What is a Nerve?
A nerve is a cable-like structure within the body designed to conduct nerve impulses that relay information from one part of the body to another.
A typical nerve is made up of a bundle of fibres which are wrapped around layers of tissue and fat, and they stretch throughout the body. These nerves transmit information along the axons to the respective organs. These are the basic elements that constitute a nerve.
Nerves are a part of the nervous system. They are primarily involved in control and the coordination of all the parts of the body.
The nervous system not only sends and receives messages but also processes them into chemical signals called impulses in the human body. A wide network of nerves is spread throughout our body, which also runs through the brain, the spinal cord and many organs.
Read More: Central Nervous System
Structure of a Nerve
Nerves are the organs that make up the peripheral nervous system. It consists of a cord-like structure with multiple nerve fibres (also called axons) wrapped in layers of tissue and fat. This axon has layers of connective tissue around it. This connective tissue is called the endoneurium. This entire nerve is further enclosed in another layer of connective tissue called the epineurium.
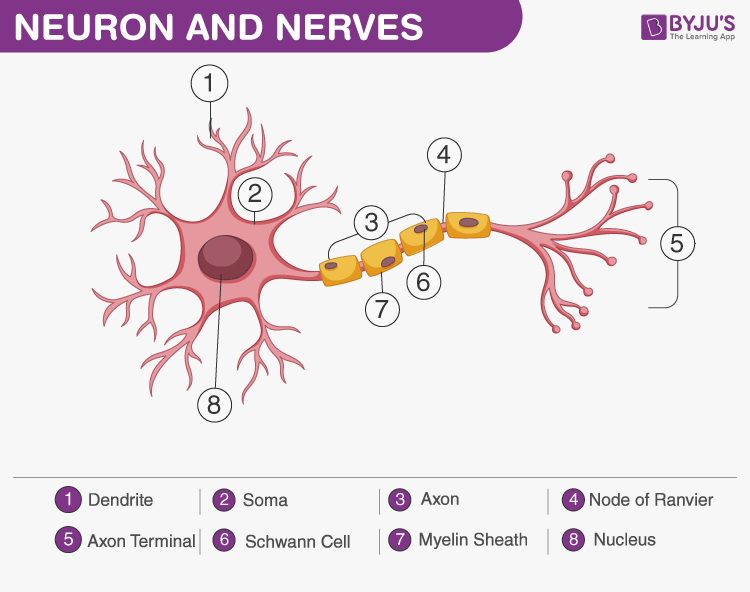
Neuron Structure
The structure of a nerve is explained below:
- A group of neurons is organized into bundles inside the nerves. This bundle is known as fascicles.
- The perineurium surrounds and holds together each fascicle.
- The perineurium is concentrically laminated and composed of flattened cells collagen fibres and basement membranes.
- Neurons and blood vessels are held inside the fascicles by a loose connective tissue known as endoneurium. It covers and holds the outer surface of the nerves together.
- Arteries and veins are present between the fascicles. These blood vessels supply nutrients and gases to the neurons inside the fascicles.
Also Read: Neuron and Nerves
Types of Nerves
There are three types of nerves in the human body which are classified based on their functions. These are the sensory nerves, motor nerves and mixed nerves.
Sensory Nerves
These are the nerves that send messages to the brain or the spinal cord from the sense organs. These are enclosed in the form of a bundle like structures or nerve fibres in the peripheral nervous system. They carry information from the PNS to the CNS( Central Nervous System).
Motor Nerves
Motor nerves are those nerves those that carry the messages in the form of a response from the brain or the spinal cord to other parts of the body such as the muscles and glands. They are responsible for carrying the information from the CNS to the PNS.
Explore More: Peripheral Nervous System
Mixed Nerves
Mixed nerves are the nerves that perform both the action of sensory nerves as well as a motor nerve. They transform electrical impulses from the central nervous system to the muscles of the body. Generally, the mixed nerves transmit impulses at the rate of 120 metres per second or 432 kilometres per hour.
Function of Nerves
The primary function of nerves to conduct an electrochemical impulse and convey information. These impulses are carried by the individual neurons that make up the nerve.
These impulses travel from one neuron to another by crossing a synapse. The messages are converted from electrical to chemical and then back to electrical.
The sensory nerves carry information from the receptor to the central nervous system where the information gets processed.
The motor nerves, on the other hand, carry information from the central nervous system to the muscles.
Nerve Disorders
Nerve disorders include:
- Pain
- Muscle Malfunction
- Changes in sensation
- Changes in the senses
- Vertigo
- Dysarthria
- Sleeping problems
- Mental disability
Explore more about nerves, types of nerves, their structure, function and nerve disorders on the BYJU’S App. Discover other interesting topics only on BYJU’S Biology.
Further Reading:
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a nerve?
Nerves are cord-like structures whose primary role is to provide a pathway to conduct electrical impulses throughout the body. It essentially relays information from one part of the body to another.
Outline the structure of a nerve.
Nerves are cord-like structures with multiple nerve fibres (also called axons) wrapped in layers of tissue and fat. These axons are surrounded by layers of connective tissue called the endoneurium. This entire nerve is enclosed in another layer of connective tissue called the epineurium.
List the various types of nerves in the human body.
Based on their function, the nerves in the human body are divided into three types, namely:
- Sensory nerves
- Motor nerves
- Mixed nerves
What are sensory nerves?
Sensory nerves are the nerves responsible for sending messages to the brain or the spinal cord from the sense organs. They are also called as afferent nerves.
What is the function of motor nerves?
Motor nerves transmit the messages from the brain or the spinal cord to other parts of the body, such as the muscles or glands.
What are mixed nerves?
A mixed nerve is a type of nerve that performs the action of sensory nerves as well as the motor nerves.
Where are the nerves located in the body?
Nerves are located in the peripheral nervous system as bundles of the axon that carry signals between the brain and spinal cord and the rest of the body.
What are the most important nerves in the human body?
The most important nerves in the human body are cranial and spinal nerves. The cranial nerves are 12 in number whereas spinal nerves are 31 in number.

This is just beautiful…. you’ve just made my day!