The type of hybridization that occurs in BCl3 is sp2 hybridization. In BCl3 molecule, boron will be the central atom which contains three bonded atoms but no lone pair of electrons. Its steric number is also said to be 3. However, we will discuss how the hybridization occurs in detail below.
| Name of the Molecule | Boron Trichloride |
| Molecular Formula | BCl3 |
| Hybridization Type | sp2 |
| Bond Angle | 120o |
| Geometry | Trigonal Planar |
What is the Hybridization of Boron Trichloride?
To know how the hybridization takes place in boron trichloride we will take the central atom boron and look at a few aspects of it. We will look at the ground state of boron’s electron configuration. It will be 1s2, 2s2, 2p1. To form bonds with chlorine, boron will require three unpaired electrons. In this case, one electron from the 2s is moved to the 2p level. Now the electron configuration will be in an excited state and will be represented as 1s2, 2s2, 2px1, 2py1.
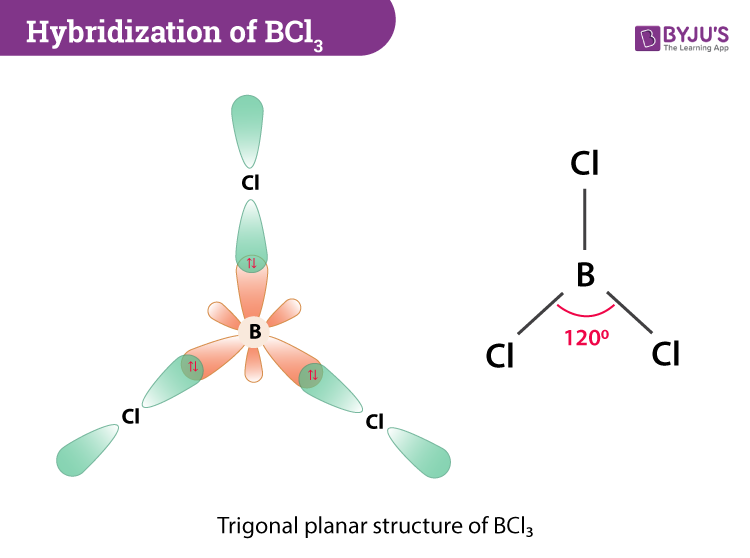
The hybridization of BCl3 now occurs where one 2s and two 2p orbitals of boron will take part in the process to form three half-filled sp2 hybrid orbitals. Each sp2 hybrid orbitals will contain unpaired electrons that will overlap with the unpaired electron in chlorine’s 3p orbital. Three σsp-p bonds are formed between boron’s half-filled sp2 hybrid orbitals and three chlorine atoms.
Important Points To Remember
- During hybridization, one 2s and two 2p orbitals of boron will form three half-filled sp2 hybrid orbitals.
- Each sp2 hybrid orbitals will have an unpaired electron.
- Boron forms 3 σsp-p bonds with three chlorine atoms.
BCl3 Molecular Geometry And Bond Angles

If we look at the structure, BCl3 molecular geometry is trigonal planar. The bond angle is 120o. The central atom also has a symmetric charge around it and the molecule is non-polar.
Read More About Hybridization of Other Chemical Compounds
- Hybridization Of XeF4
- Hybridization Of SF4
- Hybridization Of PCl3
- Hybridization Of Graphite
- Hybridization Of SO3
Chemical Bonding

Comments