Aldehydes and ketones are two different classes of organic compounds yet they exhibit remarkable similarity in chemical reactions. Aldehydes and ketones constitute an important class of organic compounds containing the carbonyl group. An aldehyde has the structure RCH(=O) while a ketone has the structure R2C(=O).
Aldol Condensation
One of the most useful sets of chemical methods for C-C bond formation is the catalytic aldol condensation. The aldol condensation is a self-condensation of two molecules of aldehydes in the presence of a dilute base to yield an aldol.
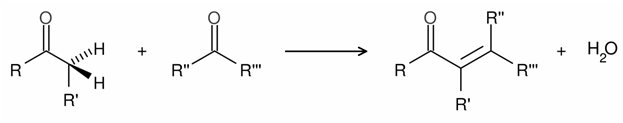
Crossed Aldol Condensation
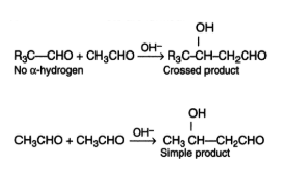
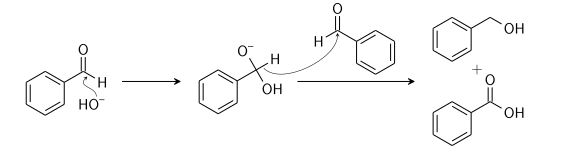
Cannizzaro Reaction
Cannizzaro reaction is a chemical reaction named after Stanislao Cannizzaro, which involves the base-induced disproportionation of two non-enolizable aldehyde molecules to produce a carboxylic acid and a primary alcohol.
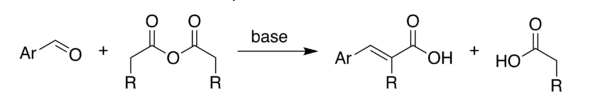
Perkin Reaction
Perkin Reaction is an organic chemical reaction discovered by the English chemist William Henry Perkin. This reaction produces an aromatic acid which is α, β -unsaturated.
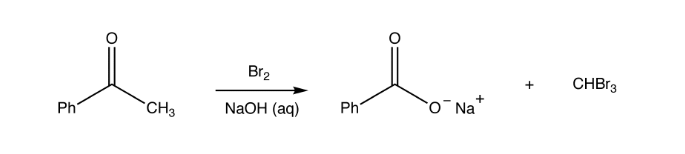
Haloform Reaction
The haloform reaction mechanism begins with the presence of the hydroxide ion disproportionation of the halogen. Haloform reaction involves the interaction of methyl ketones with alkaline halogen solution to give haloform plus a carboxylate ion.
Some Important Aldehydes and Ketones
Aldehydes and Ketones are highly reactive compounds. This is due to the presence of the carbonyl group in these compounds.
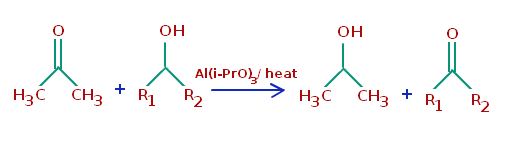
Oppenauer Oxidation
Oxidation of alcohols with acetone or its analogues as the sole Oxidant, hydrogen transfer reaction between alcohols and ketones or aldehydes is another mild and environmentally benign method for oxidation of alcohols.
Meerwein Ponndorf Verley Reduction
Meerwein Ponndorf Verley reduction is the aluminium isopropoxide reduction of the carbonyl group of a ketone or an aldehyde. The reaction is specific to aldehydes and ketones.
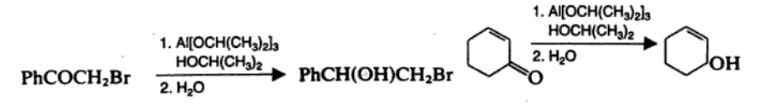
Reformatsky Reaction
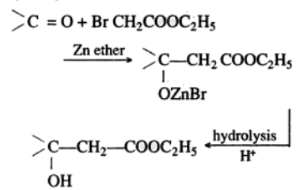
Reformatsky Reaction is a kind of reaction between an alpha-halo ester and a carbonyl compound that can be ketone, aldehyde, or ester. The reaction occurs mostly in the presence of zinc. The reaction is also a description of the extended reactions of a dialkylzinc or an alkyl zinc halide between carbonyl compounds.
Collectively, aldehydes and ketones are called Carbonyl compounds. In the basic structure of Aldehydes, in which R is any hydrocarbon chain, or may even be hydrogen. Ketones’ basic structure is similarly represented as Aldehydes, but Carbonyl Carbon (the carbon to which oxygen is double-bonded) is surrounded by two hydrocarbon chains in ketones as compared to one in aldehydes.
Recommended Video:

People also search:
- NEET Chemistry Syllabus
- How to Score 160 Plus in NEET Chemistry
- NEET Chemistry Weightage
- Chemistry Formulas for NEET
- NEET Chemistry MCQs
- NEET Chemistry Important Topics
Comments