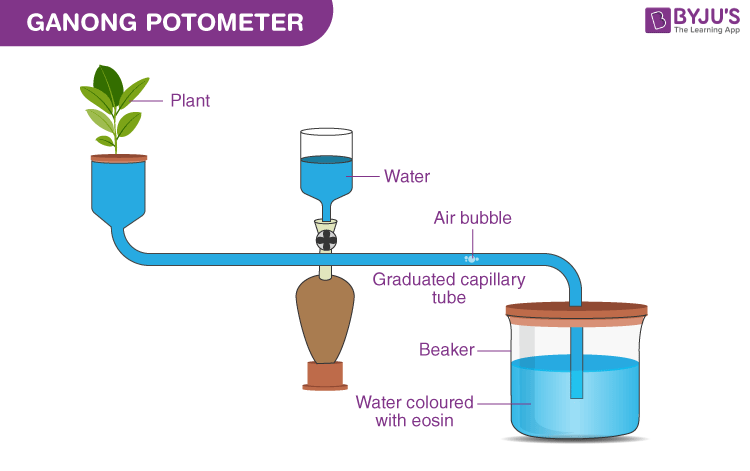
A potometer is a device, which is used to measure water uptake by the plant shoot during transpiration. It is also known as transpirometer. Ganong’s potometer is used to measure the transpiration rate in a laboratory. The Ganong’s potometer comprises a glass tube, which is bent twice, and a glass cylinder having a wide mouth. A capillary tube is inserted into a horizontal glass bar attached to a reservoir. A wide-mouthed glass cylinder is present towards the front end of the apparatus. A rubber cork with a hole is fitted on the mouth of the glass cylinder. A freshly cut twig is placed in this hole. The horizontal bar has graduated readings marked over it. It has a bent end with a nozzle opening. A beaker containing coloured water is placed below this horizontal bar with the bent end inserted into it. A reservoir is connected to the horizontal bar to store water. The entire set-up is placed on a flat surface.
Procedure
- A few drops of eosin oil are added to the water to make it coloured.
- A freshly cut twig is placed on the mouth of the glass cylinder.
- A single air bubble has to be kept at the zero reading of the horizontal bar. Lifting the bent end allows the air bubbles to enter and get trapped in the horizontal bar.
- When the experiment begins, it is observed that the air bubble at the zero reading starts to move.
As transpiration takes place, a transpirational pull is created by the shoot to make up for the loss. Due to this, the horizontal bubble starts moving in the direction of the twig. The transpiration rate is calculated by taking the distance covered by the air bubble in a certain time period. Several readings were noted by repeatedly adjusting the air bubble to zero. The average of these readings gives the transpiration rate.
Also read: Excretion in Plants
Limitations Of Ganong’s Potometer
- The potometer does not measure the transpiration rate accurately because not all the water taken up by the plant is used for transpiration. It usually measures the rate of water uptake.
- The twig placed on the glass cylinder might not stay alive for a longer time.
- The introduction of an air bubble in the horizontal bar is very difficult and time-consuming.
- A slight change in the atmospheric temperature might affect the position of the air bubble.
Also read: Transportation in Plants and Trees
For more details on Ganong’s Potometer, visit BYJU’S website or go to BYJU’S app.
By which instrument, you can count the number of stomata???
Microscope
What is the function of the resorvoir in this experiment.
Reservoir helps in bringing bubble at the start position.
What is the use of air bubble in ganong’s potometer?
The air bubble introduced into the capillary tube is used to monitor the volume of water absorbed by the plant shoot due to transpiration