Recently, the United States and its allies – New Zealand, Australia, the United Kingdom and Japan, have launched a new initiative called “Partners in the Blue Pacific” to promote “effective and efficient cooperation” with the region’s small island nations. This grouping is in response to China’s aggressive push to expand its Pacific sphere of influence. The formation of this grouping is an important event in International Relations which is a subject under GS Paper 2 in UPSC Syllabus.
In this article, the details about Partners in Blue Pacific and its significance is discussed in detail. All the aspirants would find this article very helpful while preparing for the IAS Exam.
Note: Aspirants should start practising for the UPSC exam by solving UPSC Previous Year Question Papers.
| To complement your preparation for the upcoming exam, check the following links: |
About Partners in Blue Pacific Initiative
The Pacific region’s geostrategic competition has recently heated up as China made the anticipated range of its expanding presence known by pressing for a broad, common cooperation deal with ten Pacific states. It is in this response that the Partners in Blue Pacific (PBP) initiative is launched.
- The Partners in Blue Pacific is a five-nation “informal mechanism” to support Pacific islands and boost diplomatic and economic ties in the region.
- PBP aspires to improve collaboration in the following areas
- connectivity and transportation
- climate crisis
- marine security and protection
- prosperity
- health
- education
- It speaks of strengthening “prosperity, resilience, and security” in the Pacific through greater collaboration and closer cooperation.
- It simply implies that, through the PBP, these countries will direct more resources here to offset China’s aggressive outreach.
- Members of the initiative have also stated that they intend to “elevate Pacific regionalism” and strengthen connections with the Pacific Islands Forum.
Read about String of Pearls – Strategic Implications and India’s Response, in the linked article.
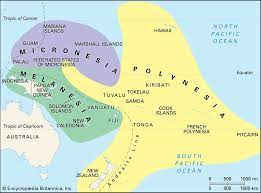
Pacific Island Nations are popular names for Pacific Ocean islands. As seen on the map, Pacific Island Nations are divided into three primary groupings of islands known as Polynesia, Micronesia and Melanesia. Polynesia is a group of islands in the eastern Pacific that are primarily surrounded by a massive triangle created by the Hawaiian Islands to the north, New Zealand to the southwest, and Easter Island (Rapa Nui) to the east. Micronesia is a group of islands located north of the Equator and east of the Philippines. Melanesia is the large arc of islands lying north and east of Australia and south of the Equator.
The Pacific Islands Forum is the region’s leading political and economic policy body. Australia, Cook Islands, Federated States of Micronesia, Fiji, French Polynesia, Kiribati, Nauru, New Caledonia, New Zealand, Niue, Palau, Papua New Guinea, Republic of Marshall Islands, Samoa, Solomon Islands, Tonga, Tuvalu, and Vanuatu are its 18 members. |
Complement your reading with the related articles linked below:
| Special Economic Zone | South China Sea Dispute – Claims, Main Causes behind Dispute | International Relations This Week |
Significance of Pacific Region
The Pacific region stretches from the west coast of the United States to the western coastlines of India. The US Department of Defense referred to the Indo-Pacific as the “single most crucial area for America’s future” in its 2019 strategy report.
- The Indo-Pacific area is home to seven of the world’s ten largest standing militaries and six of the region’s countries have nuclear weapons.
- This area is home to nine of the world’s ten busiest seaports and 60 percent of worldwide marine trade transits through Asia, with one-third of global shipping travelling through the South China Sea alone.
- It is home to
- the biggest Muslim-majority state (Indonesia)
- the most populous democracy (India)
- the world’s most populous country (China)
- more than half of the world’s population
- The area has some of the world’s largest Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZs). These large EEZs offer enormous economic potential since they may be exploited to harness the energy, abundance of fisheries, minerals and other marine resources that exist there.
Also, read about Strategic Importance of Indo Pacific: RSTV – Big Picture, in the linked article.
Reasons behind the PBP Initiative
The grouping is formed with the aim of countering China’s efforts to transform its ties with the Pacific nations. These are:
- China and the Solomon Islands have signed a security agreement: It raised severe concerns about the Chinese military establishing a station in the southern Pacific, near the US island territory of Guam and near Australia and New Zealand.
- Common Development Vision: It is an agreement between ten Pacific states that will assist China in working with “traditional and non-traditional security,” as well as expanding law enforcement cooperation with these countries. (Despite the warning that the Pacific states were entering “Beijing’s orbit“, China indicated it would continue pursuing its goal.)
Other than that the strategic significance of the pacific region, as discussed above is also one reason for the formation of this grouping.
Read about Solomon Island and other Issues, in the linked article.
Efforts of the US and Allies to Counter China
To counter China, the United States and its allies launched various initiatives:
-
- Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment (PGII): It is a plan announced by G7 to raise $600 billion in investment for poor countries, in a response to China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
- Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF): It is a US-led project that intends to promote economic collaboration among participating nations in the Indo-Pacific region in order to improve resilience, sustainability, inclusivity and economic growth, fairness, and competitiveness. It includes India and 13 other nations.
- These 13 nations are Australia, Brunei, India, Indonesia, Japan, Malaysia, New Zealand, the Philippines, Singapore, South Korea, Thailand, Fiji and Vietnam.
- Asia-Africa Growth Corridor: A collaboration between India and Japan for development, connectivity, and cooperation between Asia and Africa.
- Global Gateway launched by the EU aims to narrow the global investment gap.
- Hub-and-Spoke system: With its hub-and-spoke system, the United States has successfully maintained a balance of power in the area. America is the hub in this structure, and its friends are spokes whose security is ensured by US military force.
Read in detail about the G7 Countries and Summit, in the linked article.
UPSC aspirants can also refer to the links given below:

