Organic and inorganic compounds form one of the primary basis for chemistry. The study of organic compounds is termed as organic chemistry, and the study of inorganic compounds is inorganic chemistry.
Table of Contents
- Types of compounds
- Difference Between Organic and Inorganic Compounds
- Recommended Videos
- Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Types of compounds
Compounds are said to be of two types, namely:
-
Organic compounds
-
Inorganic compounds
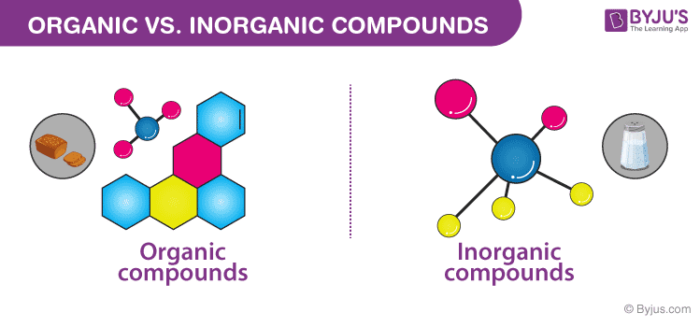
Difference Between Organic and Inorganic Compounds
Organic and inorganic compounds are said to be one of the large class of members. The primary difference that lies between these organic compounds and inorganic compounds is that organic compounds always have a carbon atom, while most of the inorganic compounds do not contain a carbon atom in them. Almost all organic compounds contain carbon-hydrogen or a simple C-H bond in them.
The most common fact that differentiates organic compounds from inorganic compounds is that organic compounds mainly result from the activities of a living being. In contrast, inorganic compounds are obtained from natural processes which are not related to any of the life forms on earth or any result of human experiments which are conducted in laboratories.
The difference between organic and inorganic compounds does not end with the presence or the absence of carbon atoms in them. These have characteristics of both types of compounds which are said to be different.
Difference Between Organic and Inorganic Compounds
S.no |
Organic Compounds |
Inorganic Compounds |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Organic compounds are characterized by the presence of carbon atoms in them | Most inorganic compounds do not have carbon atoms in them (some exceptions do exist) |
| 2 | Organic compounds consisting of hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, and their other derivatives | They do not possess hydrogen or oxygen, and their derivatives |
| 3 | Organic compounds are said to be more volatile and also highly inflammable | These compounds are not inflammable and are non-volatile in nature |
| 4 | These compounds exist in the form of solids, gases, and liquids. | These exist as solids |
| 5 | These are insoluble in water | These are soluble in water and also non-soluble in some of the organic solutions |
| 6 | These compounds have the carbon-hydrogen bonds | These do not have the carbon-hydrogen bonds |
| 7 | Organic compounds are mainly found in most of the living things | These compounds are found in non-living things |
| 8 | Organic compounds form covalent bonds | Inorganic compounds form ionic bonds between the atoms of molecules |
| 9 | In most of the aqueous solutions, these are poor conductors of heat and electricity | In aqueous solutions, these are known to be good conductors of heat and electricity |
| 10 | Examples of organic compounds include fats, nucleic acids, sugars, enzymes, proteins and hydrocarbon fuels | Example for inorganic compounds includes non-metals, salts, metals, acids, bases, and substances which are made from single elements |
| 11 | These are biological and more complex in nature | These are of mineral and not much complexity in nature |
| 12 | Organic compounds cannot make salts | Inorganic compounds can make salts |
| 13 | The rate of reaction is slow in organic compounds | Inorganic compounds have a high rate of reaction |
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is meant by organic compound?
An organic compound is one of a broad class of chemical compounds in which one or more atoms of carbon, most commonly hydrogen, oxygen, or nitrogen, are covalently bound to atoms of other elements. Carbides, carbonates, and cyanides form the only carbon-containing compounds not known as organic.
Why are organic compounds important?
Chemical compounds are essential since carbon is found in all living organisms. For example, in photosynthesis and cellular respiration, the carbon cycle requires the exchange of carbon between plants and animals. Chemical compounds interact to form organometallic compounds with metals.
How many inorganic compounds are there?
Although about 19 million known carbon compounds have been found in organic chemistry, inorganic chemistry contains only about 500,000 known compounds. However, major economic benefits are provided by inorganic compounds.
Is salt an inorganic compound?
As they do not form the complex molecular bonds that carbon makes possible, inorganic compounds are also very simple. Sodium chloride, known more generally as household salt, is a typical example of a basic inorganic compound. Just two atoms, sodium (Na) and chlorine ( Cl), are in this formula.
To learn more about topics of organic and inorganic chemistry, register with BYJU’S and download our app.

Informative content