Metabolism is a crucial part of growth, development and efficient functionality for the body. It can be categorized into two types based on their functions: Catabolism and Anabolism. The major differences between Catabolism and Anabolism are the way the molecules are utilized in the body. Anabolism creates molecules the body needs for functionality and it uses energy in the process. Catabolism, on the other hand, breaks down complex molecules and releases energy which is available for the body to use.
Read on to what is anabolism and catabolism and how are the two different from each other.
Differences Between Catabolism and Anabolism
The concept of anabolism and catabolism have been adopted in the fitness industry as well. They are employed to achieve two different goals. The anabolic workout focuses on building muscle mass whereas, catabolic workout focuses on shedding weight and burning more calories. The major differences between catabolism and anabolism are summarized below.
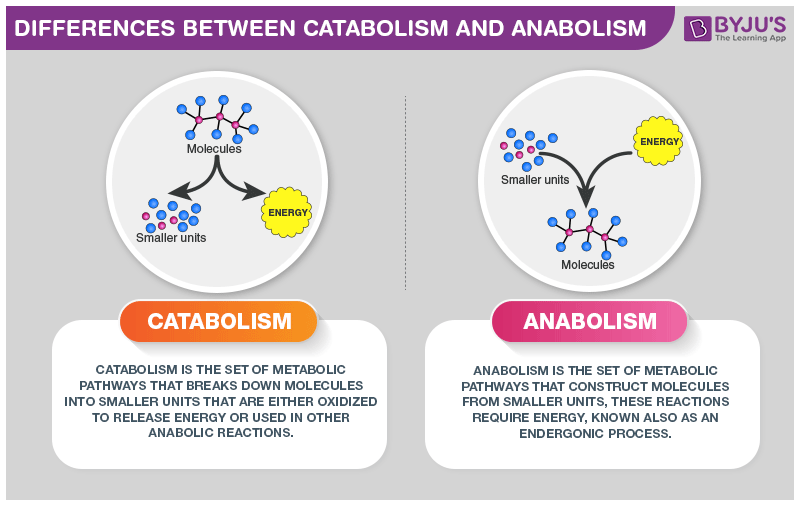
| Difference Between Catabolism and Anabolism | |
| Catabolism | Anabolism |
| Catabolism breaks down big complex molecules into smaller, easier to absorb molecules. | Anabolism builds molecules required for the body’s functionality. |
| The process of catabolism releases energy. | Anabolic processes require energy. |
| Hormones involved in the processes are adrenaline, cytokine, glucagon, and cortisol. | Hormones involved in the process are estrogen, testosterone, growth hormones and insulin. |
| Examples of catabolic processes are proteins becoming amino acids, glycogen breaking down into glucose and triglycerides breaking up into fatty acids. | Examples include the formation of polypeptides from amino acids, glucose forming glycogen and fatty acids forming triglycerides. |
| In catabolism, potential energy is changed into kinetic energy. | In anabolism, kinetic energy is converted into potential energy. |
| It is required to perform different activities in living entities. | It is required for maintenance, growth, and storage. |
What Is Catabolism?
Catabolism is referred to as a series of metabolic pathways that are involved in the conversion of macromolecules into simpler molecules or monomers. Complex molecules are disintegrated into simpler molecules that can be utilized as building blocks for other molecules that are required by cells to function such as glycogen, proteins, and triglycerides. Few of these molecules are simply broken down into waste products which is an alternate way to obtain usable energy. Some of the catabolic processes are:
- Citric acid cycle
- Glycolysis
- Lipolysis
- Oxidative deamination
- Muscle tissue breakdown
What Is Anabolism?
Anabolism is the sequence of enzyme-catalyzed reactions in which nutrients are used to form comparatively complex molecules in the living cells with moderately simpler structures. The process of anabolism is also referred to as biosynthesis. The process includes the production of components of cells such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, which require energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) which are energy-rich compounds. These compounds are synthesized during the breakdown processes such as catabolism. Anabolic processes in growing cells control catabolic processes. The balance exists between both in non-growing cells.
Conclusion
Catabolic and Anabolic processes are required for the proper functioning of the body. Catabolism, at its core, involves breaking down of complex molecules and releasing energy for the body to use. The anabolic process is the complete opposite of catabolism as it involves creating bigger, complex molecules from smaller, simpler molecules. These are usually stored by the body for future use.
To learn more about anabolism and catabolism, or any other related topics, please register at BYJU’S.
Related Links:
| Cellular Respiration |
| Metabolism |
| Life Processes |
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the anabolic state of the body?
In the anabolic state of the body, it builds muscle mass. For this, the body must consume a source of energy. Food and supplements provide the required energy to muscle tissues.
Is ATP produced during catabolism?
Yes, ATP is produced during catabolism. The energy is then stored for anabolic processes.
Give examples of catabolic and anabolic processes.
Formation of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate is an anabolic reaction. Whereas, ATP hydrolysis is a catabolic process.
What is glucose anabolism called?
The glucose anabolism is called glycolysis.

Easy to understand thanks
really helpful 👍