What are Microtubules?
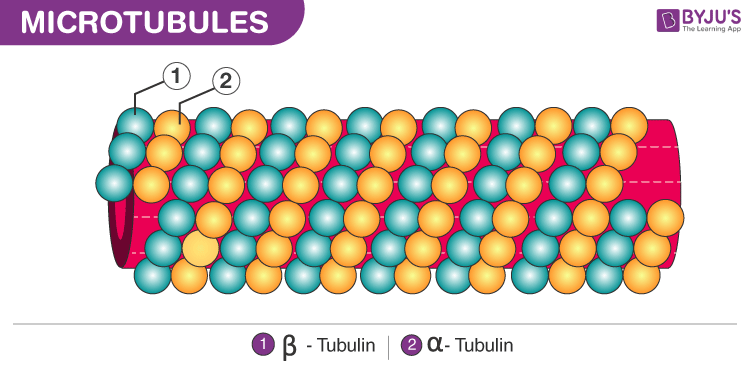
“Microtubules are microscopic, hollow tubes made of alpha and beta tubulin that are a part of the cell’s cytoskeleton.”
Microtubules extend throughout the cell providing it with proper shape and keeping the organelles in place. They are the largest structures in the cytoskeleton and are about 24 nm thick. They facilitate cell movement, cell division, and transportation of materials within the cells. They are also involved in the division of chromosomes during the process of mitosis and in locomotion.
Microtubules Structure
Microtubules are arranged in the form of microtubule-organizing centres. They are structures found in eukaryotic cells. During the interphase, most of the animal cells consist of microtubule-organizing centres. Several proteins are bound to microtubules namely dynein and kinesin.
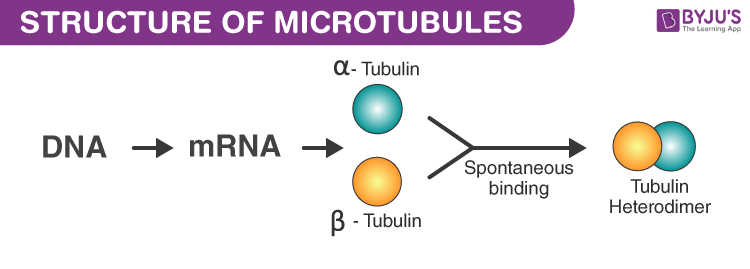
Microtubules are made of subunits called tubulin. Each tubulin is made of an alpha and a beta-tubulin attached to each other. This, tubulin is a heterodimer.
Microtubules play a vital role in all eukaryotic cells. These cells release protein tubulin in a normal manner that involves transcription of the gene coding for tubulin, which yields RNA and is followed by transcription of mRNA to produce proteins. Lumen is the inner space of the hollow cylinder of microtubules.
Also Read: Microfilaments
Microtubule Function
Following are the important functions of microtubules:
Cell Movement
Microtubules give structures to cilia and flagella. They also facilitate the contraction and expansion of the cell helping them to move from one place to another.
Cell Division
Microtubules play a major role in forming the mitotic spindles. These mitotic spindles organize and separate the chromosomes during cell division.
Cell Transport
Microtubules aid the movement of organelles inside the cytoplasm of the cells. They also help various areas of the cell to communicate with each other.
Intracellular Organization of Microtubules
In the cytoplasm, microtubules form a structural network. The function of the cytoskeleton in microtubule includes chromosomes segregation, transport, mobility and mechanical support. It can either shrink or grow to generate energy which is due to the presence of motor proteins that allow cellular components and others to be carried along with microtubules.
The arrangements in microtubules are specific to cell-type. So that it would be easy to facilitate the transportation of organelles, vesicles, and proteins along the apical-basal axis of the cell. They play a vital role in cell migration as well.
Also Read: Cytoskeleton
To know more about microtubules, its definition, functions and intracellular organization, keep visiting BYJU’S website or download BYJU’S app for further reference.

Comments