Nepenthes, commonly known as tropical pitcher plant or monkey cup, is a genus of carnivorous plants belonging to the family Nepenthaceeae. About 170 species of the genus are known. They are mostly liana-forming plants that are woody vines, rooted in the soil that take help of trees or any vertical support to get sunlight.
Classification
|
Kingdom |
Plantae |
|
Clade |
Tracheophytes |
|
Order |
Caryophyllales |
|
Family |
Nepenthaceae |
|
Genus |
Nepenthes |
Well-Labelled Diagram of Nepenthes
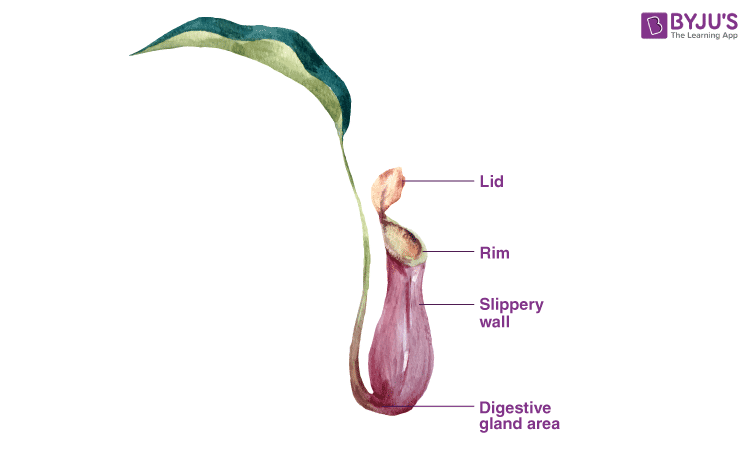
Features
- It is a carnivorous plant that is native to Madagascar, Australia and Southeast Asia.
- They are perennial herbaceous plants that mostly grow in acidic soils.
- The characteristic feature of pitcher plants is their ability to trap insects and other prey with the help of their pitcher shaped leaves.
- The leaves arise alternatively from the stem in sword shapes with full leaf margins.
- The midrib extends to form a tendril that helps in climbing. From the end of the tendril arises the pitcher.
- The pitcher arises as a small bud and then divides to form a tube-shaped or globular trap.
- The underside of the trap lid has nectaries that secrete nectar to attract the insects. The insects fall prey and often fall from the mouth into the trap that consists of a pool of liquid from which it is unable to escape.
- The insects are mostly broken down by enzymes that sources the plants with nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus.
- The lower portion of the trap contains digestive glands that help in the digestion of the insect.
- The wall of the trap is slippery with a waxy coating that makes it impossible for the prey to escape from the trap.
- The most common species of Nepenthes include N.gracilis, N.mirabilis, N.veitchii, and the critically endangered species N.attenboroughii.
Keep visiting BYJU’S Biology for more such interesting topics.
Also Read:
Comments