TABLE OF CONTENT
A. GS1 Related Social Issues 1. Unique initiative to promote small family norm B. GS2 Related Polity 1. New system for rating bureaucrats open to bias: Anand Sharma 2. Kerala, Haryana top sanitation survey C. GS3 Related Economy 1. Logistics Data Bank project to expand to South India Agriculture 1. Food for action: on food security in India Science & Technology 1. ISRO to develop full-fledged Earth observation satellite 2. The hybrid route D. GS4 Related E. Concepts-in-News: Related Concepts to Revise/Learn F. Bills/Acts/Schemes/Orgs in News G. UPSC Prelims Practice Questions H. UPSC Mains Practice Questions
1. Unique initiative to promote small family norm
- The Rajasthan government’s Medical and Health Department has decided to organise “Saas-Bahu Sammelans” in over 16,200 villages of 14 districts.
- Why: to promote the small family norm with emphasis on development of local communities.
- And to achieve the family planning targets.
Step against high fertility rate
- The 14 districts of the State have reported a high fertility rate in the past.
1. New system for rating bureaucrats open to bias: Anand Sharma
- According to the committee, the government’s new system of rating officers on the basis of a 360-degree approach is susceptible to bias, manipulation and lacks fairness.
360 degree approach:
- The 360-degree approach is a new multi–source feedback system for performance appraisal of bureaucrats.
- It relies on feedback of juniors and other colleagues for an all-round view, other than appraisal reports written by senior officers.
Counter arguments:
- Feedback in this process is obtained informally, making the process susceptible to being manipulated.
- The report notes that the 360-degree approach does not have any statutory backing, or supported by any Act.
Data from Government survey commissioned on Sanitation
- According to the survey, almost all rural households in Kerala and Haryana had access to a toilet.
- Bihar and Uttar Pradesh has least access to toilets when compared to other states.
- The survey is released by the Ministry of Drinking Water and Sanitation.
- The survey was carried out by the Quality Council of India (QCI).
Other best performers
- Northeastern States of Sikkim, Manipur and Nagaland were top performers with 95% rural households covered by toilets.
- The Himalayan States of Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand with over 90% toilet coverage of the rural houses.
Worst performers
- In Bihar, only 30% of the rural households had access to toilets while Uttar Pradesh was marginally better at 37%.
- Jharkhand, too scored the same as Uttar Pradesh.
1. Logistics Data Bank project to expand to South India
Context:
- The Logistics Data Bank (LDB) project, unveiled in July 2016 to make India’s logistics sector more efficient through the use of Information Technology, will soon expand to country’s southern region
What is The Logistics Data Bank (LDB) project?
- The logistics Data Bank Service would bring efficiency in the current Logistics & Supply Chain through use of information technology that would be helpful for tracking and viewing the movement of containers across the port to the ICD and end users.
- Every container is attached to a Radio Frequency Identification Tag (RFID) tag and then tracked through RFID readers — aids importers and exporters in tracking their goods in transit.
- This has, in turn, cut the overall lead time of container movement as well as reduced transaction costs that consignees and shippers incur.
- It is billed as a major ‘ease of doing business’ initiative aimed at boosting India’s foreign trade and ensuring greater transparency.
- The project covers “the entire movement (of containers) through rail or road till the Inland Container Depot and Container Freight Station
Context:
- National Food Security Act, 2013, has met with prolonged political indifference
- Supreme Court directed Centre to ensure that States implement key aspects of the progressive law
Key Aspects:
- Directives in the Swaraj Abhiyan case underscore that several State governments have not met key requirements in the legislation.
- Sections 14, 15 and 16, require the setting up of a grievance redress mechanism and a State Food Commission with responsibility to monitor the implementation of the law
- Article 256, which casts a responsibility on the States and the Union to ensure compliance with laws made by Parliament, also provides the remedy, as it can be invoked by the Centre to set things right.
- NFSA, which is vital for social security through the Public Distribution System and child welfare schemes, has suffered due to a lack of political will.
Way forward
- Food security through the principle of universal access, though not every citizen would need it
- An in-built mechanisms to allow for the entry of new households that suddenly find themselves in financial distress, while others can exit it based on changed circumstances.
- Full-fledged, independent machinery in the form of a Food Commission, and district-level grievance redress, besides social audits. All these are provided for under the Act, but have been ignored
- Modernisation of the PDS, could incorporate dynamic features to the supply of subsidised food to those who need it, and eliminate deficiencies and fraud.
Category: SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
1. ISRO to develop full-fledged Earth observation satellite
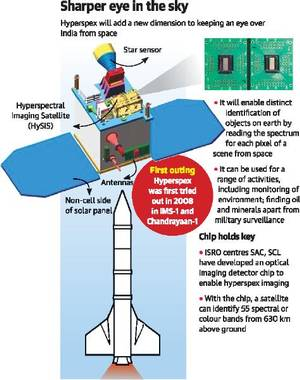
- A new set of future satellites called hyperspectral imaging satellites is set to add teeth to the way India is gleaned from about 600 km in space.
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) says it plans to launch a full-fledged niche Earth observation (EO) satellite — called the Hyperspectral Imaging Satellite or HySIS — using a critical chip it has developed.
- ISRO is endeavouring to enter the domain of operational hyperspectral imaging from earth orbit with a satellite that can see in 55 spectral or colour bands from 630 km above ground.
- Application: It can be used for a range of activities from monitoring the environment, crops, looking for oil and minerals all the way up to military surveillance — all of which need images that show a high level of differentiation of the object or scene.
- ‘Hyspex’ imaging is said to enable distinct identification of objects, materials or processes on Earth by reading the spectrum for each pixel of a scene from space.
- Previous attempts: About a decade ago, ISRO added another EO niche with microwave or radar imaging satellites RISAT-1 and 2 that could ‘see’ through clouds and the dark — an important feature useful for the military and security agencies.
Context:
- The automobile sector in India and the future of electric mobility in India
India’s performance in Automobile Sector:
- India went through a radical transformation from a minor manufacturer of automobiles to the fastest growing auto-hub within a short span
- Progressive policy has led to India emerging as the fifth largest automobile manufacturing country in the world
- How: by adopting a consistent, well thought out Automotive Mission Plan 2006-2016 (AMP)
Contribution to Employment Generation:
- The auto industry provides direct and indirect employment to 32 million people with an annual turnover of nearly Rs 6,00,000 crore
How India’s policy in this sector is different from that of China?
- India’s has achieved success without the adoption of coercive policies for localisation of production as is done in China
- India’s success is attributed to positive engagement maintained with global giants, for establishing competitive manufacturing base in India
World is now going for non-fossil fuel vehicles
- The world is still largely dependent on fossil fuels for transportation
- But there is now an increased momentum towards alternate energy sources
India’s take on non-fossil fuel vehicles
- Besides the environment, India also has strategic and economic interest in shifting away from fossil fuels
- Challenge: The challenge ahead is not only on how to encourage electric automobiles but also to take the industry forward without losing India’s current competitive advantage
Different types of Electric vehicles
- Pure electric vehicles (BEVs) that use energy stored in batteries obtained from the grid
- Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) and fuel cell vehicles (FCVs)
Global experience in Electric mobility sector
- Global experience indicates that most countries have adopted a technology-neutral approach
- And supported the full range of electric vehicle technologies till such time that they attained market acceptability
The way forward
- The government should push more aggressively for the BEV option for of two-wheelers and three-wheelers
- And support the full range of electric technologies for other vehicle segments with a clear roadmap for the evolution towards FCVs
- Hopefully, to reduce fossil fuel consumption, lower pollution and encourage electric mobility, a more holistic approach will be adopted by the government
Nothing here for Today!!!
Nothing here for Today!!!
Nothing here for Today!!!
G. Practice Questions for UPSC Prelims Exam
- It is a tree dwelling crab species.
- It is a terrestrial crab species.
- The species is named after Kani tribe in Kerala.
- Both a and c
Question 2. Consider the following statement with reference to Uttarayan Festival which
was in news recently
- It is an International Kite festival held at Ahmadabad.
- The idea of flying kites to celebrate Uttrayan was introduced by Muslims from Persia.
- Both a and b
- Neither a nor b
- Masala bonds are bonds issued outside India but denominated in Indian Rupees.
- Masala bonds are bonds issued outside India but denominated in US dollars.
- Masala bonds are bonds issued outside India but denominated in UK dollars.
- None of the above.
Question 4. Consider the statements about Organisation for Economic Co-operation and
Development(OECD) :
- 1. It is a UN agency.
- 2. It is headquartered in New York.
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- None
- Resolving NPA crisis in banking sector.
- Tax avoidance strategy.
- Free movement of skilled professionals across countries.
- Free movement of goods across countries.
GS Paper II
-
- “Traditional bureaucratic structure and culture have hampered the process of socio-economic development in India.” Comment.
GS Paper III
-
- “An incremental, technology-neutral approach to the adoption of electric vehicles is the way forward for Automobile Sector in India” Comment.
Comments