According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 10.
What is Magnet?
Objects which attract magnetic materials like cobalt, nickel and iron are called a magnet.
The ancient, elderly Greek shepherd was the first person to discover minerals. It is a naturally occurring mineral called magnetite. Therefore, this naturally occurring mineral – magnet was named by the discoverer’s name. The magnets obtained naturally from a Magnetite rock are called natural magnets, and those magnets prepared by the combination of certain mineral ores are called as artificial magnets.
Magnetic Materials: Cobalt, nickel, and iron are some examples of Magnetic Materials. These materials easily attract a magnet.
Non-magnetic Materials: Aluminium, zinc, wood, and rubber are called Non-magnetic Materials, as these materials are not attracted towards the magnet even when they are brought closer to the magnet.
To know more about Magnet, visit the link below;
Types of Magnets
There are different types of magnets, and they are classified based on their shapes. The different types of magnets include – bar magnets, dumbbell-shaped magnets, horseshoe magnets, cylindrical magnets, etc.
Magnetic Compass
The magnetic compass is a simple device which has been used since ancient times by sailors and other travellers to find directions. A magnetic compass is composed of a small box with a glass top and a magnetic needle, which moves and indicates the directions.
Introduction Magnet and Magnetite
- Substances that attract materials like iron, nickel etc.
- Magnets occur naturally as a particular type of rock.
- This rock is called magnetite.

Discovery of Magnets
Greeks used the term magnet in six hundred B.C. for the mysterious stone that seemed to attract iron and other materials. It was first discovered by a Greek shepherd named Magnes (hence the terminology) when his stick, which had an iron end got stuck to a rock.
To know more about Discovery of Magnets, visit the link below;
Magnetic and Non-magnetic Materials
- Materials that get attracted towards a magnet are called magnetic materials. E.g. iron, cobalt or nickel.
- Materials that do not get attracted by a magnet are nonmagnetic materials. E.g. wood, plastic etc.
For more information on Magnetism, watch the below video

Poles of a Magnet
Every magnet is bipolar, i.e. they have 2 poles at the extremities. This can be seen by spreading iron filings around a magnet. These filings arrange themselves in a pattern which is mostly dense towards the two ends of a magnet. These poles are called North and South poles of a magnet.

To know more about Magnetic Poles, visit here.
How to Find Your Way Using a Magnet
Magnetic Poles of the Earth
- Earth has 2 geographic poles, the north and south poles.
- They are the Arctic (South Pole of the earth’s magnet) and Antarctica (North Pole of the earth’s magnet).
- Earth’s magnetic poles are near but not exactly in the same place as the geographic poles.
- A magnetic compass aligns itself towards the magnetic north pole of the earth.
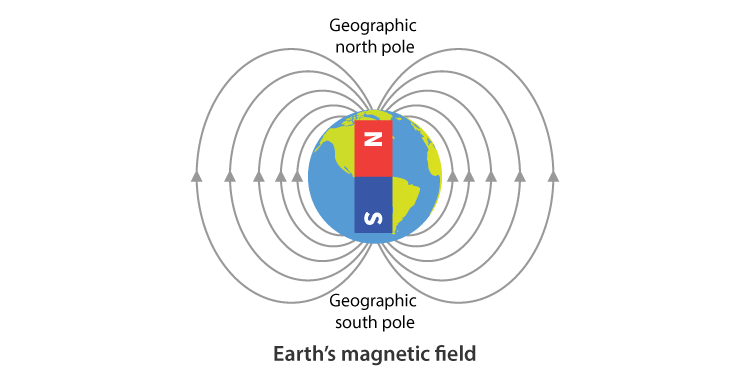
To know more about Earth’s Magnetism, visit here.
Using Magnets to Find Directions
- When a bar magnet is suspended freely by a thread, it aligns itself to the direction of North.
- Travellers have used this property of magnets for ages to find directions.
- A compass is a device with a magnetised needle pivoted inside a box covered by glass, which points to the direction of north and is a useful tool for finding directions.
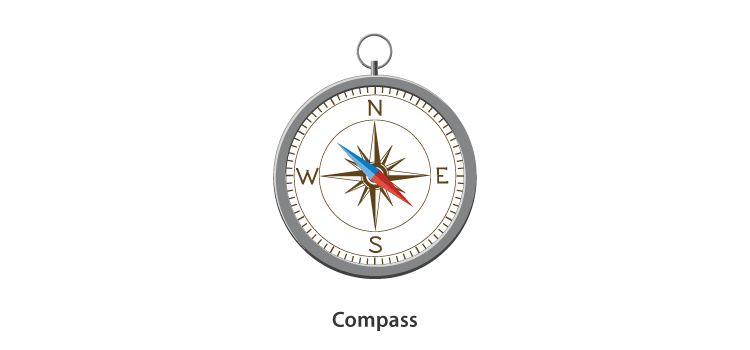
To know more about the Uses of Magnets, visit here.
Can You Make Your Own Magnet?
Making a Magnet
- The magnetic material can be made into a magnet by rubbing a magnet on the surface of the magnetic material.
- This creates an influence where the particles inside the material align themselves like the poles of a magnet.
Microscopic Cause of Magnetism
- Each particle in a magnetic material behaves somewhat like a bar magnet.
- They are normally aligned randomly within the material.
- But under the influence of a stronger magnet, they realign themselves according to the stronger magnet’s field.
Loss of Magnetic Property
The magnetic property of a magnet is lost on:
- Heating
- Hammering or hitting
- Dropping
Do Opposites Really Attract?
Attraction and Repulsion between Magnets
Like poles repel each other, while unlike poles attract each other.

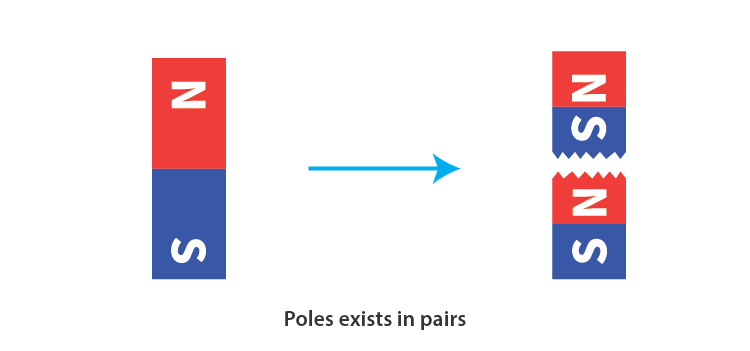
Inseparable Poles
- Magnetic poles always exist in pairs.
- If you cut a bar magnet in half, it forms 4 poles, each half having a north and a south pole.
Learn more about the Magnets from the topics given below:
| Magnet | Uses of Magnets |
| Discovery Of Magnets | Poles Of Magnets |
Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets
What are the types of magnets?
There are three types of magnets: permanent magnets, temporary magnets, and electromagnets.
How can a magnet/magnetic object lose its magnetism?
1. Heating 2. Hammering/hitting 3. Dropping from heights
What are inseparable poles?
The two poles of a magnet repel when their like poles face each other and attract each other when unlike poles are brought near. These two poles of a magnet are called inseparable poles.
Comments