Oxidation-reduction reactions involve changes in the electronic structure of atoms and molecules. Oxidation represents a loss of electrons and reduction of a gain of electrons. Electron losses and gains result from the direct transfer of electrons from one substance to another or from the transfer of electrons in association with hydrogen and oxygen or some other atom.
Reduction involves any one of the following:
Removal of Oxygen
PbO + C → Pb + CO
Addition of Hydrogen
H2 + Cl2 → 2HCl
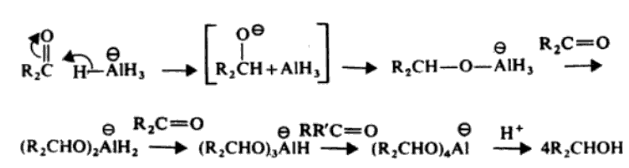
Lithium Aluminium Hydride – LiAlH4
Lithium aluminium hydride is a powerful hydride donor reagent. It reduces esters, acids, nitriles and amides as well as aldehydes and ketones.
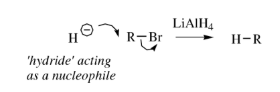
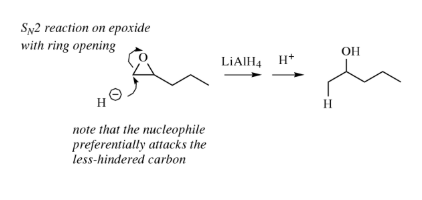
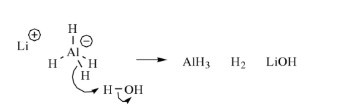
Lithium aluminium hydride reacts violently with water.
Reaction with Alcohols
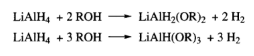
Reduction of Ketones
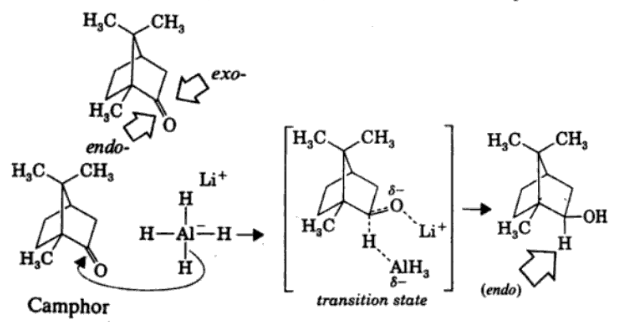
Reduction of Camphor
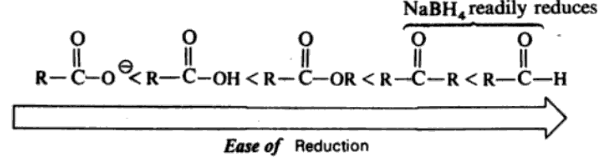
Sodium Borohydride – NaBH4
Carbonyl compounds are reduced which reagents which transfer a hydride from boron or aluminium. Sodium borohydride is a mild reducing agent which reacts rapidly with aldehydes and ketones but only slowly with esters.
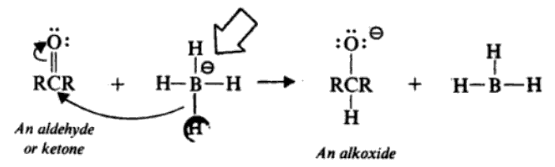
Reduction of Aldehydes and Ketones
The most commonly used reagent for the reduction of aldehydes and ketones is sodium borohydride. Since a BH4– ion contains four hydrides, it is capable of reducing four molecules of aldehyde or ketone.
The reaction takes place through the successive transfer of hydride ions from the boron to four different carbonyl carbonates. When all four of the hydrides are being moved, four aldehyde or ketone molecules can be reduced.
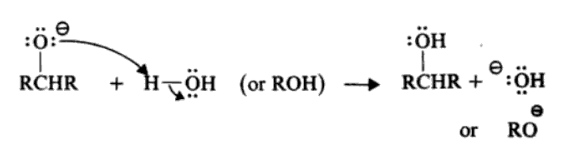
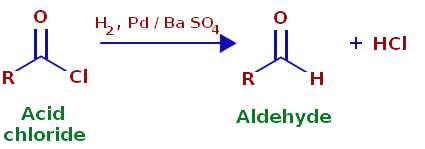
Rosenmund Reduction
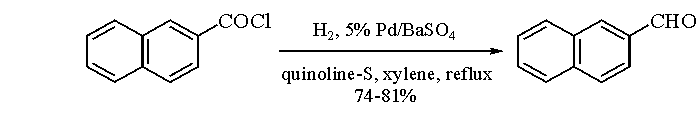
The Rosenmund reaction is a process of hydrogenation in which molecular hydrogen reacts in the presence of a catalyst with the acyl chloride-palladium on barium sulfate.
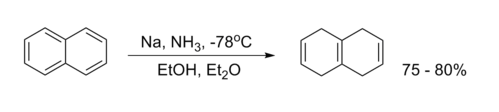
Birch Reduction
Birch reduction is an organic chemical reaction in which aromatic compounds with a benzenoid ring are converted into 1,4-cyclohexadiene.
Stephen’s Reduction
Stephen Reaction Process starts with Gaseous Hydrogen Chloride being added to Given Nitrile.
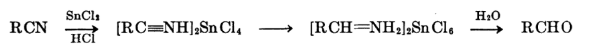
Examples of Stephen’s Reduction
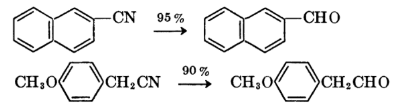
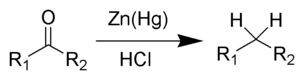
Clemmensen Reduction
The Clemmensen reduction is a reaction that uses hydrochloric acid and zinc amalgam to convert aldehydes or ketones to alkanes.
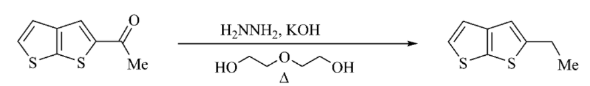
Wolff Kishner Reduction
The process of Wolff Kishner reduction starts with the formation of a hydrazone anion and then releases the nitrogen atom into a carbanion. The carbanion then reacts to give a hydrocarbon with the water in the system. This reduction is an organic reaction in which aldehydes and ketones become alkanes.
Reduction reactions in which electrons are transferred from one chemical species to another at the same time are actually composed of two different reactions.
Further reading:
- NEET Chemistry Syllabus
- NEET Chemistry Important Topics
- NEET Chemistry Weightage
- NEET Chemistry MCQs
- Chemistry Formulas for NEET
- How to Score 160 Plus in NEET Chemistry
Comments