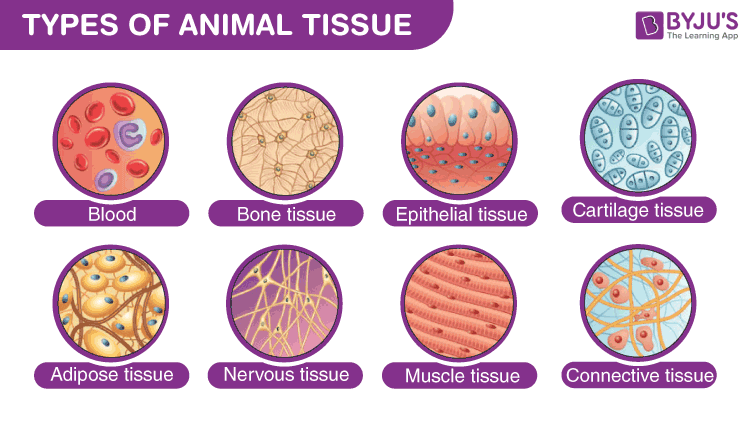
The animal cells are grouped together to form animal tissues. These tissues vary in their structure, function, and origin. The animal tissues are divided into epithelial, connective, muscular and nervous tissues. Let us have a glimpse of each type of animal tissue in detail.
Table of Contents
Types of Animal Tissue
Animal tissues are distinguished into four basic types namely epithelial, connective, nervous and muscle tissues.
Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial tissues form the protective covering and inner lining of the body and organs. These tissues were the first to evolve during evolution and were first formed during embryonic development. They develop from the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm of the embryo.
Characteristics of Epithelial Tissues
Following are the important characteristics of epithelial tissues:
- These can be single-layered or multi-layered.
- The tissues have the power to regenerate.
- These are held together by gap junctions, tight junctions, zonula adheren, desmosomes, or interdigitation.
- The plasma membrane of these cells is specialized into flagella, cilia, and microvilli.
Classification of Epithelial Tissues
The epithelial tissues can be classified as:
|
Classification |
Function |
|
Sensory epithelium |
To perceive stimuli |
| Glandular epithelium |
Secretes chemicals |
|
Pigmented epithelium |
Imparts colour in retina |
| Absorptive epithelium |
For absorption |
Also Read: Plant Tissue System
Connective Tissue
Connective tissues develop from the mesodermal cells of the embryo. they support and bind other tissues in the body. These are made up of three components:
- Intercellular Matrix: It is made up of mucopolysaccharide, specifically hyaluronic acid.
- Cells: The major cells include fibroblasts, adipocytes, plasma cells and mast cells.
- Fibres: Connective tissues are made up of three types of fibres, namely, collagen fibre, elastic fibre, reticular fibre.
The connective tissues perform the following functions:
- They attach organs and tissues together.
- They store fat in the form of adipose tissues.
- They help in repairing tissues.
- They prevent the organs from mechanical shocks.
- The organs also help in defence.
Classification of Connective Tissues
The connective tissues are classified as follows:
|
Classification |
Function |
|
Connective Tissue Proper |
Provides support and protection to the body |
| Vascular Tissue |
Transport of materials in the body |
|
Skeletal Tissue |
It supports the body and gives it proper shape and form |
Also Read: Epithelial and Connective Tissue
Muscle Tissue
The muscular tissue develops from the mesoderm of the embryo. It is classified into three types:
- Cardiac
- Smooth
- Skeletal
Muscular tissue performs the following functions:
- It helps in movement and locomotion.
- It supports the bones and other structures.
- It is responsible for peristalsis and parturition.
Classification of Muscular Tissue
The muscular tissue can be classified as:
|
Classification |
Function |
|
Cardiac |
It helps in blood circulation and keeps the heart pumping |
| Smooth |
These help in peristalsis and other involuntary functions of the body. |
|
Skeletal |
Provide support, help in movement and maintain homeostasis |
Also Read: Muscular Tissue
Nervous Tissue
Nervous tissue makes up the peripheral and the central nervous system. It develops from the ectoderm of the embryo. It possesses the ability to initiate and transmit the nerve impulse. Its main components include:
- Neurons – These are the structural and functional unit of nervous system. It comprises an axon, cell body and dendrites.
- Neuroglia – These are special cells found in the brain and spinal cord. They provide support to the neurons and fibres.
- Neurosecretory Cells – These function as endocrine organs. They release chemical from the axons direcly into blood.
Animal tissues class 9 gives a detailed overview of the epithelial, connective, muscular and nervous tissues in human body. Stay tuned with BYJU’S to know more about the animal tissues, its types or other related topics.
Recommended Video:

Further Reading:
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the four types of animal tissues?
The four major types of animal tissues are epithelial, connective, nervous and muscle tissue.
Does connective tissue have mesoderm?
Mesodermal cells are the most abundant ones in the human body. It represents a wide range of cell types, including connective tissues found all over the body.
What are the common cell types in connective tissue?
Connective tissue is mesodermal in origin. The major cell types that make this tissue include fibroblasts, adipocytes, plasma cells and mast cells.
Where are connective tissues found?
Connective tissue is one of the primary animal tissues that develops from the mesoderm. It is found everywhere in the body, including the nervous system.

Ok and good also.
But I want more information
i have a hope that this app will help me
Very nice service.
Yes very nice
Nice notes
Nice !
Very nice notes. Thanks BYJU’s to help me with my exams
can you please give me a 3-5 mark answer for this
Nice and briefly described notes well done.
it helped a lot THANK YOU BYJUS
It helped me too much it is the best app for studying I love Byjus.
Very nice It helped me so much for my exams
Thanks a lot
thank u
nice explanation
Awesome Explanation. It was a brief but yet detailed explanation. I loved watching it.
Thanks a lot!
Very good clarifications. Thank you!