Chemical Bond
If the energy released by the attraction of two atoms is more than 42KJ/mol then it is considered a chemical bond. The attractive force which holds together the atoms or groups of atoms in a chemical species is known as a chemical bond.
Atoms combine together to complete their outermost shell and to attain the configuration of noble gas which is a stable configuration.
Ionic bond or Electrovalent Bond
It is an electrostatic force of attraction between two oppositely charged ions. Ionic bonds are formed between two dissimilar atoms having a large difference in their electronegativity values. The electronic concept of this chemical bond was proposed by Kossel.

Conditions for formation of Ionic Compounds
- The electronegativity difference between combining atoms should be large.
- The atom which makes cation should have greater size and low ionization energy so that it can easily lose its outermost electron.
- The atom which forms anion should have small size and more electron affinity. Non-metals owing to their small size and more electron affinity form ionic compounds with s block elements.
- Ionic crystals have high lattice energy.
Lattice Enthalpy
Lattice energy is the most important energy term which is responsible for the formation of stable ionic bonds.
Lattice energy defined as
“Energy released when 1 mol of an ionic compound is formed by its constituent ions in the gaseous state.”
Determination of Lattice Energy
There are two methods to determine lattice energy.
- Born Haber cycle (indirect method)
- Kapustinskii equation (direct method)
Born Haber Cycle
This method is based on Hess law. For example, NaCl is formed by two methods.
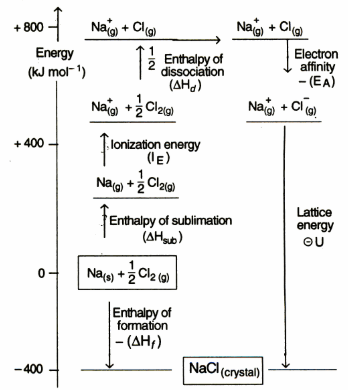
By Hess law,
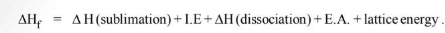
Kapustinskii Equation
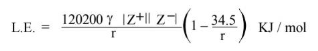
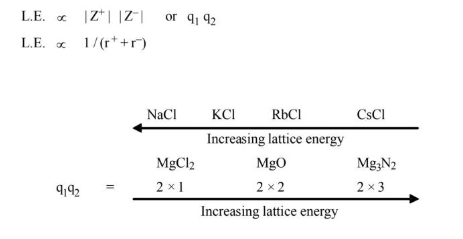
Factor Affecting Lattice Energy
From Kapustinskii relation we have
Covalent Bond
According to Lewis, “Covalent bonds are formed from the sharing of the same number of electrons between two atoms.”
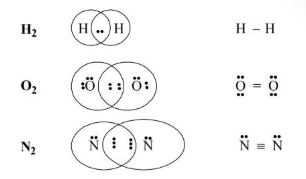

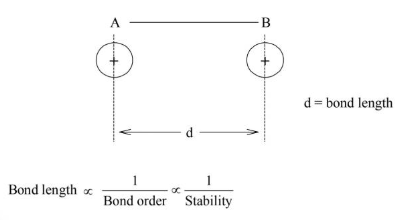
Bond Length
It is defined as the internuclear distance between two covalently bonded atoms.
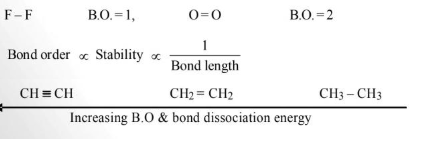
Bond Order
The number of bonds present between two covalently bonded atoms is called bond order.
Fajans Rule
Fajans rules offers a simple approach to the problem of partial covalent character in ionic compounds. Fajans considered the effect which a small, highly charged cation would have on an anion.
| Ionic | covalent |
| low positive charge | high positive charge |
| large cation | small cation |
| small anion | large anion |
Octet Rule
The tendency of atoms to react in ways that they achieve an outer shell of eight valence electrons is particularly common among Group 1A-7A elements and is given the special name of the octet rule.
Dipole Moment
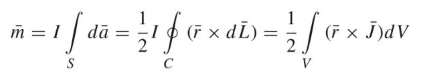
The dipole moments are parallel and perpendicular to the distance R. The magnetic energy becomes
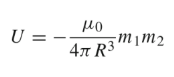
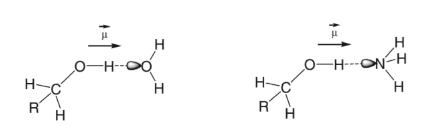
Hydrogen Bond
Hydrogen bonding occurs when a hydrogen atom is bonded to a small, highly electronegative atom, such as nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine. The partially positive hydrogen is attracted to the partial negative nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine of another molecule.
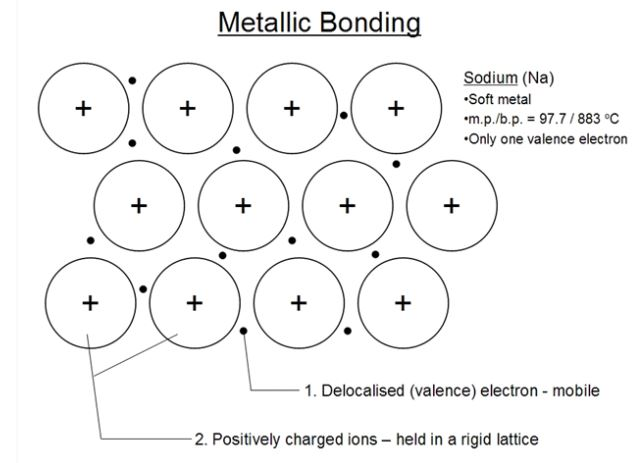
Metallic Bond
Metallic Bonding The bonding which holds the metal atoms firmly together on account of the force of attraction between metal ions and the mobile electron is called metallic bonding.
A strong force of attraction holding atoms together in a molecule or crystal. A bond is a force which holds atoms together. When atoms come together to form compounds and molecules the atoms gain a more stable configuration of electrons.
Recommended Videos:

Must read NEET Chemistry articles:
- NEET Chemistry MCQs
- Chemistry Formulas for NEET
- How to Score 160 Plus in NEET Chemistry
- NEET Chemistry Weightage
- NEET Chemistry Syllabus
- NEET Chemistry Important Topics
Comments