What is pollination?
Pollination can be defined as the natural process of transferring pollen grains from the anther (male reproductive part) to the stigma (female reproductive part) of a flower. This process can be carried out either within a flower or between flowers of the same or different plants.
Explore more: Pollination
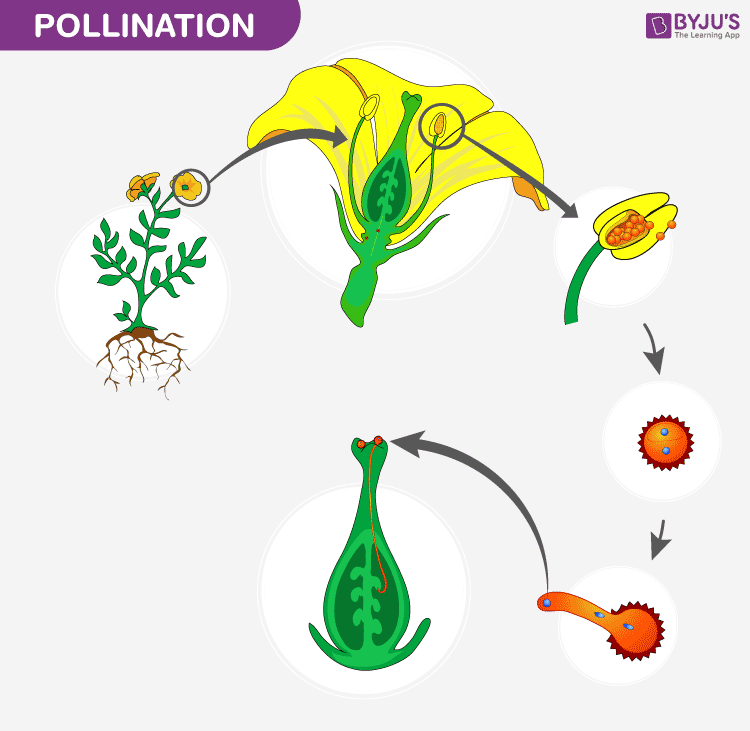
Based on the transfer of pollen grains, pollination has been classified into two different types:
- Self Pollination –— Self-pollination is a type of pollination, which occurs by transferring the pollen grains directly from the anther to the stigma of the same flower. Orchids and Caulokaempferia coenobialis (Chinese herb) are examples of self-pollinated flowers.
- Cross-Pollination — Cross-Pollination is a type of pollination during which the pollen grains are transferred from the anther of the flower to the stigma of a different flower. Most flowering plants reproduce by cross-pollination. Tulips, dandelions and daffodils are some examples of cross-pollinated flowers.
Explore more: Difference between Self-pollination and Cross-pollination.
Insect Pollinated and Wind pollinated flowers: Differences
| Wind pollinated flowers | Insect pollinated flowers |
| Pollinating Agent | |
| The pollinating agent is wind. | The pollinating agents are insects. |
| Morphological features of a Flower | |
| The wind-pollinated flowers comprise light-coloured petals without a pleasant strong smell. | The insect-pollinated flowers comprise brightly coloured petals with a pleasant strong smell. |
| Pollen Grains | |
| In wind-pollinated flowers, the produced pollen grains are smaller and lighter in weight, which can be carried by the wind easily. | In insect-pollinated flowers, the produced pollen grains are larger in size, sticky and spiny, which helps the insect to carry the pollen grains. |
| Stigma | |
| Stigma is feathery or sticky and found hanging out of petals. | Stigma is small and is situated deep inside the petals. |
| Stamens | |
| The stamens are long and visible out of the petals. | Stamens may be small and hidden inside petals. |
| Anther | |
| The anthers are often seen being supported outside the flower. | The anthers are found deep inside the flower. |
| Filaments | |
| The filaments found in these flowers are slender and long. | The filaments found in these flowers are strong and short. |
| Production of Nectar | |
| These flowers do not produce nectars. | These flowers produce a lot of nectars. |
Also Refer: Parts Of A Flower And Its Functions
There are many more differences between insect-pollinated and wind-pollinated flowers. Stay tuned to BYJU’S Biology for more differences and other Biology related topics.

Thanks it was helpful
Helps to understand the difference
I love this explanation on pollination