Derivation of escape velocity is a very common concept in the kinematics topic of physics, and often questions related to it are included in school exams. The escape velocity derivation is also important to understand the in-depth concepts better and thoroughly understand the related concepts.

With the help of the escape velocity formula, it is possible to calculate the minimum velocity that an object requires to overcome a particular planet’s or object’s gravitational pull. Here, the derivation of escape velocity is given in a very simple and easy-to-understand way that can help students learn this concept more effectively.
Derivation of Escape Velocity:
Before checking the escape velocity derivation, it is important to know what escape velocity is and what are its related concepts. Check out the escape velocity of Earth for a detailed understanding of the minimum velocity required to overcome the earth’s gravitational pull.
Escape Velocity Formula:
Derivation:
Assume a perfect sphere-shaped planet of radius R and mass M. Now, if a body of mass m is projected from a point A on the surface of the planet. An image is given below for better understanding:

In the diagram, a line from the centre of the planet i.e. O is drawn till A (OA) and extended further away from the surface. In that extended line, two more points are taken as P and Q at a distance of x and dx, respectively from the centre O.
Now, let the minimum velocity required from the body to escape the planet b
Thus, kinetic energy will be

At point P, the body will be at a distance x from the planet’s centre and the force of gravity between the object and the planet will be
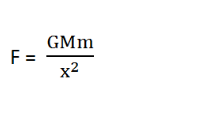
To take the body from P to Q i.e. against the gravitational attraction, the work done will be->
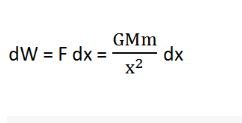
Now, the work done against the gravitational attraction to take the body from the planet’s surface to infinity can be easily calculated by integrating the equation for work done within the limits x = R to x = ∞.
Thus,
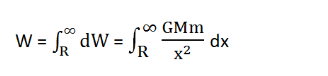
By integrating it further, the following is obtained:
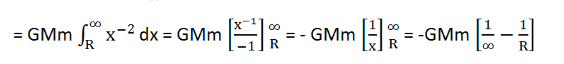
Thus, the work done will be:
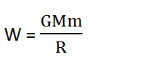
Now, to escape from the surface of the planet, the kinetic energy of the body has to be equal to the work done against gravity going from the surface to infinity. So,
K.E. = W
Putting the value for K.E. and Work, the following equation is obtained:
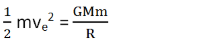
From this equation, the escape velocity can be easily formulated which is:
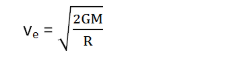
Putting the value of g = GM/R2, the value of escape velocity becomes:
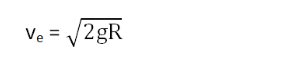
From these two equations, it can be said that the escape velocity depends on the planet’s radius and the planet’s mass only and not on the body’s mass.
Escape Velocity of Earth:
From the above equation, the escape velocity for any planet can be easily calculated if the mass and radius of that planet are given. For earth, the values of g and R are:
g = 9.8 ms-2
R = 63,781,00 m
So, the escape velocity will be:
Escape Velocity of Earth= 11.2 km/s.
This was the derivation of the escape velocity of earth or any other planet. This escape velocity derivation is crucial as questions related to this topic are common in physics exams. To learn more similar concepts, check out the related articles below.
Related Articles
| Escape Speed | Relation Between Escape Velocity And Orbital Velocity |
| Gravitational Pull of The Earth-Escape Velocity | Orbital Velocity Derivation |
For more important derivations of physics formulas, stay tuned with BYJU’S.

Thanks so much
Thankyou so much byjus experts. You cleared my doubts🌹