Aim
To study by demonstrating the osmosis process by potato osmometer.
Theory
What is Osmosis?
Osmosis is the phenomena in which solvent molecules pass through a semi-permeable membrane from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. The process continues until the quantity of fluid is balanced or equalized in both regions, the region of higher concentration and the region of lower concentration of the semipermeable membrane. In other words, osmosis is the diffusion or movement of water from a region of higher water potential to a region of lower water potential.
In osmosis, what are solvent and solute?
The fluid that permeates through the semipermeable membrane is called the solvent, whereas the solute is the dissolved particles in the fluid.
What is the solution?
The mixture of solute and solvent form the solution.
List the different types of solutions.
The following are the types of solutions:
- Hypertonic solution – It is a solution with a high solute level. If living cells are placed in a hypertonic solution, because of lower concentration water moves out of the cell causing it to shrink and becomes plasmolyzed.
- Hypotonic solution – It is a solution with low concentration levels of solute. If living cells are placed in this solution, water passes into the cells because of higher water concentration in comparison to the cell causing the cells to swell and turn turgid.
- Isotonic solution – A solution is said to be isotonic if both solutions have an equal concentration of solute. If living cells are placed in an isotonic solution, no change is shown as there is the equal concentration on both the regions hence the cell retains its original shape.
Material Required
- A fresh large-sized potato tuber
- 20% sucrose solution
- Beaker
- Water
- Scalpel/blade
- Petri dish
- A Bell pin needle that is labelled with a waterproof ink
Diagram
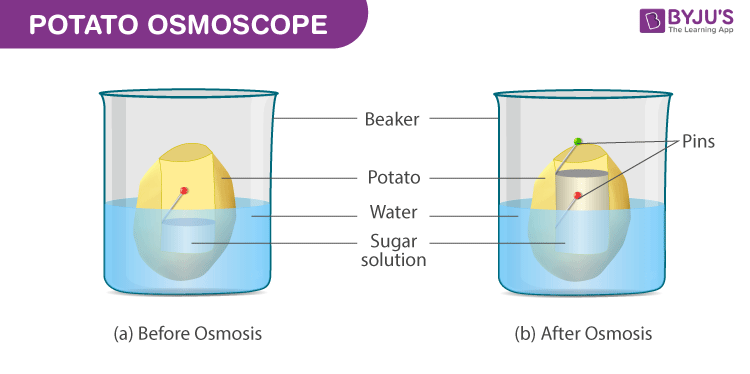
Procedure
- Slice the potato tuber into two equal halves with the help of a scalpel or a blade. The outer skin is to be peeled off. Since the tuber shape is irregular, slice the halves into squares
- From the mid-region of the tuber, scoop from the soft parenchyma, so as to form a tiny cavity of a square or a circular shape. At the base, the cavity prepared should have a minimum thickness.
- Fill up half the cavity with the freshly prepared 20% sugar solution. Into the cavity, fix a pin in a way that the mark is in the same line with the layer of the sucrose solution.
- Set up the osmometer in a Petri dish/beaker that is filled with water in a way such that 75% of the potato osmometer is immersed in water
- The set up should remain uninterrupted for close to 1 hour.
- Notice the sugar solution in the osmometer towards the end of the experiment
- Carry out the experiment with the help of water in the cavity and the sucrose solution in the petri dish/beaker.
Observation
After a period of time, within the osmoscope, the sugar solution rises and is seen coloured.
Conclusion
- An increase in the level of sucrose solution is observed in the osmometer. It is because of the entrance of water due to endosmosis from the beaker.
- Also, a water potential gradient is built between the sucrose solution in the external water and the osmometer.
- Though both the liquids are divided by living cells of the potato tuber, they allow the entrance of water into the sugar solution.
- This demonstrates the entrance of water into the sugar solution through the tissues of potato serving as a selectively permeable membrane.
Viva Questions
Q.1. What is plasmolysis?
A.1. It is a process, wherein the protoplasm of the plant cell turns round as a result of contraction when placed in a hypertonic solution due to exosmosis resulting in the decline in the tension of the cell wall.
Q.2. What is the significance of osmosis?
A.2. Osmosis maintains cell turgidity. It causes the transportation of nutrients and discharge of metabolic waste products. It preserves the interior environment of a living entity to maintain an equilibrium between the intracellular fluid levels and water.
Q.3. What is diffusion?
A.3. The movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Osmosis is a type of diffusion.
For more information on related biological concepts and experiments, please register at BYJU’S.
Related Links:
| Difference Between Endosmosis And Exosmosis |
| Plant Water Relations |
| Difference between Osmosis and Diffusion |

Good
Thank you BYJU’S!!