Liliaceae is a family of angiosperms. It is a family of monocotyledonous plants. It is also known as the ‘lily family’. It is widely distributed all over the world. It includes ornamental plants such as lilies, tulips, medicinal plants, e.g. Aloe vera, Colchicum, etc. Vegetables like onion, garlic, asparagus also belong to the Liliaceae family.
Download Complete Chapter Notes of Morphology in Flowering Plants
Download Now
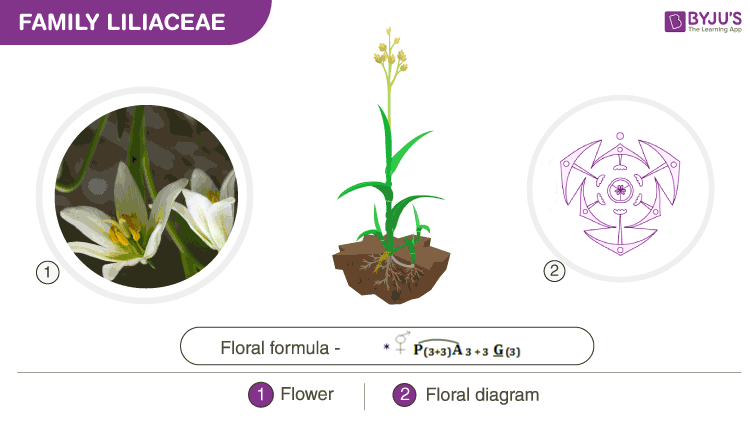
Table of Content:
- Floral Formula
- Systematic Position Of Liliaceae
- Features Of Liliaceae Family
- Economic Importance
- Frequently Asked Questions
Floral Formula
A floral formula is a symbolic representation of different floral parts, their numbers, arrangement pattern and how they are related. The floral formula of Allium cepa (onion) of the Liliaceae family is as follows:
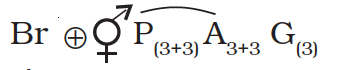
Here the symbols represent:
| Br | Bracteate |
| ⊕ | Actinomorphic (radial symmetry) |
| ⚥ | Bisexual |
| P(3+3) | Perianth – 6 tepals in two whorls, gamophyllous (united) |
| A3+3 | Androecium – 6 stamens, polyandrous (free), epiphyllous (attached to tepals) |
| G(3) | Gynoecium – tricarpellary, syncarpous (united), superior ovary |
Systematic Position Of Liliaceae
Kingdom: Plantae
Subkingdom: Tracheobionta
Super Division: Spermatophyta
Division: Magnoliophyta
Class: Liliopsida
Subclass: Liliidae
Order: Liliales
Family: Liliaceae
Features Of Liliaceae Family
Some Common Plants
Liliaceae is a big family of flowering plants. Some common examples are:
| Common name | Scientific name |
| Onion | Allium cepa |
| Garlic | Allium sativum |
| Asparagus | Asparagus officinalis |
| Aloe vera | Aloe vera |
| Lily | Lilium sp. |
| Tulip | Tulipa sp. |
| Dragon plant | Dracaena marginata |
| Butcher’s broom | Ruscus aculeatus |
| Autumn Crocus | Colchicum autumnale |
Description Of The Family
Habit: Liliaceae family contains perennial herbaceous plants. They are monocot with great morphological diversity. Some are climbers and some are also trees.
Root: Typically they possess fibrous root system.
Stem: Mostly herbaceous stem, which is aerial or underground. Underground stems are often present as bulbs, corms or rhizomes. Some of the aerial stems bear phylloclades, which are modified leaf-like branches.
Leaf: Leaves are mostly alternate, basal with parallel venation. Leaves are exstipulate, petiolate or sessile with variable shapes such as scaly, succulent or modified to tendrils.
Inflorescence: Variable inflorescence, e.g. solitary, cymose umbel, etc.
Flower: Mostly bracteate, actinomorphic and hermaphrodite. The flower is generally trimerous and hypogynous.
Perianth: Tepals 6, biseriate (2 whorled), mostly united and have valvate aestivation.
Androecium: Stamens 6, polyandrous and epiphyllous or epitepalous. Present in two whorls.
Gynoecium: Tricarpellary, syncarpous with the superior and trilocular ovary. Each locule contains many ovules. Axile placentation. It contains one style and a three-lobed stigma.
Fruit: Mostly capsule, rarely a berry.
Seeds: Endospermic and with one cotyledon. The endosperm is fleshy or horny and contains aleuron or oil.
Pollination: Members of Liliaceae family mainly exhibit entomophilous pollination, i.e. pollinated by insects.
Economic Importance
Many species of Liliaceae are grown as vegetables and ornamental plants. The following sums up their economic importance –
- Many plants are used as vegetables, e.g. onion, garlic, asparagus, etc.
- Many plants are of medicinal importance, e.g. Aloe vera, Smilax, etc. Colchicine is obtained from Colchicum.
- Many ornamental plants also belong to this family. E.g. Lilies, tulips, etc.
- Some of the plants yield fibres, e.g Yucca.
To sum up, in general, the flowers of the Liliaceae family are bracteate, actinomorphic, bisexual, trimerous and hypogynous.
The perianth is with six tepals, gamophyllous and biseriate.
Androecium contains six polyandrous stamens, which are epiphyllous and present in two whorls.
The gynoecium is tricarpellary and syncarpous with a superior ovary having axile placentation.
You just read about the floral formula of the Liliaceae family. For more such information, visit BYJU’S.
Further reading:
- Floral Formula Of Fabaceae
- Floral Formula Of Solanaceae
- Floral Formula Of Hibiscus
- Morphology Of Flowering Plants
Recommended Video:

Frequently Asked Questions
Is Liliaceae trimerous?
The perianth of Liliaceae has 6 sepals, arranged in a whorl of two in two bunches.
What are the characteristics of a Liliaceae flower?
A Liliaceae flower is hermaphroditic(both sexes on the same flower), actinomorphic(radial symmetry), pedicellate(short secondary stem) and has a superior ovary.

Comments