Table of Contents
- Plasmolysis
- Aim
- Theory
- Materials Required
- Procedure
- Observation
- Conclusion
- Precautions
- Viva Questions
Plasmolysis
Plasmolysis is the process during, which cells lose water when placed in a hypertonic solution, that is greater in the concentration of solutes compared with the inside of a cell. During plasmolysis, the organelles inside the cell shrink away from the cell wall, which results in severe water loss and leads to the collapse of the cell wall and finally results in cell death.
Osmosis is primarily responsible for the occurrence of plasmolysis. There are three stages in plasmolysis. Based on certain criteria, plasmolysis can be classified into two different types:
- Concave plasmolysis – It is a reversible process.
- Convex plasmolysis- It is an irreversible process.
Also Refer: Plasmolysis
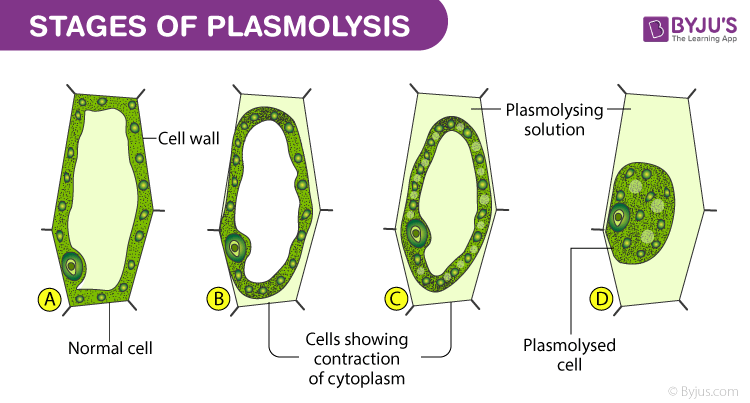
Let us perform a simple experiment to study in detail the process of plasmolysis in the plant cell.
Aim
To study the phenomena of plasmolysis in epidermal peels of Rhoeo plant leaves in hypotonic and hypertonic solutions using salt solution.
Theory
- What is Plasmolysis?
It is a process of contraction or shrinkage of the protoplasm of a plant cell due to the loss of water from the cell. It takes place in extreme conditions and hence occurs rarely. Plasmolysis can be carried out in a laboratory by submerging a living cell in a concentrated sugar or salt solution for water loss from the cell.
- Why are the Rhoeo plant’s leaves are used in this experiment?
The Rhoeo plant’s leaves are used in this experiment because the Rhoeo leaf has coloured cell sap, which can be examined clearly under a compound microscope.
- How does water permeate through the cell membrane?
The cell membrane serves as a semipermeable membrane dividing the inner of all cells from that of its surroundings. This membrane permits movement of a few of the particles including, water molecules, and ions across the membrane while blocking others. There is the continuous movement of water molecules in and out of the cell across the cell membrane ad also it serves as an important attribute for enabling cells to absorb water.
Also Refer: Cell Wall and Cell Membrane
Materials Required
- Needle.
- Forceps.
- Droppers.
- Glass slides.
- Watch glass.
- Rhoeo leaf.
- Coverslips.
- Compound microscope.
- Sodium chloride 5% solution.
- Sodium chloride 0.1% solution.
Procedure
- Take two clean and dried glass slides and place them on a table.
- Select the fresh and cleaned Rhoeo leaves and place them on the watch glass.
- Fold the leaves in such a way that it tears from the lower side of the leaf. Or, with the help of a clean blade.
- Extract two small fragments of a fine and transparent layer with the help of forceps from the lower surface of the epidermis of the Rhoeo leaf.
- Now set up the epidermal peels on each of the glass slides.
- With the help of a dropper, add 1 to 2 drops of sodium chloride 0.1% solution to one of the prepared slides.
- With the help of another dropper, add 1-2 drops of sodium chloride 5% solution to the other prepared slide.
- Now carefully set a cover slip on the peel of both sides with the help of a needle. Make sure, no bubbles are present.
- Leave the prepared glass slide undisturbed for a few minutes.
- Now carefully place the slides under a compound microscope and observe the changes.
Observation
After a period of 30 minutes, we can notice that cells placed in the sodium chloride 0.1% solution seem to be turgid and the cells placed in the sodium chloride 5% solution seem to be shrunk with the loss of water and it exhibits the process of plasmolysis.
Conclusion
Plasmolysis is observed when the plant cells are immersed in the concentrated salt solution or sodium chloride 5% solution. During this process, 4 to 5 per cent of water passes through the cell membrane into the encircling medium. This occurs as the concentration of water inside the cell is higher than the outside of the cell hence the protoplasm induces shrinkage and takes a spherical shape.
When the plant cells are immersed in a dilute salt solution or sodium chloride 0.1% solution, the water in the plant cells moves from the outside to the inside of the cell as the water concentration is higher outside the cell as compared to the inside of the cell which causes the turgidity of the cell.
Also Read: Plant Water Relations
Precautions
- The part of the Rhoeo leaf that needs to be extracted for the experiment is the epidermal peel from the lower surface
- Care needs to be taken to ensure that the peel is moist and not dry.
Viva Questions
Q.1. What is Plasmolysis?
A.1. It is a process wherein the protoplasm of the plant cell turns rounded as a result of contraction when placed in a hypertonic solution due to exosmosis resulting in the decline in the tension of the cell wall.
Q.2. What is Incipient Plasmolysis?
A.2. It is the initial phase of plasmolysis wherein the protoplasm is just about to leave the cell wall.
Q.3. List any two significance of Plasmolysis?
A.3. Listed below are the importance of plasmolysis :
- Helps to better understand and study the nature of a living cell
- It is used in the preservation of food materials such as jellies, and meat. Used in pickling as its salting is known to kill bacteria
Q.4. What is Osmotic pressure?
A.4. It is a pressure that checks the osmosis process. It needs to be applied to check the passage of the solvent as a result of osmosis.
Q.5. What is turgor pressure?
A.5 It is the pressure that presses the plasma membrane against the cell wall. It is a hydrostatic pressure that arises within the cell as a result of endosmosis on the cell wall.
Q.6. What is wall pressure?
A.6. The turgor pressure on the rigid walls of the cells causes exerting equal pressure in the opposing direction. That is termed wall pressure.
Q.7. When does the water potential become equal to that of its surroundings?
A.7. It happens when the turgor pressure becomes equal to the wall pressure thereby stopping the entry of water into the cells.
For more information on plasmolysis and other related biological concepts and experiments, visit us @ BYJU’S Biology.


Byjus is the best learning platform, love you BYJUS