NEET 2023 is approaching, and it is time to do thorough revisions and give your best for the entrance exam. This article contains the NEET Biology 2023 Important Questions and Answers for students’ practice. Class 12 Botany questions are being solved in this smart mock test to achieve a 720 NEET score. Topics covered in this smart mock test are Cell, The Living World, Biological Classification, Plant Kingdom, Morphology of Flowering Plants, Anatomy of Flowering Plants, Plant Physiology, Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants, Genetics and Evolution, and Biotechnology and Its Applications.
Question 1: Which of the given cell organelles do not contain DNA?
I. Mitochondria
II. Chloroplast
III. Golgi complex
IV. Lysosome
- I and II
- I and III
- II and III
- III and IV
Answer: d) III and IV
Explanation: In addition to the cell’s nucleus, both mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA. Lysosomes and Golgi complexes do not contain DNA.
Question 2: What will be the DNA content at the end of the S-phase of a cell if its meiotic products have 8 pg of DNA in each cell?
- 8 pg
- 16 pg
- 4 pg
- 32 pg
Answer: d) 32 pg
Explanation: Both chromosomes and DNA in the daughter cell are reduced by half during meiosis. Therefore, if the DNA content of daughter cells is 8 pg following meiosis, the parent cell’s DNA content is 16 pg. During the S phase, the cell’s DNA content duplicates without impacting the number of chromosomes; as a result, in this instance, the DNA content following the S-phase would be 32 pg.
Question 3: Select the incorrect match w.r.t. the Taxonomic categories of wheat.
- Family – Poaceae
- Order – Monocotyledonae
- Division – Angiospermae
- Genus – Triticum
Answer: b) Order – Monocotyledonae
Explanation:
| Wheat | |
| Kingdom | Plantae |
| Division | Angiospermae |
| Subdivision | Spermatophytina |
| Class | Monocotyledonae |
| Order | Poales |
| Family | Poaceae |
| Genus | Triticum |
Question 4: The parasitic fungi on mustard causing white rust of leaves is _______.
- Phytophthora
- Albugo
- Pythium
- Colletotrichum
Answer: b) Albugo
Explanation: Albugo is the parasitic fungus on mustard. Albugo candida, also referred to as white rust, is a species of oomycete in the Albuginaceae family. A. candida is a dangerous plant pathogen that contaminates Brassicaceae species and causes the disease known as white rust or white rankle rust. Compared to other oomycetes, it has a genome that is a bit smaller.
Question 5: Select the incorrect statement w.r.t. cymose inflorescence.
- Peduncle terminates into a flower
- Shoot axis continues to grow indefinitely
- Flowers are borne in a basipetal order
- It can be seen in begonia and teak
Answer: b) Shoot axis continues to grow indefinitely
Explanation:
| Inflorescence | |
| Racemose | Cymose |
| The growth of the floral axis is indefinite | The growth of the floral axis is limited, and the main axis terminates into a flower |
| Flowers are borne laterally in acropetal succession | Flowers are borne laterally in a basipetal order |
| E.g. Crotalaria | E.g. Jasmine, begonia and teak |
Question 6: Refer to the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement A: Cork cambium is also called the extrastelar cambium.
Statement B: Phelloderm develops during secondary growth
- Only statement A is correct
- Only statement B is correct
- Both statements are correct
- Both statements are incorrect
Answer: c) Both statements are correct
Explanation: Due to its origin outside the stele, cork cambium is called the extrastelar cambium.
Phelloderm is called the secondary cortex because it is the cortex that develops during secondary growth.
Question 7: Water channels are made up of how many different types of aquaporins?
- Eight
- Four
- Five
- Twenty
Answer: a) Eight
Explanation: The proteins known as porins create enormous pores in the outer membranes of certain bacteria, mitochondria, and plastids that permit external molecules coupled to the transport protein to pass through. The transport protein then rotates and releases the molecule inside the cell. For instance, there are eight different kinds of aquaporins that make up water channels.
Question 8: Which of the given sets of elements’ deficiency causes necrosis?
- N, S and Fe
- N, S and Mo
- Ca, Mg, Cu and K
- Zn, Mo, Fe and S
Answer: c) Ca, Mg, Cu and K
Explanation: When cells or tissues senescence or die, the condition is called necrosis. Necrosis in plants typically results in the darkening and wilting away of the leaves, stems, and other sections. It has no illness. It’s more of a sign of a sickness or some kind of stress the plants are going through. It results from a lack of magnesium, calcium, copper, and potassium.
| Deficiency symptom | Deficient nutrient elements |
| Chlorosis: Yellowing of leaves | Mn, Mg, Fe, Zn, Mo, N, K, S |
| Necrosis: Death of tissues | Mg, Cu, Ca, K |
| Inhibition of division of cells in the plants | Mo, K, S, N |
| Delay in flowering | Mo, N, S |
Question 9: Which of the given prokaryotes fixes nitrogen symbiotically as well as in a free-living state?
- Rhizobium
- Thiobacillus
- Anabaena
- Azotobacter
Answer: c) Anabaena
Explanation: Rhizobium: Bacteria that live in symbiotic association with the root nodules of the leguminous plants.
Thiobacillus: Carry out denitrification
Anabaena: Fixes nitrogen symbiotically as well as in a free-living state.
Azotobacter: Convert atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia, which in turn is taken up and utilised by the plants.
Question 10: How many ATPs are consumed to fix one molecule of CO2 in the C3 pathway?
- Two
- Three
- Eighteen
- Twelve
Answer: b) Three
Explanation: 3 ATP and 2 NADPH molecules are required for each CO2 molecule that enters the Calvin cycle. To produce one molecule of glucose, 6 turns of the cycles are required.
6 x 3ATP = 18ATP and 6 x 2NADPH = 12NADPH
| In | Out |
| 6 CO2 | 1glucose |
| 18ATP | 18ADP |
| 12NADPH | 12NADP |
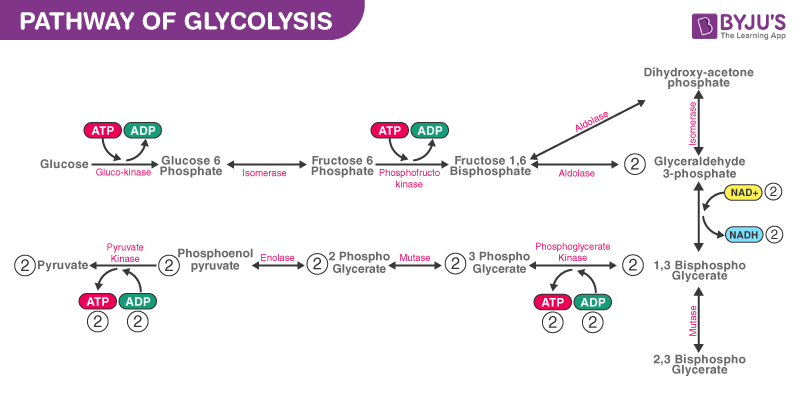
Question 11: Conversion of glucose to glucose 6-phosphate in EMP pathway is catalysed by ________.
- Aldolase
- Phosphofructokinase
- Enolase
- Hexokinase
Answer: d) Hexokinase
Explanation: Glucose is converted to glucose-6-phosphate by hexokinase. It uses ATP to carry out the reaction.
Question 12: Cells in the meristematic phase exhibit all of the given characteristics, except __________.
- Dense protoplasm
- High respiration rate
- Presence of large nucleus
- Increased vacuolation
Answer: d) Increased vacuolation
Explanation: Meristematic phase: Primarily responsible for the growth of the plant by the production of new cells. The rate of respiration is high. Cells have dense cytoplasm and thin cell walls. Presence of large nucleus.
Elongation phase: Cell enlargement occurs. Size increases due to vacuolation.
Question 13: Wind-pollinated flowers show all of the given characteristics, except _______.
- Pollen grains are light and non-sticky
- Flowers have well-exposed stamens
- Flowers have a large feathery stigma
- Pollen grains are generally surrounded by a mucilaginous covering
Answer: d) Pollen grains are generally surrounded by a mucilaginous covering
Explanation: Characteristics of anemophilous flowers:
- Light and non-sticky pollen grains
- Well-exposed stamens
- Large feathery stigma
Characteristics of anemophilous flowers:
- Long, ribbon-like pollen grains with mucilaginous covering
Question 14: In the Mendelian dihybrid cross, out of 240 individuals obtained in the F2 generation, how many of the offspring would be pure homozygous?
- 60
- 30
- 120
- 40
Answer: a) 60
Explanation: There are a total of 4 pure homozygous offspring (1 YYRR, 1 yyRR, 1 YYrr, 1 yyrr) obtained in the F2 generation of the Mendelian dihybrid cross.
Hence, out of 240 individuals;
4/16 X 240 = 60 individuals would be pure homozygous.
Question 15: Which of the given population interactions is an example of Epiphytes growing on mango trees?
- Commensalism
- Mutualism
- Amensalism
- Competition
Answer: a) Commensalism
Explanation: Plants, known as epiphytes, grow on other plants but do not use their nutrients. As a result, the coexistence of an orchid and a mango tree is an illustration of commensalism, in which one species gains while the other does not.
Question 16: Select the incorrect statement w.r.t anthropogenic ecosystem.
- It possesses a self-regulatory mechanism
- It has little diversity
- A simple food chain is present in it
- It shows high productivity
Answer: a) It possesses a self-regulatory mechanism
Explanation: Characteristics of Anthropogenic ecosystem:
- Little diversity
- Simple food chain
- Shows high productivity
- Do not possess self regulatory mechanism
Question 17: Which of the following is not a seral community w.r.t. xerarch succession?
(I) Lichens
(II) Bryophytes
(III) Herbs
(IV) Forest
- Only (I)
- Both (II) and (III)
- Both (I) and (IV)
- Only (III)
Answer: c) Both (I) and (IV)
Explanation: A xerarch succession is a type of plant growth that starts from very dry, water-limited bare ground and gradually gives way to an established forest. Such communities typically develop in arid landscapes like sand dunes and rock deserts. Actually, “Xero” means “dry” in Greek. Additionally, psammoseres (sand) and lithoseres can also be classified as xeroseres (rocks). In other words, the type of plant succession known as “xerarch succession” is found in extremely arid regions. The actual procedure entails plants populating a desolate area and turning it into a mature forest (over a period of time). These woods represent the peak of the succession process.
Question 18: Match Column I and Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| a. Cyclosporin A | i. Blood-cholesterol lowering agent |
| b. Statins | ii. Clot buster |
| c. Streptokinase | iii. Immunosuppressive agent |
- a(iii), b(i), c(ii)
- a(ii), b(iii), c(i)
- a(i), b(ii), c(iii)
- a(iii), b(ii), c(i)
Answer: a) a(iii), b(i), c(ii)
Explanation: Streptococcus → Streptokinase → “Clot buster”
Streptokinase removes blood clots from patients who have undergone myocardial infarction.
Trichoderma polysporum (fungus) → cyclosporin A → Immunosuppressive agent
Cyclosporin A is an immunosuppressant that facilitates the acceptance of donor organs.
Monascus purpureus (fungus) → Statins → Blood cholesterol-lowering agents
Question 19: How many meiotic divisions are required to produce 100 seeds in a typical flowering plant?
- 25
- 100
- 50
- 125
Answer: d) 125
Explanation: Number of meiotic divisions required to produce ‘n’ number of seeds
n + n/4 = 100 + 100/4 = 125
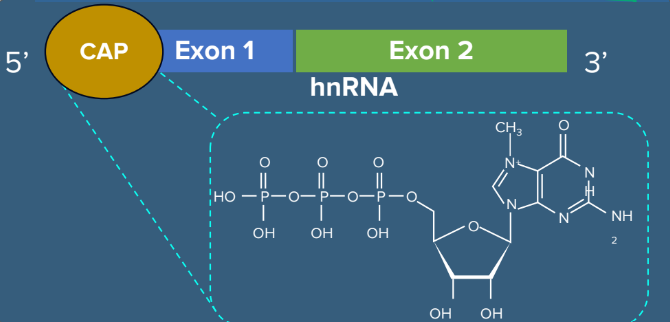
Question 20: During post-transcriptional processing, ______ is added to the 5’– end of hnRNA.
- Adenylate residues
- Methyl guanosine triphosphate
- Adenosine monophosphate
- Deoxythymidine
Answer: b) Methyl guanosine triphosphate
Explanation: During post-transcriptional processing, capping is done at 5’- end of hnRNA by adding methyl guanosine triphosphate.
Recommended Video:


Related Links:
Comments