Esters are chemical compounds that are derived from organic or inorganic acids where at least one hydroxyl group is replaced by an alkoxy group. Esters with low molecular weight are found in pheromones and essential oils. They are less polar than alcohol and more polar than ethers. They are characterized by some water solubility due to their participation in hydrogen bonding.
In simple, Hydrolysis is a simple reaction with water. It can be a reverse of water condensation where it involves the ejection of a water molecule when two molecules react together to form a larger molecule. Technically this is what happens when esters are hydrolyzed by dilute acids such as dilute hydrochloric acid and water.
Table of Contents
- Ester Hydrolysis
- Methyl Propanoate Hydrolysis
- Mechanism of Base Hydrolysis of Esters
- Applications of ester hydrolysis
Ester Hydrolysis
Below illustrates hydrolysis using an acid catalyst. The reaction that uses water is very slow. Here dilute acid is used as an acid catalyst.
Methyl Propanoate Hydrolysis
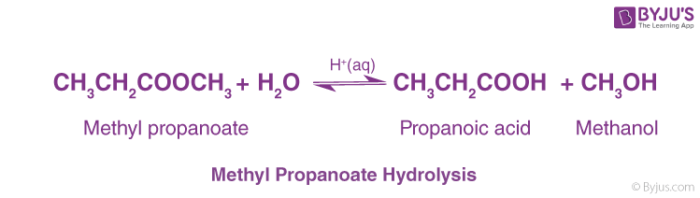
Ester is heated in reflux with dilute hydrochloric acid (dilute acid). Reactions are reversible. This is termed Ester Hydrolysis.
Mechanism of Base Hydrolysis of Esters
The below reaction is an illustration of Reactive System – Type the reaction leads to acyl-oxygen cleavage.
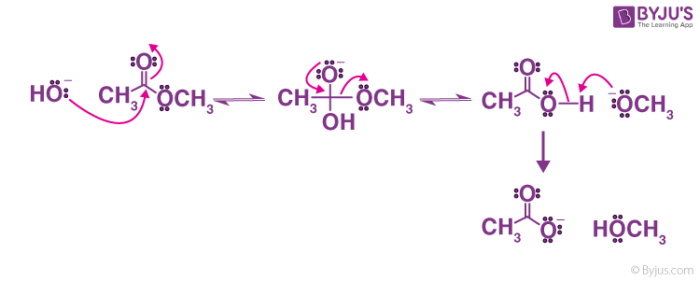
- The electrophilic reagent that is present is attacked by hydroxide nucleotides at C=0; thus creating the tetrahedral intermediate.
- When the intermediate collapses, C=O will result in the loss of leaving the group alkoxide.
- An equilibrium exists in an acid and base reaction, where an acid workup would allow carboxylic acid to obtain from the reaction.
Applications of ester hydrolysis
- Sodium acetic acid derivative is a kind of salt. At the point when water is added to sodium acetic acid derivative, the compound securities separate, making it isolated into sodium particles and acetic acid secondary particles. At that point, acetic acid secondary particles in the water then join with hydrogen iotas to make a corrosive called acidic corrosive.
- Alkyl halides are synthetic mixes frequently utilized as a part of refrigerants as CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons). At the point when water is added to alkyl halides, the substance is then changed over to a kind of liquor, which is for the most part more secure for the earth.
Sucrose is a disaccharide otherwise called table sugar. Hydrolysis of these compound outcomes in the making of two separate monosaccharide sugars known as glucose and fructose. These sugars are utilized as a part of an assortment of uses, generally in the sustenance business.
To know more in detail about Ester Hydrolysis and other related topics, such as esterification, download BYJU’S – The Learning App.


Comments