A polynomial function is a function that involves only non-negative integer powers or only positive integer exponents of a variable in an equation like the quadratic equation, cubic equation, etc. For example, 2x+5 is a polynomial that has exponent equal to 1.
Study Mathematics at BYJU’S in a simpler and exciting way here.
A polynomial function, in general, is also stated as a polynomial or polynomial expression, defined by its degree. The degree of any polynomial is the highest power present in it. In this article, you will learn polynomial function along with its expression and graphical representation of zero degrees, one degree, two degrees and higher degree polynomials.
|
Table of Contents: |
Polynomial Function Definition
A polynomial function is a function that can be expressed in the form of a polynomial. The definition can be derived from the definition of a polynomial equation. A polynomial is generally represented as P(x). The highest power of the variable of P(x) is known as its degree. Degree of a polynomial function is very important as it tells us about the behaviour of the function P(x) when x becomes very large. The domain of a polynomial function is entire real numbers (R).
If P(x) = an xn + an-1 xn-1+.……….…+a2 x2 + a1 x + a0, then for x ≫ 0 or x ≪ 0, P(x) ≈ an xn. Thus, polynomial functions approach power functions for very large values of their variables.
Polynomial Function Examples
A polynomial function has only positive integers as exponents. We can even perform different types of arithmetic operations for such functions like addition, subtraction, multiplication and division.
Some of the examples of polynomial functions are here:
- x2+2x+1
- 3x-7
- 7x3+x2-2
All three expressions above are polynomial since all of the variables have positive integer exponents. But expressions like;
- 5x-1+1
- 4x1/2+3x+1
- (9x +1) ÷ (x)
are not polynomials, we cannot consider negative integer exponents or fraction exponent or division here.
Also, see:
Types of Polynomial Functions
There are various types of polynomial functions based on the degree of the polynomial. The most common types are:
- Constant Polynomial Function: P(x) = a = ax0
- Zero Polynomial Function: P(x) = 0; where all ai’s are zero, i = 0, 1, 2, 3, …, n.
- Linear Polynomial Function: P(x) = ax + b
- Quadratic Polynomial Function: P(x) = ax2+bx+c
- Cubic Polynomial Function: ax3+bx2+cx+d
- Quartic Polynomial Function: ax4+bx3+cx2+dx+e
The details of these polynomial functions along with their graphs are explained below.
Graphs of Polynomial Functions
The graph of P(x) depends upon its degree. A polynomial having one variable which has the largest exponent is called a degree of the polynomial.
Let us look at P(x) with different degrees.
Constant Polynomial Function
Degree 0 (Constant Functions)
- Standard form: P(x) = a = a.x0, where a is a constant.
- Graph: A horizontal line indicates that the output of the function is constant. It doesn’t depend on the input.
E.g. y = 4, (see Figure 1)
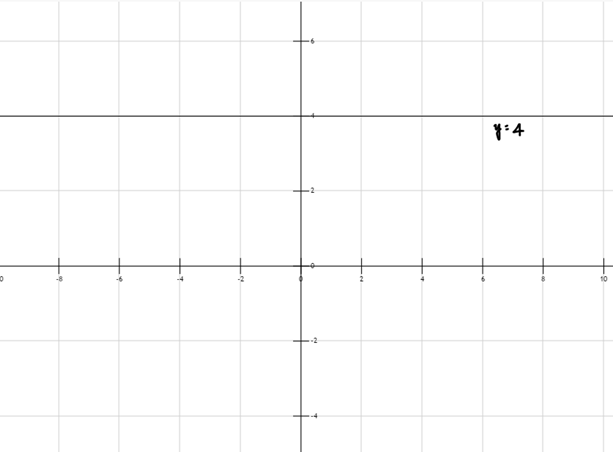
Figure 1: Graph of Zero Polynomial Function
Figure 1: y = 4
Zero Polynomial Function
A constant polynomial function whose value is zero. In other words, zero polynomial function maps every real number to zero, f: R → {0} defined by f(x) = 0 ∀ x ∈ R. For example, let f be an additive inverse function, that is, f(x) = x + ( – x) is zero polynomial function.
Linear Polynomial Functions
Degree 1, Linear Functions
- Standard form: P(x) = ax + b, where a and b are constants. It forms a straight line.
- Graph: Linear functions have one dependent variable and one independent which are x and y, respectively.
In the standard formula for degree 1, a represents the slope of a line, the constant b represents the y-intercept of a line.
E.g., y = 2x+3(see Figure 2)
here a = 2 and b = 3
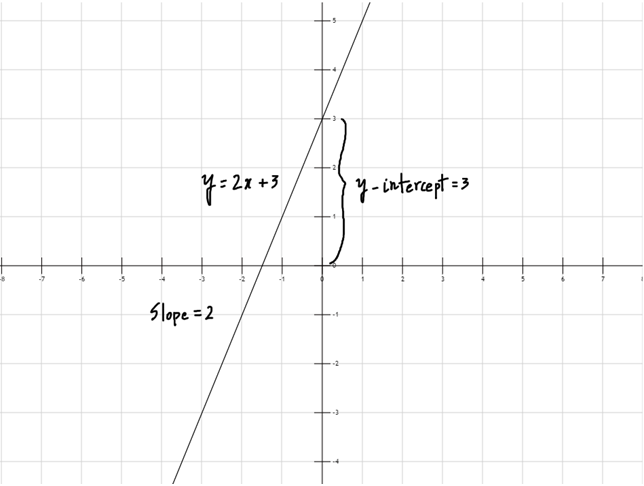
Figure 2: Graph of Linear Polynomial Functions
Figure 2: y = 2x + 3
Note: All constant functions are linear functions.
Quadratic Polynomial Functions
Degree 2, Quadratic Functions
- Standard form: P(x) = ax2+bx+c , where a, b and c are constant.
- Graph: A parabola is a curve with one extreme point called the vertex. A parabola is a mirror-symmetric curve where any point is at an equal distance from a fixed point known as Focus.
In the standard form, the constant ‘a’ represents the wideness of the parabola. As ‘a’ decreases, the wideness of the parabola increases. This can be visualized by considering the boundary case when a=0, the parabola becomes a straight line. The constant c represents the y-intercept of the parabola. The vertex of the parabola is given by
(h,k) = (-b/2a, -D/4a)
where D is the discriminant and is equal to (b2-4ac).
Note: Whether the parabola is facing upwards or downwards, depends on the nature of a.
- If a > 0, the parabola faces upward.
- If a < 0, the parabola faces downwards.
E.g. y = x2+2x-3 (shown in black color)
y = -x2-2x+3 (shown in blue color)
(See Figure 3)
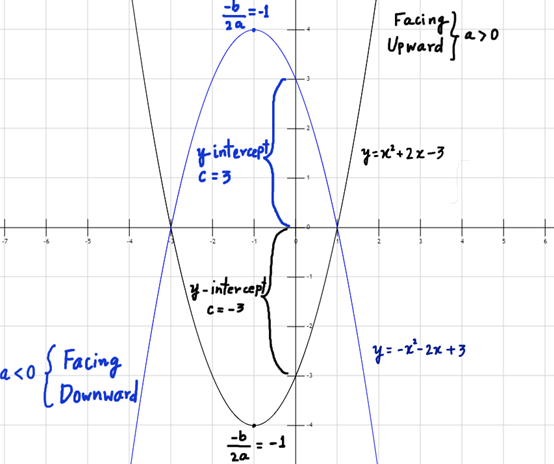
Figure 3: Quadratic Polynomial Functions
Figure 3: y = x2+2x-3 (black) and y = x2-2x+3 (blue)
Graphs of Higher Degree Polynomial Functions
- Standard form– P(x) = an xn + an-1 xn-1+.……….…+ a0, where a0,a1,………,an are all constants.
- Graph: Depends on the degree, if P(x) has degree n, then any straight line can intersect it at a maximum of n points. The constant term in the polynomial expression, i.e. a0 here represents the y-intercept.
- E.g. y = x4-2x2+x-2, any straight line can intersect it at a maximum of 4 points (see fig. 4)
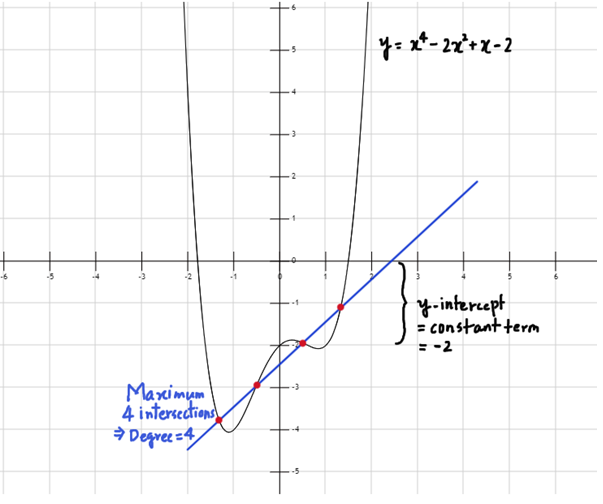
Figure 4: Graphs of Higher Degree Polynomial Functions
Video Lesson on Quadratic Equations

Polynomial Function Questions
Q.1: What is a Polynomial?
A polynomial is defined as an expression formed by the sum of powers of one or more variables multiplied to coefficients. In its standard form, it is represented as:
an xn + an-1 xn-1+.……….…+a2 x2 + a1 x + a0
where all the powers are non-negative integers.
And, a0,a1,………,an ∈ R
A polynomial is called a univariate or multivariate if the number of variables is one or more, respectively. So, the variables of a polynomial can have only positive powers.
Q.2: What is the Degree of Polynomial?
The degree of any polynomial expression is the highest power of the variable present in its expression. Constant (non-zero) polynomials, linear polynomials, quadratic, cubic and quartics are polynomials of degree 0, 1, 2, 3 and 4 , respectively. The function f(x) = 0 is also a polynomial, but we say that its degree is ‘undefined’.
To learn more about different types of functions, visit us. To enjoy learning with interesting and interactive videos, download BYJU’S -The Learning App.
Frequently Asked Questions on Polynomial Functions
What is meant by a Polynomial function?
A polynomial function is a function that can be expressed in the form of a polynomial. It has a general form of P(x) = anxn + an – 1xn – 1 + … + a2x2 + a1x + ao, where exponent on x is a positive integer and ai’s are real numbers; i = 0, 1, 2, …, n.
What is a zero polynomial function?
A polynomial function whose all coefficients of the variables and constant terms are zero. In other words, zero polynomial function maps every real number to zero, f: R → {0} defined by f(x) = 0 ∀ x ∈ R.
What is the domain of a polynomial function?
The domain of a polynomial function is real numbers.
What does a quadratic polynomial function graphically represent?
A quadratic polynomial function graphically represents a parabola.

I found this little inforformation very clear and informative.
Thank you.
I like the web it’s quite good and 💯%
This article is really helpful and informative. You guys are doing a fabulous job and i really appreciate your work
what is the polynomial function formula?
Check: https://byjus.com/polynomial-formula/
an xn + an-1 xn-1+.……….…+a2 x2 + a1 x + a0
Happy to learn with you