NEET 2023 is approaching, and it is time to do thorough revisions and give your best for the entrance exam. This comprehensive session has provided the NEET Smart Crash Course 2023 to boost your NEET Chemistry 2023 exam preparation. Some of the topics covered are Coordination Compounds, Electrochemistry, Chemical Kinetics, Surface Chemistry, Equilibrium, and The Structure of Atom.
Question 1: Which of the following has the maximum number of electrons?
- 14 g of N3− ion
- 4 g of Ca2+ ion
- 16 g of O3
- 2.3g of Na+ ion
Answer: a) 14 g of N3− ion
Explanation: a) Given, N = 14g
Atomic mass of N = 14
No. of electrons = 10
∴ (14/14 x 10)NA = 10 NA
b) (4/14 x 18)NA = 1.8 NA
c) (16/48 x 24)NA = 8NA
d) (2.3/23 x 10)NA = 1NA
Question 2: For hydrogen atom, the correct order of energy of orbitals is:
- 4f > 4d > 4p > 3d > 3p > 3s
- 4f = 4d > 3d > 4p > 3p > 3s
- 4f > 4p > 4d = 3d > 3p > 3s
- 4f = 4d = 4p > 3d = 3p = 3s
Answer: d) 4f = 4d = 4p > 3d = 3p = 3s
Explanation: The Energy of Orbitals in Hydrogen depends only on ‘n’. Thus, it begins as:
1s < 2s = 2p < 3s = 3p = 3d < 4s = 4p = 4d = 4f. It only depends on the number of shells (n).
Question 3: If the value of ionisation enthalpy of K is x eV, then the value of electron gain enthalpy of K+ is:
- –x eV
- –2x eV
- +2x eV
- –½ x eV
Answer: a) –x eV
Explanation: The electron gain enthalpy of potassium cation is equal in magnitude and opposite in sign to the first ionisation energy of the potassium atom. It is equal to –x eV.
Question 4: The number of σ and π bonds in the following compound, respectively, are:
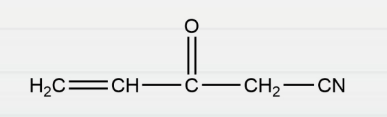
- 12 and 3
- 11 and 3
- 12 and 4
- 11 and 4
Answer: d) 11 and 4
Explanation: All single bonds are known as sigma bonds, while multiple bonds are composed of one sigma bond and the remaining pi bonds.
There are a total of 11 sigma bonds and 4 pi bonds in the given compound.
Question 5: The temperature at which the RMS velocity of CH4 will be the same as that of O2 at 27°C is:
- 150 K
- 450 K
- 600 K
- 900 K
Answer: c) 600 K
Explanation:
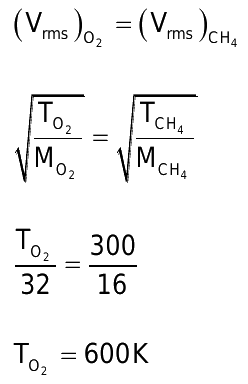
Thus, at 27°C, the RMS velocity of CH4 will be the same as that of O2.
Question 6: For the reversible reactions, CaCO3(s) ⇌ CaO(s) + CO2(g), which of the following does not affect the equilibrium state?
- Increase in the volume of the container
- Decrease in the volume of the container
- Addition of CaO(s)
- Addition of inert gas at constant pressure
Answer: c) Addition of CaO(s)
Explanation: CaCO3(s) ⇌ CaO(s) + CO2(g)
The equilibrium constant for the reaction CaCO3(s) ⇌ CaO(s) + CO2 (g) is Kc = [CO2] and K2 = PCO2.
The equilibrium constant can be expressed as
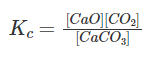
The molar concentration of pure solids or liquids is constant. It does not affect the equilibrium state.
[CaCO3(s)] = [CaO(s)] = 1∴ Kc = [CO2]
Question 7: The characteristic colour exhibited by the Rb atom to an oxidising flame is:
- Crimson red
- Yellow
- Red violet
- Blue
Answer: c) Red violet
Explanation: When introduced to a flame, the alkali metals Li, Na, K, and Rb and their salts give the flame colours of crimson red, golden yellow, lilac (pale violet), and red-violet, respectively.
This characteristic of alkali metals helps us to identify them using the highly accurate and sensitive flame test.
Question 8: The 13th group element which has the least melting point is:
- B
- Al
- Ga
- In
Answer: c) Ga
Explanation: In the Boron family, Gallium (Ga) has the least melting point.
Question 9: Thermodynamically, the most stable allotrope of carbon is:
- Coke
- Fullerene
- Diamond
- Graphite
Answer: d) Graphite
Explanation: Graphite is the allotrope of carbon that is the most thermodynamically stable.
It has a standard entropy value of zero.
Graphite possesses one delocalised electron for every carbon. These increase the affinity between carbon atoms, resulting in stronger bonds and higher structural stability.
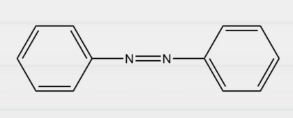
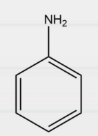
Question 10: In which of the following compounds is Kjeldahl’s method applicable?
Answer: d) 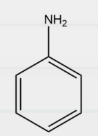
Explanation: Kjeldahl method can not be applied for compounds containing nitrogen in nitro, azo groups and nitrogen in the ring, as the N of such compounds does not change to ammonium sulphate under these conditions. Therefore, Kjeldahl’s method can only be used to estimate nitrogen using aniline.
Question 11: Which of the following metals has the highest conductivity at room temperature?
- Na
- Cu
- Ag
- Au
Answer: c) Ag
Explanation: Silver (Ag) has the highest conductivity at room temperature. In fact, silver is the standard by which conductivity in all other metals is measured. Silver ranks 100 on a scale of 0 to 100, followed by copper at 97 and gold at 76. Due to this property and the fact that it doesn’t spark easily, silver is frequently employed in electrical contacts and circuits. Silver is also used in batteries for portable medical devices, hearing aids, pacemakers, and space flight when reliability is required and weight limits are present.
Question 12: Which of the following quantities changes with the addition of a catalyst during a chemical reaction?
- Equilibrium Constant
- Activation Energy
- Gibbs Energy
- Enthalpy
Answer: b) Activation Energy
Explanation: The activation energy of a chemical reaction changes when a catalyst is added. The catalyst provides a different, lower-activation-energy pathway.
Question 13: Select the incorrect statement about electrolytic refining.
- Impure metal is made to act as an anode
- The pure metal is used as cathode
- Zinc can be refined using this method
- Impurities deposit as cathode mud
Answer: d) Impurities deposit as cathode mud
Explanation: The impure metal serves as the anode, and the pure metal serves as the cathode in electrolytic refining.
Impure metals can be cleaned using electricity through the process of electrolytic refining. In this procedure, the cathode is a strip of pure metal, whereas the anode is an impure metal. A solution is created using a soluble salt made from the same material as the electrolyte.
Metal ions from the electrolyte are deposited as a pure metal in the cathode during the transmission of an electric current, and impure metal from the anode dissolves as ions in the electrolyte. The mud anode is the term for the area beneath the anode where metal impurities are collected.
Question 14: The compound which has the highest reducing character among the following is:
- H2O
- H2S
- H2Se
- H2Te
Answer: d) H2Te
Explanation: The reducing nature of hydrides increases, so the order is H2O < H2S < H2Se < H2Te. The bond dissociation enthalpy decreases down the group as a result of the H-E bond length increasing down the group. The acidic nature of group 16 elements gets stronger as it moves down the group due to the decreasing bond dissociation enthalpy.
Question 15: Which of the following has the highest magnetic moment?
- Sc3+
- Ni2+
- Ti3+
- Zn2+
Answer: b) Ni2+
Explanation: Spin-only magnetic moment depends on the number of unpaired electrons. More the number of unpaired electrons, the higher the magnetic moment.
Sc3+: 3d1 4s2 (3d0 4s0) ∴ Magnetic moment = 0
Zn2+: 3d10 4s2 (3d10 4s0) ∴ Magnetic moment = 0
Ti3+: 3d2 4s2 (3d1) ∴ Magnetic moment = 1
Ni2+: 3d8 4s2 (3d8) ∴ Magnetic moment = 2
Question 16: Consider the following reaction sequence, major product D is:
- CH3CH2NH2
- CH3CH2CONH2
- CH3CH2CH2NH2
- CH3CH = NH
Answer: a) CH3CH2NH2
Explanation: A:
B:
C:
D:
Question 17: Consider the following reaction,
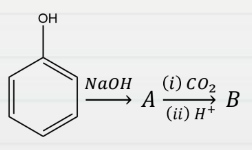
The major product (B) obtained in the above reaction is:
- Salicylaldehyde
- Salicylic acid
- Benzoic acid
- Phthalic acid
Answer: b) Salicylic acid
Explanation: The Kolbe’s Schmidt reaction, an electrophilic substitution reaction in which phenol reacts with sodium hydroxide and carbon dioxide to produce salicylic acid, is demonstrated in the reaction.
Salicylic acid is the main end product formed when phenol interacts with sodium hydroxide and carbon dioxide.

Question 18: The given reaction is known as:
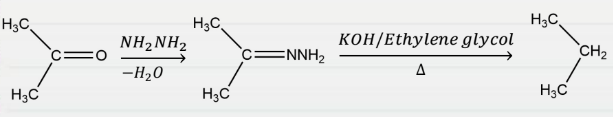
- Rosenmund reduction
- Clemmensen reduction
- Wolff-Kishner reduction
- Stephen reaction
Answer: c) Wolff-Kishner reduction
Explanation: In organic chemistry, the Wolff-Kishner reduction is used to change carbonyl functionalities into methylene groups. The rate-determining step in the reaction is the deprotonation of the hydrazone by an alkoxide base to produce a diimide anion by a concerted, solvent-mediated protonation/deprotonation process.
Question 19: If the standard electrode potential for a cell, A2+(aq) + 2B(s) → A(s) + 2B+(aq), is 1.9 V, then the standard Gibbs energy for the reaction is:
- 3.8 kJ/mol
- –1.9 kJ/mol
- –3.8 kJ/mol
- –7.6 kJ/mol
Answer: c) –3.8 kJ/mol
Explanation:
ΔG = –nF E°cell
⇒ ΔG = –2 x F x 1.9
∴ ΔG = –3.8 kJ/mol
Question 20: Most basic compound among the following is:
- La(OH)3
- Eu(OH)3
- Er(OH)3
- Lu(OH)3
Answer: a) La(OH)3
Explanation: As the size of lanthanide ions decreases from La3+ to Lu3+ due to lanthanide contraction, the covalent property of the hydroxides increases and the basic strength decreases.
Thus, La(OH)3 is the most basic and Lu(OH)3 is the least basic.
Recommended Video:


Related Links:
- MCQs on Electrochemistry
- MCQs on Chemical Kinetics for NEET
- Coordination Compounds MCQ
- Flashcards for NEET Chemistry – Electrochemistry
- Flashcards for NEET Chemistry – Chemical Kinetics
- Flashcards for NEET Chemistry – Coordination Compounds
- NEET Chemistry MCQS – Important Questions and Answers
- NEET Chemistry 2023 – Important Topics and Preparation Tips
Comments