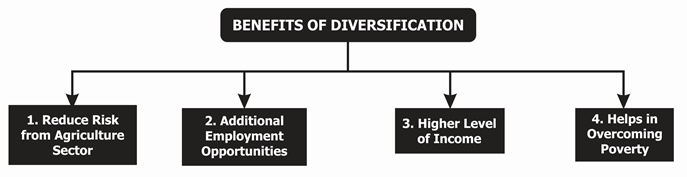
- For rural people, diversification, or focusing on associate activity, is important because it gives them an opportunity to earn extra income and overcome poverty.
Quick link: Infrastructure in India during British Rule
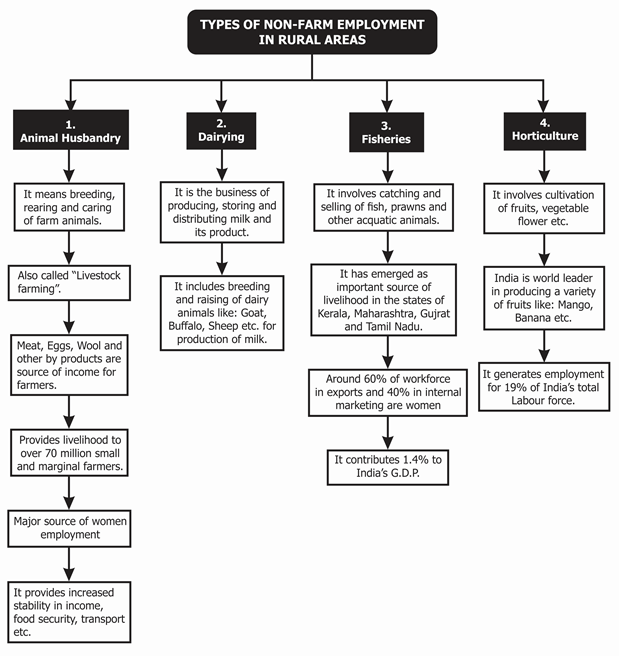
Poultry and Livestock
Animal husbandry – Most of the farmers use the mixed crop-livestock system to increase their standards of living and income. Animal husbandry is an agricultural branch that deals with the practices of farming, breeding, and the care of farm animals like cattle, dogs, sheep, and horses. In India, about 70 million small and medium farmers, labourers, and a large number of women are dependent on the livestock sector.
Fisheries – Aquaculture, or fisheries, is an important part of food production that provides economic security to the millions of people besides livelihood support. In India, the total fish production contribution from inland sources is about 64% and 36% from the marine sector (sea and oceans). Today, fisheries contribute a total of 0.8% to the total GDP.
Horticulture – It is agriculture that deals with the plantations of the garden crop, especially that of vegetables, fruits, flowers, tuber crops, species, and ornamental or medicinal plants. These plants provide food and nutrition besides providing employment. In India, the horticulture sector contributes 6% of GDP and one-third of the agricultural output.
| You Might Also Like To Read: |
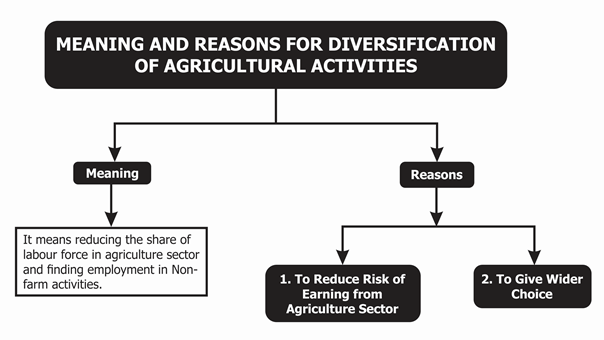
Reason for Diversification of Agricultural Activities
Types of Diversification
Benefits of Diversification
Types of Non-Farm Employment in Rural Areas
Golden Revolution in India
| Also, Explore: |
Short Questions:
| Q.1- Why is agricultural diversification essential for a sustainable livelihood? |
| Answer: It is essential for rural people to generate supplementary and gainful employment, and realising a higher level of income. |
| Q.2- Why do people seek employment in the non-farm sector? |
| Answer: People seek employment in the non-farm sector, as agriculture is already overcrowded and cannot offer additional employment. |
Do you know: What is Globalisation?
For more data on Economics Class 11 Syllabus, Commerce notifications and sample papers for Class 11 Commerce, stay tuned to BYJU’S.

I like it ✨😊