TABLE OF CONTENT
A. GS1 Related B. GS2 Related Polity 1. SC notice to govt on abortion deadline 2. TB patients will need Aadhaar for cash benefits 3. Bad for health B. GS2 Related International Relations 1. Text of the Speech of Defence Minister at TECHNOPROM- 2017 in Russia C. GS3 Related Science and Technology 1. NASA finds 10 Earth-sized exoplanets D. GS4 Related E. Concepts-in-News: Related Concepts to Revise/Learn F. Bills/Acts/Schemes/Orgs in News G. Practice Questions for UPSC Prelims Exam
UPSC Current Affairs 2017: News Analysis
A. GS1 Related
Nothing here for Today!!!
B. GS2 Related
1. SC notice to govt on abortion deadline
Context:
- A woman challenged a Section 3 of the Medical termination of Pregnancy Act, 1971 which says that pregnancy cannot be terminated after 20 weeks.
- A 2014 pending bill proposes to extend the legally permissible period for termination to 24 weeks.
- Taking note of the distress plea, a vacation bench of SCsought response from the Bengal govt.
Key Fact: Out of the 26 million births that occur in India every year, approximately 2-3% had severe congenital or chromosomal abnormality
Basic Information: What is MTP Act, 1971? Abortion in India is legal only up to twenty weeks of pregnancy under specific conditions and situations. One, the continuance of the pregnancy would involve a risk to the life of the pregnant woman or of grave injury of physical or mental health, or Two, there is a substantial risk that if the child were born, it would suffer from such physical or mental abnormalities as to be seriously handicapped. What the draft MPT bill 2014 provides? The draft MTP increased the legal limit for abortion from 20 weeks to 24 weeks. It provides for abortion beyond 24 weeks under defined conditions. The Bill amends Section 3 of the 1971 Act to provide that “the length of pregnancy shall not apply” in a decision to abort a foetus diagnosed with “substantial foetal abnormalities” or if it is “alleged by the pregnant woman to have been caused by rape”. Under the 1971 Act, even pregnant rape victims cannot abort after 20 weeks, compelling them to move court. It allows a woman to take an independent decision in consultation with a registered health-care provider. It also takes into account the reality of a massive shortage of both doctors and trained midwives, and seeks to allow Ayurveda, Unani and Siddha practitioners to carry out abortions. Why is it essential to change the MTP law? Foetal abnormalities show up only by 18 weeks, so just a two-week window after that is too small for the would-be parents to take the difficult call on whether to keep their baby. Even for the medical practitioner, this window is too small to exhaust all possible options before advising the patient. There is an urgent need to empower women with sexual rights, legal protection against sex crimes and sex choices both in their own interest and for the sake of reducing the fertility rate as a whole. The lack of legal approval moves abortion to underground and they are done in unhygienic conditions by untrained, thus, putting thousands of women at risk.
2. TB patients will need Aadhaar for cash benefits
In news:
New register norms:
- Tuberculosis patients, hospitals and healthcare workers availing cash assistance from the government will need to register with the Aadhaar database.
Revised National Tuberculosis Control Programme (RNTCP):
- Under this scheme the government requires that patients diagnosed with TB and availing treatment be registered with Nikshay, a web-based application used by the authorities to track funds, treatment outcomes and health providers connected to the RNTCP.
- It is being implemented by State governments and Union Territory administrations via government health facilities and registered private health facilities across the country.
Who is eligible to receive payments now?
Tribals, and health care workers involved with the DOTS (Directly Observed Treatment, Short Course). But to meet TB elimination goals, the cash benefits are likely to be made available to all patients.
Key fact:
- The World Health Organization has said that tuberculosis epidemic in India was “larger” than what had been previously estimated and asserted that the country was one of six nations which accounted for 60% of the new cases in 2015.
- According to reports, the prevalence of TB in India was at 217 per 1,00,000 population in 2015 as against the previously estimated 127.
- The government has pledged its commitment to eliminate tuberculosis by 2025, five years ahead of the global goal to reduce the number of such deaths by 90 per cent by 2030.
Context:
- A notice issued by a health ministry expert committee in the first week of June signals the government’s intention to usher major change in India’s pharmaceutical sector
- It invites comments from stakeholders about replacing widely-used animal parts-based gelatin capsules with those derived from cellulose
- In 2015, the scientific committee which advises the Drug Controller General of India (DGCI) gave an in-principle approval to the shift to cellulose-based capsules
Current situation: Currently, 98 per cent of the Indian pharmaceutical industry uses animal parts-based capsules
What government wants?
- Government has been pitching for “vegetarian capsules” for the past two years
- But there is little medical or commercial reasoning behind this proposal
What this could lead to?
A switch over to cellulose-based capsules could jeopardise the government’s recent initiatives to make medicines accessible to all.
Difference in opinions:
- In an e-mail last year to the joint secretary, health ministry, the DGCI pitched for “vegetable capsules for vegetarian society”
- The DGCI’s vegetarian fetish found support from the Women and Child Development Minister Maneka Gandhi
- She argued, “In a country where there are millions of people, this hurts religious sentiments and many people avoid medicines that are in a capsule form”
- The Drug Technical Advisory Board, health ministry’s premier advisory agency, had dismissed Gandhi’s representation on the grounds that: “Unlike food, drugs are not taken as choice but are prescribed by doctors to save lives and marking them as vegetarian or non-vegetarian is not desirable”
- The health ministry has overruled this reasoning
Concerns/opinions of industry:
- They have argued that the gelatin capsules have been in use all over the world for more than 180 years
- They also questioned viability of cellulose-based capsules
- Various industry associations cited the huge economic cost of the switch, which may also impact accessibility of medicines
- The cost of raw material required to make cellulose capsules is approximately four times that of gelatin and the manufacturing cost of cellulose-based capsules approximately three times the cost of gelatin capsules
Category: INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
1. Text of the Speech of Defence Minister at TECHNOPROM- 2017 in Russia
Key point:
- Defence Minister Arun Jaitley has urged Russian defence companies to set up local joint ventures with Indian firms to produce spares and components for use by the Indian military as well as for exports.
- TECHNOPROM:
- Technoprom is an international business platform devoted to the issues of forming the sixth technological mode based on the active development of science, technologies, and engineering, international and inter-regional integration.
- The focus this year on breakthrough technologies in the scientific, technological and innovative fields has established this event as a key forum for insights and business opportunities into leading technological products and technologies.
Relationship with Russia a key priority:
- India and Russia are celebrating the 70th Anniversary of the establishment of diplomatic relations. For India, relations with Russia are a key foreign policy priority. Russia is been a trusted and time-tested partner.
- India-Russia Strategic Partnership in 2000 covers areas like defence and security cooperation, trade and economic partnership, science and technology linkages and cultural exchanges.
- Area of military technical cooperation: relationship escalated from just being buyer-seller relationship to one involving joint research, development and production of advanced defence systems.
Example: The Brahmos Missile System and the licensed production of advanced Sukhoi 30 aircraft in India are recent highlights of our bilateral cooperation
Government of India initiatives:
- Under Defence Procurement Procedure (DPP) of 2016, a new category of acquisition called ‘Buy (IDDM)’,has been introduced. In this first preference would be given to the equipments, which are designed, developed and manufactured within the country. This will encourage Indian companies to invest in R&D and technology.
- Liberalised license norms:
- For manufacturing of parts, components, sub-systems, production equipments and testing equipments, no license is required from the Government.
- For the items for which license is required, the initial validity has been increased from 3 years to 15 years.
C. GS3 Related
Category: SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
1. NASA finds 10 Earth-sized exoplanets

Context
- NASA revealed new rocky, Earth-sized planets
- These could potentially have liquid water and support life
The Kepler mission
- The Kepler mission team released a survey of 219 potential exoplanets
- These planets are outside of our solar system
- They had been detected by the space observatory launched in 2009 to scan the Milky Way galaxy
Location of these exoplanets:
- Ten of the new discoveries were orbiting their suns
- Their orbit is at a distance similar to the Earth’s orbit around the sun
- This is the habitable zone that could potentially have liquid water and sustain life
Habitable zones
- Kepler has already discovered 4,034 potential exoplanets
- 2,335 of these have been confirmed by other telescopes as actual planets
- The 10 new Earth-size planets bring the total to 50 that exist in habitable zones around the galaxy
- The telescope detects the presence of planets by registering minuscule drops in a star’s brightness
Basic Information: Kepler Mission Kepler is a space observatory launched by NASA to discover Earth-size planets orbiting other stars Named after astronomer Johannes Kepler It was launched into an Earth-trailing heliocentric orbit Kepler is part of NASA’s Discovery Program of relatively low-cost, focused primary science missions The scientific objective of Kepler is to explore the structure and diversity of planetary systems This spacecraft observes: To determine how many Earth-size and larger planets there are in or near the habitable zone (often called “Goldilocks planets”) To determine the range of size and shape of the orbits of these planets To estimate how many planets there are in multiple-star systems To determine the range of orbit size, brightness, size, mass and density of short-period giant planets To identify additional members of each discovered planetary system using other techniques Determine the properties of those stars that harbor planetary systems
D. GS4 Related
Nothing here for Today!!!
E. Concepts-in-News: Related Concepts to Revise/Learn
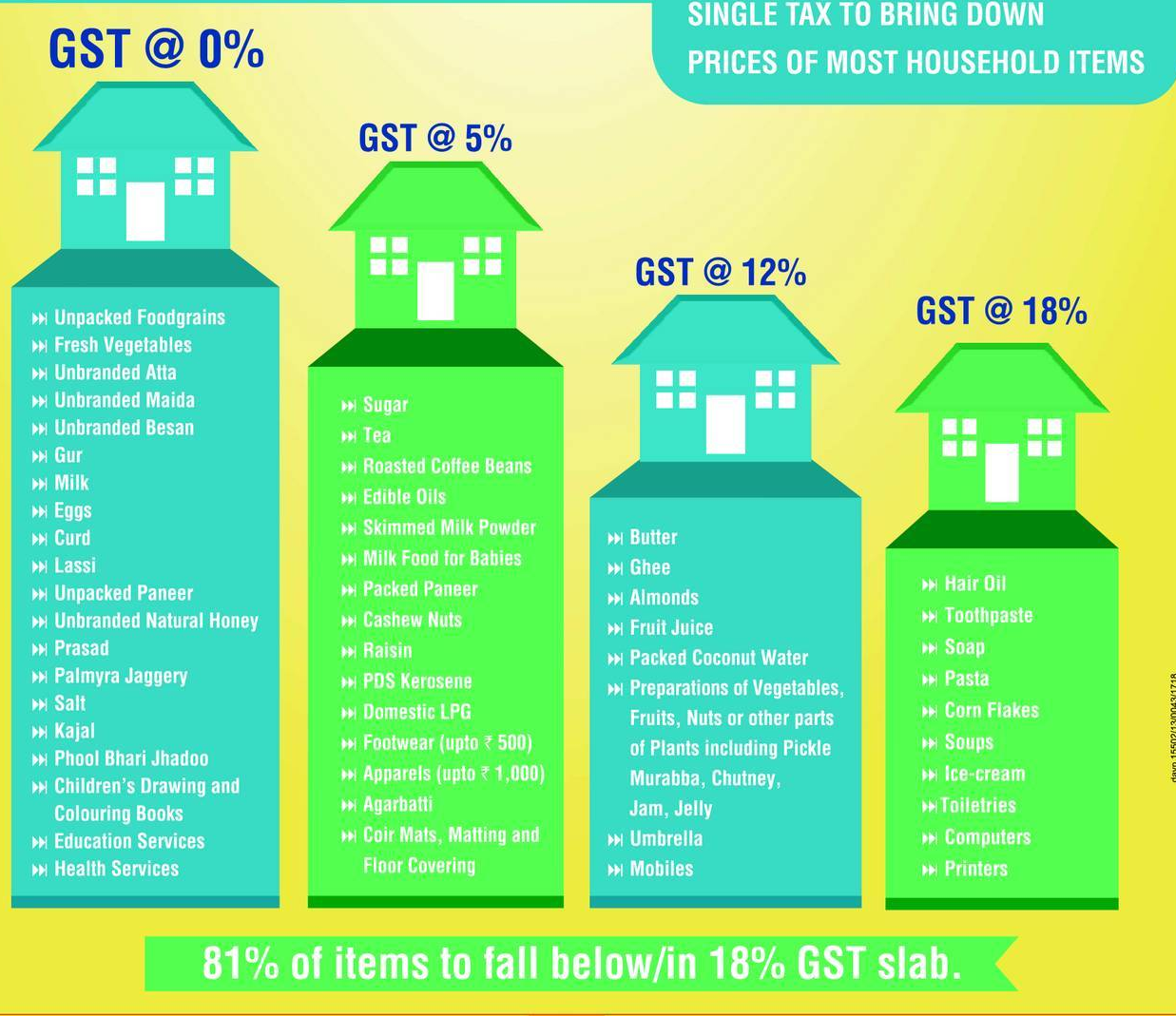
1. GST slabs for reference
2. Wassenaar Arrangement:
About:
- The Wassenaar Arrangement on Export Controls for Conventional Arms and Dual-Use Goods and Technologies, commonly known as the Wassenaar Arrangement, is a multilateral export control regime (MECR) with 41 participating states
- The Wassenaar Arrangement was established to contribute to regional and international security and stability by promoting transparency and greater responsibility in transfers of conventional arms and dual-use goods and technologies, thus preventing destabilizing accumulations.
- Participating States seek, through their national policies, to ensure that transfers of these items do not contribute to the development or enhancement of military capabilities which undermine these goals, and are not diverted to support such capabilities.
- Every six months member countries exchange information on deliveries of conventional arms to non-Wassenaar members that fall under eight broad weapons categories:
Control List:
- The list of restricted technologies is broken into two parts, the “List of Dual-Use Goods and Technologies” (also known as the Basic List) and the “Munitions List”.
The Basic List is composed of ten categories based on increasing levels of sophistication:
- Category 1 – Special Materials and Related Equipment
- Category 2 – Materials Processing
- Category 3 – Electronics
- Category 4 – Computers
- Category 5 – Part 1 – Telecommunications
- Category 5 – Part 2 – “Information Security”
- Category 6 – Sensors and “Lasers”
- Category 7 – Navigation and Avionics
- Category 8 – Marine
- Category 9 – Aerospace and Propulsion
Basic List has two nested subsections—Sensitive and Very Sensitive. Items of the Very Sensitive List include materials for stealth technology—i.e., equipment that could be used for submarine detection, advanced radar, and jet engine technologies.
- The Munitions List has 22 categories, which are not labeled.
Admission requires states to:
- Be a producer or exporter of arms or sensitive industrial equipment
- Maintain non-proliferation policies and appropriate national policies, including adherence to:
- Non-proliferation policies, such as (where applicable) the Nuclear Suppliers Group, the Missile Technology Control Regime, and the Australia Group
- Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty, the Biological Weapons Convention, the Chemical Weapons Convention and, where applicable, START I (including the Lisbon Protocol)
- Maintain fully effective export controls
- Admission of new members requires the consensus of all members.
The People’s Republic of China and Israel are not members, but they have aligned their export controls with Wassenaar lists, and are significant arms exporters.
New amendment: In December 2013, the list of export restricted technologies was amended to include internet-based surveillance systems. New technologies placed under the export control regime include “intrusion software”—software designed to defeat a computer or network’s protective measures so as to extract data or information—as well as IP network surveillance systems.
F. Bills/Acts/Schemes/Orgs in News
| Schemes/Programs in News | About the Scheme |
| Revised National Tuberculosis Control Program |
About and objectives:
Program strategy:
|
G. Practice Questions for UPSC Prelims Exam
Question 1: The term ‘Goldilocks Zone’ is often seen in the news in the context of
- The limits of habitable zone above the surface of the Earth
- Regions inside the Earth-like planets in outer space
- Search for the Earth-like planets in outer space
- Search for meteorites containing precious metals
Question 2: Consider the following statement with reference to Wassenaar arrangement:
- China is a member of the arrangement
- Recently in the year 2013, the list of export restricted technologies under the arrangement was amended to include internet-based surveillance systems
Choose the correct answer
- 1 Only
- 2 Only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Question 3: When a bill is referred to a joint sitting both the Houses of the Parliament, has to be
passed by
- A simple majority of member present and voting
- Three-fourths majority of member present and voting
- Two-thirds majority of the House
- Absolute majority of the House
Question 4: Which country has highest air pollution among all European Union (EU)
countries?
- Poland
- France
- Greece
- Germany
Question 5: Which among the following is the only breeding ground for Indian Skimmer,
an endangered fresh water bird species?
- Chambal River
- Sunder bans
- Ganga-Yamuna basin
- Godavari Delta
“Proper Current Affairs preparation is the key to success in the UPSC- Civil Services Examination. We have now launched a comprehensive ‘Online Current Affairs Crash Course’. Limited seats available. Click here to Know More.”
Practice More: Enroll for India’s Largest All-India Test Series


Comments