Table of Content:
- Down Syndrome
- Down Syndrome Causes
- Down Syndrome Types
- Down Syndrome Symptoms
- Down Syndrome Diagnosis
- Frequently Asked Questions
Download Complete Chapter Notes of Principles of Inheritance and Variation
Download Now
Down Syndrome
Down syndrome Definition – It is a genetic disorder, which leads to various physical and mental disabilities. It is due to the presence of an extra chromosome 21 also known as trisomy of chromosome 21. Down syndrome is one of the leading causes of genetic disorders around the world.
It is named after the physician Langdon Down, who first observed this condition.
Other than physical attributes and mental retardedness, they are also susceptible to various diseases like leukaemia and Alzheimer’s. There is no cure, only the quality of life can be improved by taking extra care and training the individual to perform daily essential activities. Down syndrome can be diagnosed during early screening in pregnancy, which can decrease the occurrence of disease.
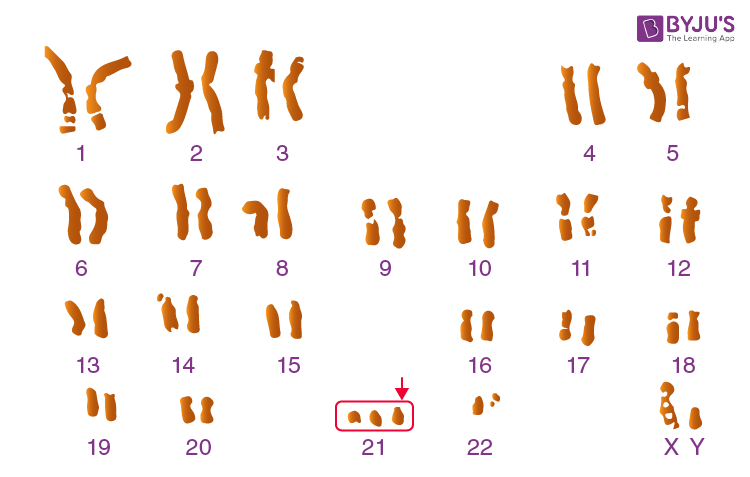
Karyotype of Down’s syndrome (Trisomy of Chromosome 21)
Down Syndrome Causes
Down syndrome is a chromosomal disorder. It is due to aneuploidy of the autosome. There is one extra chromosome 21 or part of the chromosome present in all the cells or some cells.
The occurrence of Down syndrome is 1:800 live births. The major risk factor is the age of the mother. Most of the trisomy cases occur in the mother having age more than 35.
Down syndrome is caused due to abnormal cell division. During mitotic and meiotic cell division the chromosome pair separate so that each cell gets a copy of each chromosome. In down syndrome, the chromosomes are not able to separate, giving rise to cells with an unequal number of chromosomes. This phenomenon is called nondisjunction.
Nondisjunction happens, when chromosome segregates in anaphase before all of the replicated chromosomes’ kinetochores are attached to microtubules from opposite poles during metaphase. It results in one daughter cell having one less chromosome and another with one extra chromosome.
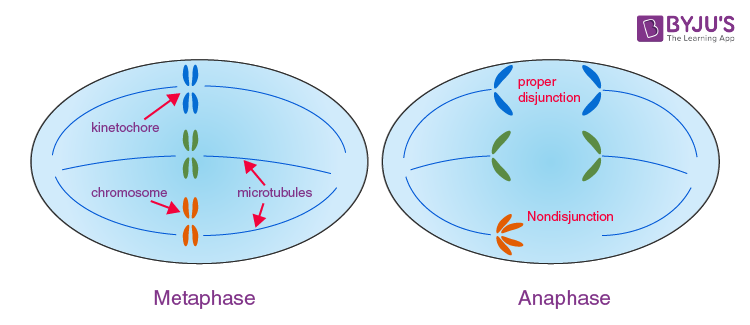
Down syndrome is also due to the translocation of a part of a chromosome to another chromosome. The number of chromosomes is normal but one chromosome has an extra part of chromosome 21.
There is no genetic information missing in these individuals but the extra copy of genes of chromosome 21 causes abnormal physical and mental development.
Down syndrome is mostly not inherited. Translocation Down syndrome can be passed from parent to child. It might be hidden in the parent due to balanced translocation with no symptoms but can pass the unbalanced translocation to the child and cause Down syndrome.
The life span of an individual with Down syndrome is around 60 years, it depends on the number of health complications present.
Down Syndrome Types
Down syndrome is of three types: Trisomy 21, Mosaicism and Translocation
1. Trisomy of chromosome 21: Trisomy is the most common type of Down syndrome. It accounts for 95% of cases of Down syndrome.
There is one extra chromosome 21. The total number of chromosome present is 47 instead of the normal 46 chromosomes.
The main cause of trisomy is Nondisjunction of chromosome 21 during meiosis at the time of gamete formation. The abnormal cell with trisomy of chromosome 21 is fertilised giving rise to trisomy in all the cells of the foetus.
2. Mosaicism: This is the rare form of Down syndrome, accounting for only 1% of the total cases.
In this type of Down Syndrome, some cells are normal having 46 chromosomes and some cells have abnormal 47 chromosomes. Symptoms may be less prominent in mosaicism.
Mosaicism is caused when nondisjunction occurs during mitotic division in the zygote after fertilization. It results in some normal cells and some cells with trisomy of 21.
3. Translocation Down Syndrome: This type of Down syndrome accounts for 4% of the total cases.
Here an extra chromosome 21 is not present but there is an extra part of the chromosome 21 present attached to a different chromosome. Total 46 chromosomes are present of which one is abnormal.
This is due to the translocation of the long arm (q arm) of chromosome 21 to another chromosome during the replication process. The extra portion often gets translocated to chromosome 14. So a person with translocation Down syndrome contains one chromosome 14, one chromosome 14/21 and a pair of normal chromosome 21. Its occurrence is not related to the mother’s age and it may run in families.
Down Syndrome Symptoms
Individuals with down syndrome are borne with many abnormalities. They are found to have physical and mental disabilities. They have poor immunity and are prone to get many diseases. They reach developmental milestones at a later age than normal. Many times they are found to be borne with congenital heart defects, thyroid disease, sleep apnea, gastrointestinal defects. They are more susceptible to get diseases like leukaemia and Alzheimer’s.
People with down syndrome can be easily identified by their physical attributes and facial features. Slowly after they are borne different symptoms start appearing. Infants may be of normal size but as they grow slowly, their height remains much less than those of the same age.
The main symptoms of Down syndrome are:
- Short stature and stunted growth
- Fold of the skin above the eye, slanted eyes
- Protruding furrowed tongue, flattened nose
- Mental retardation
- Cardiac deformities
- Single transverse palm crease and hand is broad and short
- Poor muscle tone and excessive flexibility
- Small head, short neck and abnormal teeth
- Delay in language development
- Cognitive impairment may be mild to moderate
Down Syndrome Diagnosis
Children with Down syndrome can be diagnosed before or after birth.
Due to peculiar facial features, they are easily identifiable. If diagnosed after birth, there is no cure available and only quality of life can be improved by training, education and extra care.
Down syndrome can be diagnosed during pregnancy and if the foetus is found to have Down syndrome, pregnancy is terminated.
Down syndrome can be diagnosed by the amniocentesis technique. In amniocentesis, the amniotic fluid is taken out with the help of a needle and the karyotype of the dividing cells are done in the lab. Cells of amniotic fluid have the same genetic content as the foetus. The karyotype is studied for any chromosomal abnormality. If the karyotype is abnormal, the foetus is aborted.
This was a brief note on Down’s syndrome. Explore notes on other important concepts related to NEET, only at BYJU’S.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes Down syndrome?
Down syndrome is a genetic disorder caused due to abnormal cell division. It is caused due to the presence of an extra chromosome 21 also known as trisomy of chromosome 21. It can be one extra chromosome 21 or a part of the extra chromosome present in all the cells or some cells.
What are some characteristic features of Down syndrome?
The main feature of Down syndrome is mental retardation. Other features include stunted growth, protruding furrowed tongue, flattened nose, short neck, small head, poor muscle tone, etc.
Recommended Video:

Further reading:

Comments