NEET 2023 is approaching, and it is time to do thorough revisions and give your best for the entrance exam. This article contains the NEET Biology 2023 Important Questions and Answers for students’ practice. Class 12 Zoology questions are being solved in this smart mock test to achieve a 720 NEET score. Topics covered in this smart mock test are human reproduction, circulation system, respiration, digestion, endocrine system, nervous coordination, animal husbandry, excretion and osmoregulation, nutrition, and the human population.
Question 1: The number of chromosomes present in the meiocyte of a house fly is ________.
- 12
- 6
- 24
- 48
Answer: a) 12
Explanation: Meiocytes are specialised cells (also called gamete mother cells) which undergo meiosis. They go through meiosis to create gametes. If a housefly’s gamete chromosome number is 6, the meiocytes have 12 chromosomes.
Question 2: Small amounts of urea could be eliminated through ________.
- Lungs
- Saliva
- Bile
- Liver
Answer: b) Saliva
Explanation: Small amounts of urea could be eliminated through saliva. Urea produced via the urea cycle in the liver is then released into the bloodstream, where it travels to the kidneys and is ultimately excreted in the urine.
Question 3: The first human hormone produced by recombinant DNA technology is _______.
- Insulin
- Melatonin
- Testosterone
- Progesterone
Answer: a) Insulin
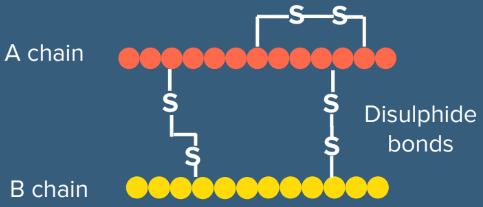
Explanation: In 1983, Eli Lilly, an American company, prepared two DNA sequences corresponding to A and B chains of human insulin and introduced them into plasmids of E. coli to produce insulin chains.
Chains A and B were produced separately, extracted and combined by creating disulfide bonds to form human insulin (Humulin).
Question 4: The human embryo develops from _______.
- Only hypoblast cells
- Inner cell mass
- Allantois
- Trophoblast
Answer: b) Inner cell mass
Explanation: After fertilisation, the zygote undergoes repeated mitotic divisions called cleavage divisions. The blastocyst is formed after rapid cleavage in the zygote. It contains 200-300 cells.
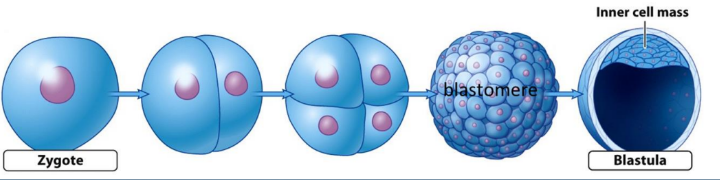
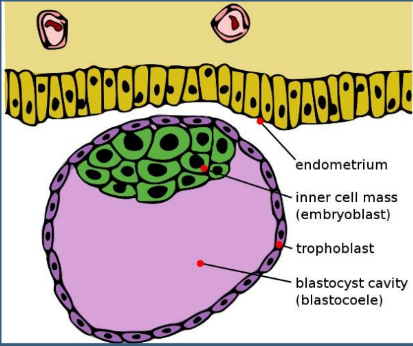
The inner cell mass differentiates into an embryo and gives rise to three germinal layers and subsequent foetal tissues.
Question 5: Given below is the percentage of nitrogenous bases present in four different samples of the genetic material. Identify which sample belongs to an RNA virus.
- Sample A : A-23%, G-27%, C-27%, T-23%
- Sample B : G-22%, A-28%, C-22%, T-28%
- Sample C : U-22%, G-23%, C-23%, A-32%
- Sample D : C-8%, A-42%, G-8%, T-42%
Answer: c) Sample C : U-22%, G-23%, C-23%, A-32%
Explanation: 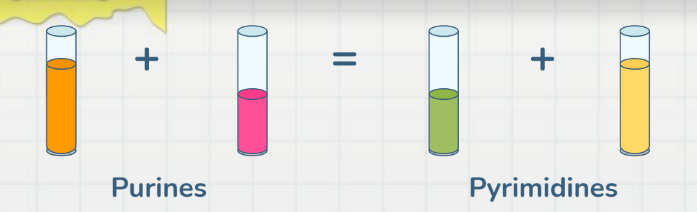
Chargaff’s Rule:
- In DNA, Adenine = Thymine; Cytosine = Guanine
- A + G = C + T
- Total number of purines = Total number of pyrimidines
Chargaff’s rule is not applicable to ssDNA or RNA. In sample C, the percentage of adenine and uracil are not equal.
Question 6: Select the mismatch among the following.
- ZIFT – Transfer of zygote or early embryos (with up to 8 blastomeres) into the fallopian tube
- GIFT – Gametes are transferred in the uterus
- IUT – Transfer of embryos with more than 8 blastomeres within the uterus
- Intracytoplasmic sperm injection – Sperm is directly injected into the ovum
Answer: b) GIFT – Gametes are transferred in the uterus
Explanation: Gamete Intra Fallopian Transfer (GIFT): Transfer of ovum from a donor into the fallopian tube of another woman who cannot produce an egg, but provides a suitable environment for fertilisation and further development.
Question 7: Read the following statements about echinoderms and choose the option that correctly fills the blanks A and B.
Adult echinoderms show ___A____ symmetry, but their larvae show __B____ symmetry.
- (A) – Radial; (B) – Radial
- (A) – Bilateral; (B) – Bilateral
- (A) – Radial; (B) – Bilateral
- (A) – Bilateral; (B) – Radial
Answer: c) (A) – Radial; (B) – Bilateral
Explanation: Marine animals belong to the phylum of echinoderms.
Echinoderms have two types of symmetry. Adult echinoderms are radially symmetrical, but their larvae are bilaterally symmetrical.
Similar to starfish, sea urchins, sand dollars, and sea cucumbers, echinoderm adults are identified by their radial symmetry.
Question 8: Which type of vector is used to introduce a functional ADA cDNA into lymphocytes in gene therapy for ADA deficiency?
- Plasmid
- Bacteriophage
- BAC
- Retrovirus
Answer: d) Retrovirus
Explanation: Adenosine deaminase deficiency is another name for ADA deficiency. Immunodeficiency results from an autosomal recessive disease and gene therapy is used in treatment. In this, lymphocytes from the patient’s blood are cultivated in an in vitro culture. Using a retroviral vector, a functional ADA cDNA is delivered to these cells. The patient receives these cells once more. This procedure is performed periodically. The defect might be permanently repaired if a functional ADA gene is extracted from bone marrow cells and inserted at early embryonic stages.
Question 9: Match column I with column II and choose the correct option.
| Column I | Column II |
| a) Foetus develop limbs and digits | i) End of the second trimester |
| b) First movements of the foetus | ii) End of the first month |
| c) Heart formed | iii) Fifth month |
| d) Eye-lids separate and eyelashes are formed | iv) End of the second month |
- a(i), b(iv), c(ii), d(iii)
- a(iv), b(iii), c(ii), d(i)
- a(iii), b(iv), c(ii), d(i)
- a(iv), b(i), c(ii), d(iii)
Answer: b) a(iv), b(iii), c(ii), d(i)
Explanation: Trimester: First; Month: End of the first month; Important development: Heart is formed.
Trimester: First; Month: End of the second month; Important development: Develop limbs and digits.
Trimester: Second; Month: Fifth month; Important development: First movements of the foetus.
Trimester: End of the second trimester; Month: Sixth month; Important development: Eyelids separate, and eyelashes are formed.
Question 10: Which of the following is an active ATPase enzyme?
- Light meromyosin
- Globular head of meromyosin
- Tropomyosin
- Tail of meromyosin
Answer: b) Globular head of meromyosin
Explanation: The globular head is an active ATPase enzyme and has binding sites for ATP and active sites for actin.
Each meromyosin contains two essential components: a globular head with a short arm and a tail; the former is known as the heavy meromyosin (HMM), and the latter as the light meromyosin (LMM). In addition to having an active site for actin and an ATP binding site, the globular head is an active ATPase enzyme.
Question 11: Which of the following animals evolved into the first amphibians that lived on both land and water?
- Neopilina
- Lobe-finned fishes
- Archaeopteryx
- Ichthyosaurs
Answer: b) Lobe-finned fishes
Explanation: Lobe-finned fishes evolved into the first amphibians.
The proof that birds evolved from reptiles came from fossil studies of Archeopteryx.
Neopilina is the connecting link between Annelida and Mollusca.
Ichthyosaurs are highly specialised aquatic reptiles.
Question 12: Choose the option that correctly fills the blanks (A) and (B).
Statement I: The intercellular material of cartilage is ___(A)____ and resists compression.
Statement II: Bones have a ___(B)___ ground substance rich in calcium salts and collagen.
- (A) – Hard and non-pliable (B) – Solid and pliable
- (A) – Solid and pliable (B) – Hard and non-pliable
- (A) – Soft and non-pliable (B) – Solid and pliable
- (A) – Solid and pliable (B) – Soft and non-pliable
Answer: b) (A) – Solid and pliable (B) – Hard and non-pliable
Explanation: The intercellular material of cartilage is solid and pliable and resists compression.
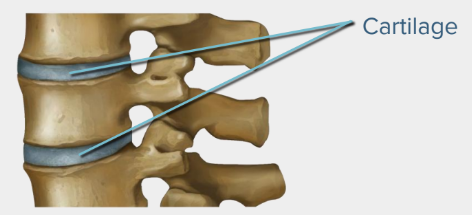
Bones have a hard and non-pliable ground substance rich in calcium salts and collagen fibres, giving bone its strength.
Question 13: Use of bioresources by multinational companies and organisations without authorisation from the concerned country and its people is called _________.
- Bio-infringement
- Biopatent
- Biopiracy
- Bio-exploitation
Answer: c) Biopiracy
Explanation: Biopiracy term refers to the use of bio-resources by multinational companies and other organisations without proper authorisation from the countries and people concerned without compensatory payment.
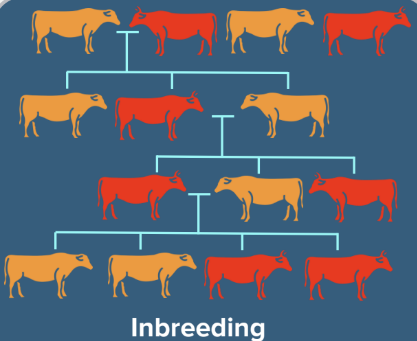
Question 14: The mating of more closely related individuals within the same breed for 4-6 generations is known as ________.
- Out-crossing
- Inbreeding
- Cross-breeding
- Interspecific hybridisation
Answer: b) Inbreeding
Explanation: Inbreeding: Mating of more closely related individuals within the same breed for 4-6 generations.
When closely related animals of the same breed are mating, this practice is referred to as inbreeding. By removing undesirable genes, inbreeding promotes the accumulation of superior genes. However, inbreeding lowers fertility and output. It is referred to as inbreeding depression.
Question 15: Colostrum is the milk produced during the initial few days of lactation. It is essential in developing resistance to newborn babies because it contains antibodies of _________.
- IgG type
- IgM type
- IgA type
- IgE type
Answer: c) IgA type
Explanation: Colostrum is the milk produced during the initial days of lactation. Colostrum contains antibodies called “secretory immunoglobulin” (IgA), which are essential in developing resistance to infections in newborn babies.
Question 16: All of the following structures of the internal ear are responsible for the maintenance of the balance of the body and posture except ________.
- Crista ampullaris
- Macula utriculi
- Macula sacculi
- Organ of Corti
Answer: d) Organ of Corti
Explanation:
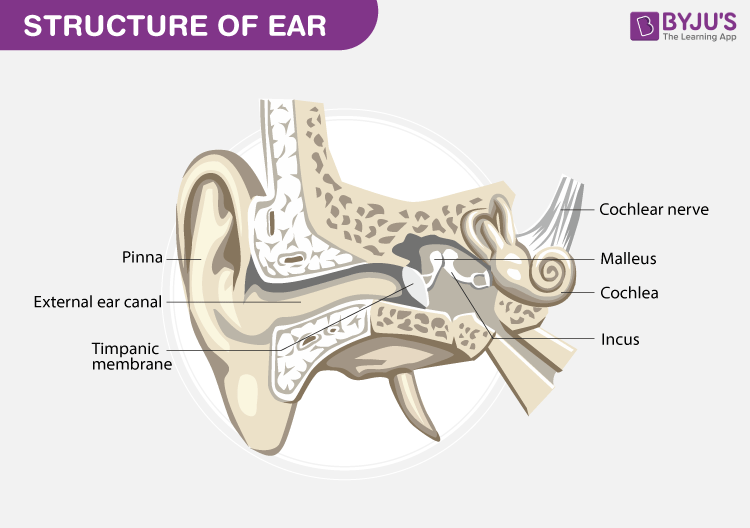
The organ of the Corti is responsible for hearing.
The organ of the Corti, which is the hearing organ, is located in the basilar membrane of the inner ear. It has hair cells having auditory receptor cells, which are arranged in rows on the internal side of the organ.
Question 17: Which part of the brain is involved in the regulation of sexual behaviour?
- Corpora quadrigemina
- Only hypothalamus
- Limbic system and hypothalamus
- Cerebellum
Answer: c) Limbic system and hypothalamus
Explanation: Limbic lobe or limbic system, along with the hypothalamus, is involved in the following:
● Regulation of sexual behaviour
● Expression of emotional reactions
● Motivation
The forebrain includes the cerebrum, thalamus, and hypothalamus. The cerebral cortex refers to the exterior of the brain. The right and left hemispheres make up the cerebrum.
The limbic lobe, also known as the limbic system, is a complex structure made up of the inner sections of the cerebral hemispheres and a number of related deep structures, including the amygdala and hippocampus.
It collaborates with the hypothalamus to control motivation, sexual behaviour, and the expression of many emotions (such as excitement, pleasure, fury, and fear).
The thalamus is a key centre for the coordination of sensory and motor signalling.
Question 18: Read the following statements w.r.t the regulation of respiration and choose the correct option.
Statement I: Respiratory rhythm centre present in the medulla region of the brain is primarily responsible for the regulation of the normal rhythm of breathing.
Statement II: The role of oxygen in the regulation of respiratory rhythm is very significant.
- Statement I is incorrect, but statement II is correct
- Statement I is correct, but statement II is incorrect
- Both statements are correct
- Both statements are incorrect
Answer: b) Statement I is correct, but statement II is incorrect
Explanation: The role of oxygen in the regulation of respiratory rhythm is quite insignificant.
Question 19: How many external rows of ciliated comb plates are usually present in the body of comb jellies?
- 8
- 12
- 10
- 16
Answer: a) 8
Explanation: Ctenophores are commonly known as sea walnuts or comb jellies and are exclusively marine. The body bears eight external rows of ciliated comb plates, which helps in locomotion.
Question 20: Evolution of DDT-resistant mosquitoes is an example of ________.
- Stabilising selection
- Balancing selection
- Disruptive selection
- Directional selection
Answer: d) Directional selection
Explanation: Directional selection is when members of one population survive better than the other members of the same population.
The evolution of DDT-resistant mosquitoes is an example of directional selection.
Recommended Video:

Related Links:
Comments