Protective Tissues
Protective tissues are an essential aspect of the plant tissue system. The epidermal cells and cork cells are two kinds of protective cells found in the peripheral layer of the plant. Epidermal cells are organised in a solitary layer to cover the entire plant body. These protective cells contain water-repellent substances, which prevents desiccation. Also, they protect against infections and injuries. The fundamental distinction between epidermal and cork cells is their existence.
Epidermal Cells
The epidermis is the top or primary cell layer of the plant body. These cell structures are covered with cuticles or a waxy sheet, for a means of protection. They are firmly connected and give mechanical strength and security to the plant.
Also see: Difference between Epidermis and Dermis
Cork Cells
The Cork is the external defensive layer of a plant/tree. As plants become more established, the superficial defensive tissues go through specific changes. Due to the changes, the secondary meristem restores the epidermis of the stem. This meristematic layer makes up the cork cells.
Furthermore, the cambium helps in the secondary thickening of these cork cells. They are also the dead cells that make the bark.
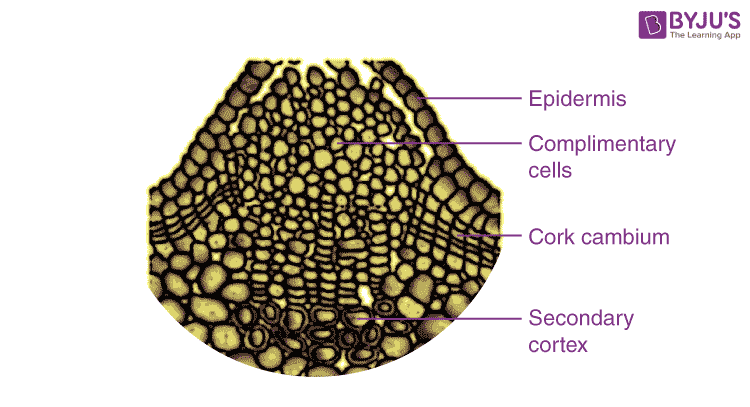
Characteristic Differences in the Protective Tissues
Contents |
Epidermal Cells |
Cork Cells |
| Characteristic Features | Single Layer Living Cells | Multi-Layer Non-Living Cells |
| During Primary Growth Phase | Present | Absent |
| During Secondary Growth | Present | Present |
| Secretions | Cutin | Suberin |
| Observed in | All plants | Woody dicots, a few monocots, and Gymnosperm |
Refer: Difference between Monocots and Dicots
Frequently Asked Questions
How do cork cells differ from the epidermis?
A segment of secondary meristem replaces the outer epidermis. This layer structures the cork cells, which is also a kind of protective tissue. Also, cork cells are found only in mature roots and stems. In contrast, the epidermis is located in the immature parts.
What are the similarities between cork and epidermal cells?
Chloroplasts are absent in both epidermal and cork cells. Furthermore, both epidermal cells and cork cells protect the plant’s inside designs from water and air loss.
What are the functions of cork cells?
The cork cells are dead cells that secrete suberin. This secretion helps the cell wall to be impermeable to water and gases. This layer of dead cells also gives additional protection to the plants.
Also Read: Vascular Cambium and Cork Cambium
Visit BYJU’S Biology for more interesting topics.
Comments