What are Oximes?
Oximes are the chemical compounds that belong to the class of imines, having the general formula of R1R2C=N O H.
Where R1 is the organic side-chain whereas R2 is the hydrogen, which forms an aldoxime, or like another group of organic compounds such as ketoxime. The O-substituted group of oximes forms a very closely related group of compounds.
Table of Content
Oximes Structure
- Oximes are also called nitrogen possessing organic compounds which are obtained from hydroxylamine, ketone, and aldehyde.
- These compounds are also derived from the reaction of hydrogen-donating reagents with the nitro compounds or another way is by the process of isomerisation of the nitroso compounds.
- Oximes that are obtained from aldehydes or called aldoximes can also be dehydrated forming nitriles.
- The other chemical reactions are the conversion of it to amines by treating it with hydrogen or other reducing agents and also by converting it to amides.
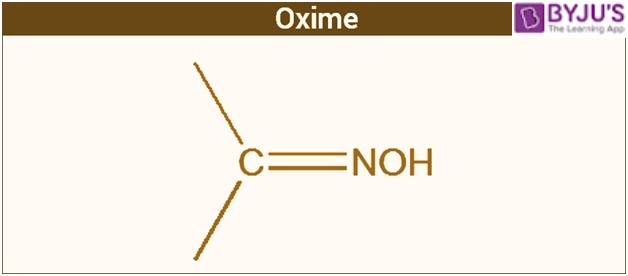
The structure of oxime is a two-sided chain with a central atom consisting of carbon. The two side chains differ entirely from each other. One of the two chains comprises a hydroxyl group.
Some examples of oximes include Aldicarb oxime, aldoxime, dimethylglyoxime, ketoxime, methoxime, etc.
Preparation of Oximes
When an aldehyde or ketone reacts with hydroxylamine (NH2OH) in a weakly acidic medium, it produces oxime and eliminates water molecules.
1. Acetaldehyde reacts with hydroxylamine forming Acetaldoxime and water.
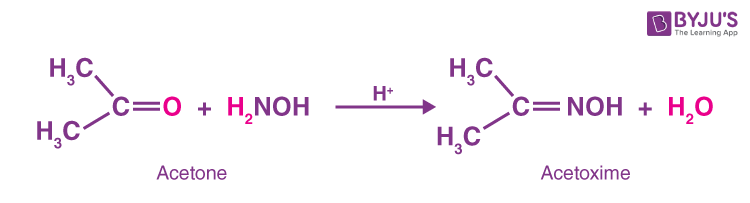
 2. Acetone reacts with hydroxylamine and forms Acetoxime and water.
2. Acetone reacts with hydroxylamine and forms Acetoxime and water.
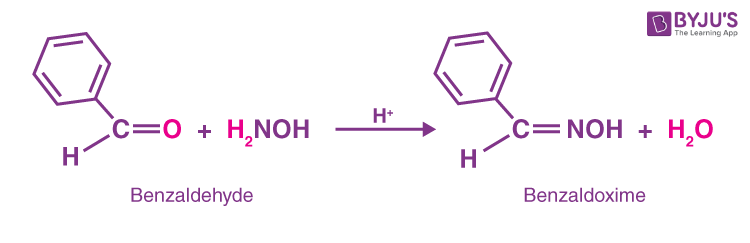
3. Benzaldehyde reacts with hydroxylamine and forms Benzaldoxime and water.
Properties of Oximes
- Oximes have about 3 characteristics bands with wave numbers measuring 3600 (O-H), 945 (N-O) and 1665 (C=N) in the infrared spectrum.
- The aliphatic group of oximes is resistant to the process of hydrolysis more than the analogous hydrazones.
- These compounds are present in the form of colourless crystals and are said to be less soluble in water.
- Oximes are said to exhibit weak acidic and base properties and are said to be toxic in nature.
- The salts of acids affect the temperature of these compounds.
- Oximes tend to decompose when heated further resulting in a massive explosion.
Applications of Oximes
- In industries, oximes are used in the production of an organic compound called Caprolactam, which is a precursor for the polymer named Nylon 6.
- In Organic chemistry, these are utilised in catalytic reactions.
- The compounds of oximes are also used as antidotes which are used to serve as nerve agents.
- In Japan, the oxime naming perillaldehyde is used as an artificial sweetener.
- In oil paints, the oxime called Methyl ethyl ketoxime is used as a skinning agent.
- The oxime called Acetone oxime is used as a de-oxidant or a corrosion inhibitor which lowers the toxicity.
The compound is used in the synthesis of other organic compounds such as cobalt, ketones, etc.
Frequently Asked Questions-FAQs
Is oxime a functional group?
An oxime is a functional group consisting of a hydroxyl group bonded to the nitrogen atom of an imine. An oxime derived from an aldehyde is called an aldoxime and derived from ketone is called ketoxime.
How can I reduce my oxime?
Oxime is formed by the reaction of aldehydes or ketones with hydroxylamine. In the presence of a reducing agent of lithium aluminium hydride or by catalytic hydrogenation oxime can be reduced to a primary amine.
What is hydroxylamine used for?
Hydroxylamine is used as a reducing agent in photography, in synthetic and analytical chemistry, to purify aldehydes and ketones, as an antioxidant for fatty acids and soaps, and as a dehairing agent for hides. In addition, hydroxylamine is used in the production of cyclohexanone oxime or caprolactam.
Is hydroxylamine water soluble?
Hydroxylamine is a polar compound so it dissolves in water.
Is hydroxylamine toxic?
Hydroxylamine is moderately toxic to man, animals, and even plants. However, their toxic reactions become manifest only at concentrations substantially greater than those resulting from normal cell metabolism.

Comments