“Amniocentesis is a medical procedure used in prenatal diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities, foetal infections and sex determination.”
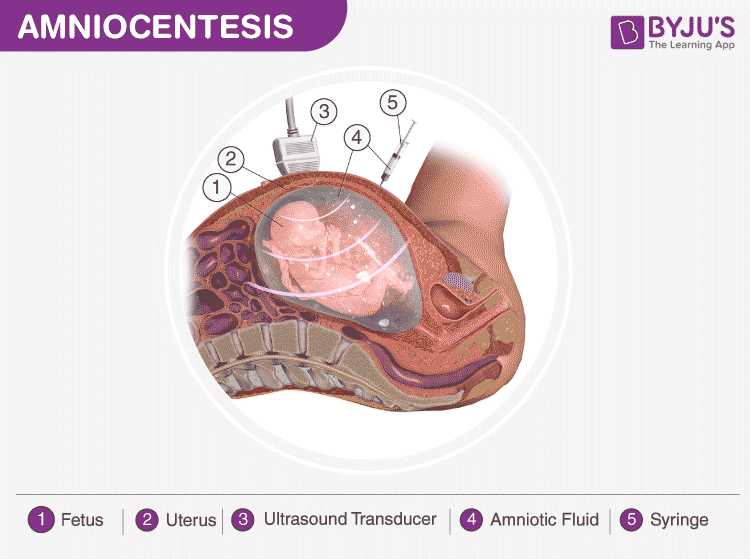
What is Amniocentesis?
Amniocentesis is a diagnostic procedure undergone during pregnancy. It is most commonly used to check the baby’s chromosomes.
Amniocentesis is performed occasionally to examine diseases during pregnancy such as infections or genetic disorder. This procedure is done by taking out the amniotic fluid. We do not usually need a local anaesthetic.
The foetus is surrounded by the amniotic fluid that contains foetal cells and other substances such as alpha foetoprotein. It also protects the foetus from any mechanical injury and helps in regulating the temperature of the foetus. The cells and substances present in the amniotic fluid provide important information about the baby’s health before birth.
Why is Amniocentesis performed?
The amniocentesis is performed to check:
- If the karyotype (the chromosomes) of the baby is (are) normal
- If there is evidence of a neural tube defect (spina bifida or open spine)
- If there is evidence that the baby might have had an infection
- If the lungs of the baby are ready to breathe
Also Read: Overview of Chromosomal Abnormalities
Procedure of Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis follows the following procedure:
- The patient is made to lie down on the table and asked to place the hands behind the head.
- The blood pressure, heart rate and breathing rate are checked.
- An ultrasound is performed to scan the heart rate of the foetus, position of the placenta, foetus, umbilical cord and locate the pocket of amniotic fluid.
- The abdomen is cleansed with an antiseptic and is injected with anaesthesia.
- A long, thin, hollow needle is inserted into the uterus to collect the amniotic fluid.
- The collected fluid is placed in a light protected container.
- The heart rate of the foetus and the patient are reassessed.
- The collected fluid is sent to the laboratory for examination.
Risks Involved In Amniocentesis
The risks involved in amniocentesis include:
- Risk of Miscarriages
- Risk of Injuries.
- Cramping
- Leaking of amniotic fluid from the puncture site or vagina
- Preterm labour
Risk of Injuries
Injuries to the baby by the needle are exceedingly rare now since the procedure is done under ultrasound guidance.
Risk of Miscarriages
Risks of miscarriages still exist but have also come down significantly.
Miscarriages might result from bleeding from the baby if one of the vessels of the baby is cut by the needle (this is very rare) or might result from an infectious disease, rupture of the membranes, or spontaneous labour.
This is the reason why we clean the skin very carefully before inserting the needle.
Occasionally a baby might also die after a normal amniocentesis due to unexplained reasons.
Also Read: Medical Termination of Pregnancy
Care after the Amniocentesis
Complications of the amniocentesis are rare, but in order to be on the safe side, one can follow the following precautions.
- No lifting kids or groceries
- no aerobic classes
- no jogging
- no intercourse
- strenuous activity.
By the next day, one can get back to their normal schedule. In case of any unusual cramps, bleeding, leakage of fluid, chills or fever, let the doctor be informed about the same.
Ban on Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis had been banned in India in 1994, under the Preconception and Prenatal Diagnostic Techniques Act. This was because amniocentesis could reveal the sex of the foetus. Since a girl child is not accepted in many parts of the country, the female foetus is aborted in most of the cases. To stop this, amniocentesis was banned in India.
Also Read: Reproductive Health
To learn more about what is amniocentesis, its definition, procedure and the risks involved, keep visiting BYJU’S website or download BYJU’S app for further reference.

Comments