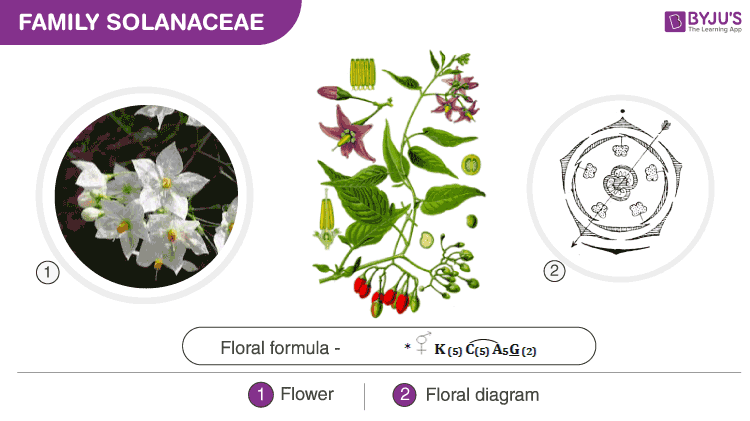
Solanaceae is a family of angiosperms. It is also known as the ‘potato family’. It is widely distributed all over the world in tropical, subtropical and temperate zones. It includes a number of spices, medicinal plants, agricultural crops, etc. Vegetables like potatoes, tomatoes, bell peppers, eggplant are included in the Solanaceae family.
Download Complete Chapter Notes of Morphology of Flowering Plants
Download Now
Floral Formula
A floral formula is a symbolic representation of different floral parts, their numbers, arrangement pattern and how they are related. The general floral formula of Solanaceae family is as follows:
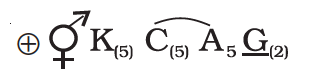
Here the symbols represent:
| ⊕ | Actinomorphic (radial symmetry) |
| ⚥ | Bisexual |
| K(5) | Calyx – 5 sepals, gamosepalous (united) |
| C(5) | Corolla – 5 petals, gamopetalous |
| A5 | Androecium – 5 stamens, polyandrous (free), epipetalous (attached to petals) |
| G(2) | Gynoecium – bicarpellary, syncarpous (united), superior ovary |
| Also see: |
Systematic Position Of Solanaceae
Kingdom: Plantae
Subkingdom: Tracheobionta
Super Division: Spermatophyta
Division: Magnoliophyta
Class: Magnoliopsida
Subclass: Asteridae
Order: Solanales
Family: Solanaceae
Features Of Solanaceae Family
Some Common Plants
Solanaceae is a big family of flowering plants having ~102 genera accounting for ~2500 species. Some common examples are:
| Common name | Scientific name |
| Potato | Solanum tuberosum |
| Eggplant | S. melongena |
| Tomato | S. lycopersicum |
| Bell pepper | Capsicum annuum |
| Tobacco | Nicotiana tabacum |
| Belladonna | Atropa belladonna |
| Ashwagandha | Withania somnifera |
| Datura | Datura stramonium |
| Black nightshade | S. nigrum |
| Petunia | Petunia hybrida |
Description Of The Family
Habit: Solanaceae family contains herbs, shrubs and also some small trees.
Root: Typically they possess a tap root system with branching.
Stem: Aerial, branched, erect, mostly herbaceous, cylindrical, hairy or glabrous. Potato is an example of an underground stem.
Leaf: Leaves are simple, alternate and sometimes pinnately compound. Venation is reticulate. Leaves are exstipulate or sessile. Sometimes transformed into spines.
Inflorescence: Flowers are solitary or grouped having axillary or cymose inflorescence.
Flower: Bracteate or ebracteolate, actinomorphic and generally hermaphrodite. The flower is pentamerous and hypogynous.
Calyx: Sepals green or coloured, typically 5 sepals, gamosepalous, persistent and show valvate aestivation.
Corolla: Petals 5, gamopetalous and valvate or imbricate aestivation.
Androecium: Stamens 5, polyandrous and epipetalous.
Gynoecium: Bicarpellary, syncarpous with the superior and bilocular ovary. Each locule contains many ovules (1-50). The placenta is swollen and axile placentation. The ovary is placed obliquely. It contains one style and one simple or bilobate stigma.
Fruit: It can be berry, e.g. tomatoes or capsule as in datura.
Seeds: Contains many seeds that are endospermic. Seeds are mostly round and flat. The embryo is curved or straight with two cotyledons. Mostly plants contain 2n = 24 (2 x 12) chromosomes but polyploidy is also seen with chromosomes in multiples of 12.
Pollination: Members of this family mainly exhibit entomophilous pollination, i.e. pollinated by insects.
Economic Importance
- Many plants are used as vegetables, e.g. potatoes, tomatoes, bell peppers, brinjal, etc.
- Many plants are of medicinal importance. Some alkaloids are toxic too. Some of the important alkaloids are tropanes, nicotine, capsaicin, solanine, hyoscyamine, etc. The main medicinal plants are Atropa belladonna, Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha), Datura, etc. Tobacco is a commercially very important plant.
- Many ornamental plants also belong to this family. E.g. Petunia, Lycianthes, Cestrum, etc.
To sum up, in general, the flowers of the Solanaceae family are complete, pedicellate, bracteate or ebracteate, actinomorphic, bisexual, pentamerous and hypogynous.
Calyx has five sepals, which are united or gamosepalous with valvate aestivation.
Corolla consists of five petals, which are united, i.e. gamopetalous with valvate or imbricate aestivation.
Androecium contains five polyandrous or free stamens, which are epipetalous.
The gynoecium is bicarpellary and syncarpous with superior ovary having axile placentation.
You just read about the floral formula of the Solanaceae family. For more such information, visit BYJU’S.
Recommended Video:
How To Remember Examples Of Morphology Class 11 Biology Chapter 5 | NEET 2022 Botany Preparation

Also read:

Comments