Embryo development refers to the different stages in the development of an embryo. Embryonic development of plants and animals vary. Even in animals, every species undergoes different stages during embryonic development.
Let us learn about human embryonic development and various stages.
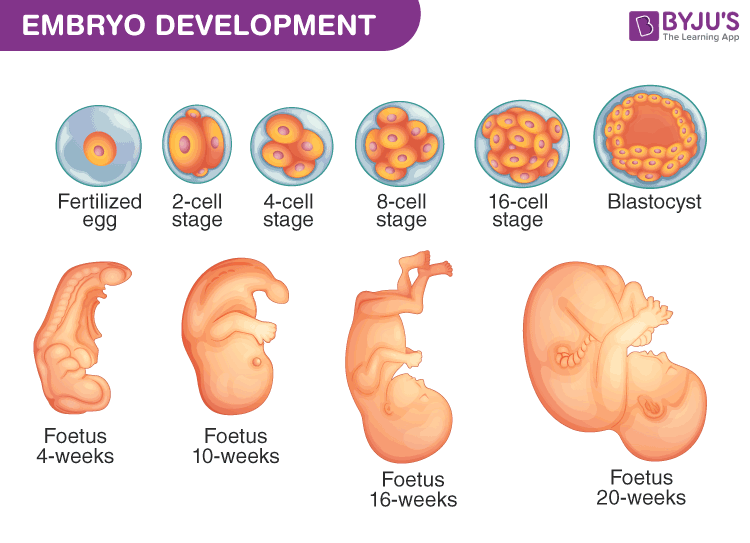
After fertilization, the zygote is formed. The zygote divides mitotically to form 2, 4, 8, 16 celled stages. These cells are known as blastomeres.
Morula- Embryo having 8 to 16 blastomeres.
The morula continues dividing mitotically and gets transformed to blastocyst. The outer layer of the blastocyst is called trophoblast and it gets attached to the uterine wall known as the endometrium. The implantation starts in the first week but gets completed by 2nd week.
The inner cell mass of blastocyst forms embryo. Blastocyst differentiates further to embryonic and extraembryonic tissues. The implantation completes at the 2nd week.
The interdigitated chronic villi of trophoblast and uterine cells form the placenta, which is the connection between the mother and the growing foetus.
The placenta provides nourishment and oxygen to the embryo and helps in removing carbon dioxide and waste produced by the embryo. It also acts as an endocrine gland and secretes various hormones like hCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin), estrogen, progestogens, etc. for maintenance of pregnancy.
Gastrulation starts in the 3rd week, the inner cell or embryo starts differentiating into three germinal layers, i.e. ectoderm, endoderm and mesoderm. These cells transform and get differentiated to all the tissues and organs, like nerve, blood, muscle, bone, digestive tract, etc.
Ectoderm- nervous system, brain, spinal cord, epidermis, hair, nails, etc.
Mesoderm- connective tissue, muscles, circulatory system, notochord, bone, kidney, gonads
Endoderm- internal organs, stomach, liver, pancreas, bladder, lung, gut lining
| Weeks after Fertilization | Embryonic Development |
| Week Three | Gastrulation and formation of three germinal layers. Neurulation follows gastrulation. Notochord is formed |
| Week Four | The heart is the first organ to start functioning. The heart starts beating. Arm buds and optic pits become visible |
| Week Five | Size ~ 4 mm. Starts becoming C-shape, inner ear starts developing, pharyngeal arches develop, liver, pancreas, spleen and gall bladder start developing |
| Week Six | Size ~ 8 mm. Development of eyes and nose, leg buds and hand as flat paddles appear, stomach and kidney precursors start developing |
| Week Seven | Size ~ 13 mm. Lungs and lymphatic system and primary sex organs start developing, arms and legs lengthen and digits start appearing |
| Week Eight | Size ~ 20 mm. External ear starts appearing, nipples and hair follicles start developing, most of the organs start developing by this time |
To sum up, the heart is the first organ to start working. After the 1st month of pregnancy, the heart develops.
Limbs and digits develop in the 2nd month.
By the end of 1st-trimester or 3rd month all the major organ systems develop. Genital organs are visible.
During 5th month the embryo starts moving and hairs start appearing on the head.
By the end of 2nd trimester (24 weeks or 6 months), eyelashes are formed, eyelids separate and the body gets covered with fine hair.
By the end of the 9th month, the foetus fully develops and is ready for birth.
Stay tuned with BYJU’S to know more about the Embryo Development.


Comments