The Class 11 Chapter Locomotion and Movement covers important concepts like types of movements, skeletal system, muscle and disorders of skeletal and muscular systems. Here, let’s look at some important NEET questions from the Chapter Locomotion and Movement. This will help NEET aspirants during last-minute revisions.
1. Assertion: All locomotions are movements but all movements are not locomotions.
Reason: Movement does not always cause a change in position.
- Both the assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation for the assertion
- Both the assertion and reason are true but the reason is not the correct explanation for the assertion
- The assertion is true but the reason is false
- The reason is true but the assertion is false
Answer: a. Both the assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation for the assertion
Discussion: Locomotory movements are voluntary movements that result in a change of location or place. Although locomotion is brought about by the movement of limbs or specialised structures like cilia or flagella, all movements will not result in locomotion. This is because the movement does not always cause a change in position. For example, human limbs move when an individual changes body posture like from a sitting to a standing position or during actions like clapping.
2. Which property of muscles allows locomotion and other movements in humans?
- Contractility
- Excitability
- Elasticity
- All of the above
Answer: All of the above
Discussion: The following unique properties enable the muscles to bring about various movements in the body.
- Excitability – ability to respond to a stimulus
- Contractility – property to shorten and return back to its original state
- Extensibility – ability of a muscle to be stretched
- Elasticity – ability to recoil or bounce back to its original length
3. Match the following:
|
Column 1 |
Column 2 |
||
|---|---|---|---|
|
A |
Skeletal muscle |
1 |
Myocardium |
|
B |
Cardiac muscle |
2 |
Muscle of forelimbs |
|
C |
Smooth muscle |
3 |
Reproductive system |
- A-2, B-1, C-3
- A-1, B-2, C-3
- A-1, B-3, C-2
- A-2, B-3, C-1
Answer: a. A-2, B-1, C-3
Discussion:
- Skeletal muscle is found in the forelimbs. It helps in locomotion and movement.
- Smooth muscle is present in the reproductive tract and aids in the transport of gametes.
- Cardiac muscles or heart muscle is a contractile tissue which aids in pumping blood to all tissues of the body. They are also called myocardium.
4. Which of the following is common in skeletal and cardiac muscles?
- Voluntary
- Involuntary
- Striated
- Unstriated
Answer: c. Striated
Discussion: Both cardiac and skeletal muscles appear to have dark and light bands or striations under the microscope, although the striations are more prominent in skeletal muscle.
Also Check:Difference between striated muscles and smooth muscles
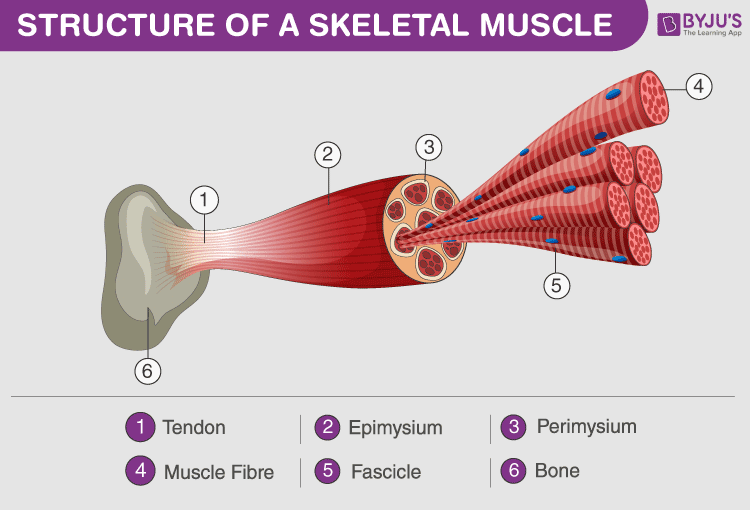
5. Which of the following are parts of a fascicle?
- Perimysium
- Endomysium
- Both a and b
- Epimysium
Answer: Both a and b
Discussion: Fascicles are a bundle of muscle fibres. A muscle has many fascicles, each of which is covered by a tissue called perimysium. Likewise, each muscle fibre is itself covered by a tissue called endomysium. Epimysium is the layer of connective tissue which covers the entire muscle.
6. Statement 1: Myofibrils have thick and thin myofilaments
Statement 2: Thick myofilaments consist of actin. Thin myofilaments constitute myosin.
- Both statements are true
- Both statements are false
- Statement 1 is true and statement 2 is false
- Statement 2 is true and statement 1 is false
Answer: c. Statement 1 is true and statement 2 is false
Discussion: Myofilaments are filaments in myofibrils which play a role in muscle contraction. Here, the thin filament contains the actin protein and the thick filament contains myosin.
7. Which of the following statements are not true about the sarcomere?
- The portion between successive M-lines is the sarcomere
- I-band is also called the dark band
- The Z-line bisects I-band
- The A-band is held together by the M-line
- 1 and 2
- 1, 3, 4
- 2 and 3
- Only 2
Answer: a. 1 and 2
Discussion: Sarcomere is the region between Z-lines that forms the functional unit. This Z-line bisects the light band or I-band. The I-band is followed by the A-band, which is held together by the M-line.
8. During muscle contraction, which of the following shortens?
- A band
- I-band
- Sarcomere
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 1 and 3
- 1,2 and 3
Answer: b. 2 and 3
Discussion: During muscle contraction, the I-band is reduced in size as the overlap between the thin and thick filaments increases. The Z-lines come together, and so the sarcomere shortens as well. However, the A band does not change length during muscle contraction, since its length is the same as the length of the thick filaments.
9. G-actin or globular actin is the monomer of
- Filamentous actin
- Troponin
- Tropomyosin
- Myosin
Answer: a. Filamentous actin
Discussion: Each actin (thin) filament is made of two F (filamentous) actin molecules helically wound around each other. Each F actin is a polymer of monomeric G (globular) actins. Two filaments of another protein, tropomyosin, also run close to the F actin molecules throughout their lengths.
Troponin is a complex protein, which is distributed at regular intervals on tropomyosin.
10. With which of the following molecules do calcium ions released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum bind?
- Myosin
- Actin
- Troponin
- Tropomyosin
Answer: c. Troponin
Discussion: When an action potential arrives, calcium ions are released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum into the sarcoplasm. They bind with the troponin molecules. Binding with the troponin molecules causes the strands of tropomyosin to shift, thereby exposing the myosin-binding sites on the thin filaments.
11. Arrange the order of events in the cross-bridge cycle:
- The myosin head pulls the actin filament towards the M-line
- The myosin head releases ADP and phosphate
- The myosin head hydrolases ATP
- The myosin head binds actin
- 1,2,3,4
- 1,3,2,4
- 2,3,1,4
- 3,4,1,2
Answer: d. 3,4,1,2
Discussion: The cross-bridge cycle events are as follows:
- The myosin head hydrolases ATP and is full of energy
- Myosin head binds actin
- Then, the myosin head pulls the actin filament
- Myosin head releases ADP and P (phosphate)
12. What happens to a muscle fibre when it is constantly acted upon by stimuli?
- The muscle stops contracting
- Tetanic contraction
- The duration of response decreases
- The muscle relaxes
Answer: b. Tetanic contraction
Discussion: If the stimuli for contraction reach a muscle at a high rate, the muscle would have no time to relax; the contractions would overlap, and the muscle, as a result, would continuously twitch or contract. This is called tetanic contraction or tetanic twitch.
13. Which of the following is not included in the axial skeleton system?
- Skull
- Pelvic girdle
- Vertebral column
- Sternum
Answer: b. Pelvic girdle
Discussion: Axial skeleton comprises 80 bones distributed along the main axis of the body. The skull, the vertebral column, the sternum and the ribs constitute the axial skeleton. The appendicular skeletal system is present along the lateral axis of the body. It consists of the pectoral girdle, pelvic girdle, bones of arms and bones of legs.
14. Which part of the vertebral column is considered a vestigial tail?
- 7 fused sacral vertebrae
- 5 fused sacral vertebrae
- 5 fused coccygeal vertebrae
- 4 fused coccygeal vertebrae
Answer: d. 4 fused coccygeal vertebrae
Discussion: Bones of the cervical, thoracic and lumbar vertebrae do not fuse. Five sacral vertebrae are fused forming the sacrum and 4 coccygeal vertebrae fuse to form the vestigial tail.
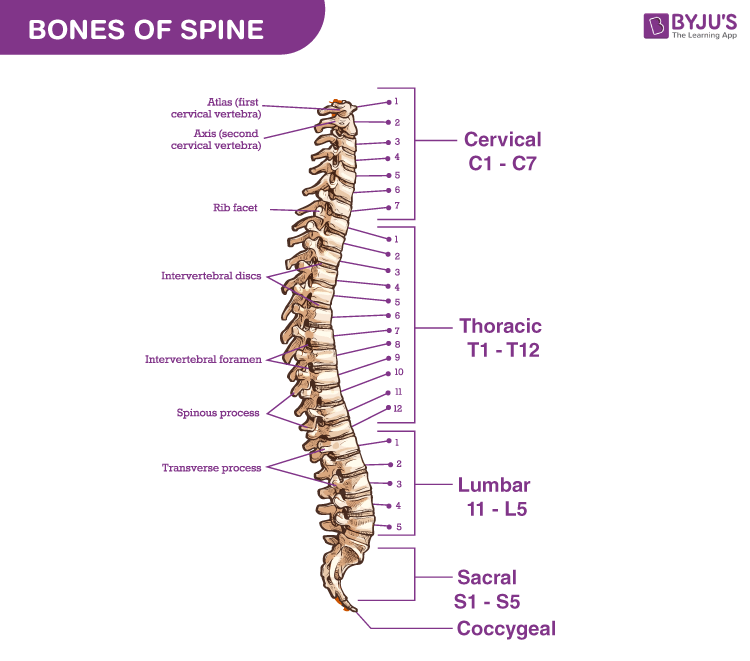
Explore: Bones of Spine
15. ⸻ pairs of ribs are called false ribs
- First 7
- 8th, 9th and 10th
- 11th and 12th
- 6th, 7th and 8th
Answer: b. 8th, 9th and 10th
Discussion: There are 12 pairs of ribs in the human body. The ribs that are dorsally connected to the thoracic vertebrae and ventrally connected to the sternum are called true ribs (vertebrosternal ribs). But the 8th, 9th and 10th pair are connected ventrally to the 7th rib by cartilage and not to the sternum directly. So, they are called false ribs (vertebrochondral ribs).
16. Acetabulum joins or articulates with
- Two coxal bones
- Head of humerus
- Sternum
- Head of thigh bone
Answer: d. Head of thigh bone
Discussion: The acetabulum is the depression on the surface of the pelvis. The head of the thigh bone or femur meets with the pelvis at the acetabulum, forming the hip joint.
17. Match the following
|
Column 1 |
Column 2 |
||
|---|---|---|---|
|
A |
Ligament |
1 |
Muscle to bone |
|
B |
Tendon |
2 |
Bone to bone |
|
C |
Fibrous cartilage |
3 |
Intervertebral discs |
- A-2, B-1, C-3
- A-1, B-2, C-3
- A-1, B-3, C-2
- A-2, B-3, C-1
Answer: a. A-2, B-1, C-3
Discussion:
- Tendons are fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. They have different shapes and sizes. They are flexible enough to move and support the bones.
- Ligaments are connective tissues that have a lot of collagen fibres in them. They connect bones to bones. They also allow movement and flexibility.
- Cartilage is a smooth, elastic connective tissue. It consists of a firm, elastic matrix called chondrin, which is secreted by cells called chondrocytes. In cartilaginous joints, the bones involved are joined together with the help of fibrous cartilages like in intervertebral discs.
18. Which of the following joints does not allow any movement?
- Fibrous joints
- Cartilaginous joints
- Synovial joints
- Hinge joint
Answer: a. Fibrous joints
Discussion: Fibrous joints are commonly found in the skull where flat skull bones are connected by the dense white fibrous connective tissues. This type of joint doesn’t allow any movement.
19. The leg bones do not rub against each other when the knee moves back and forth while a person walks. Which among the following is responsible for it?
- Smooth muscle sheath
- Synovial fluid
- Articular cartilage
- Both b and c
Answer: d. Both b and c
Discussion: A layer of smooth articular cartilage is present between the articular (adjoining) surfaces of the bones. Along with it, a clear, thick liquid is between the joints called synovial fluid. This synovial fluid lubricates the surfaces that glide past each other. It also prevents the bones from rubbing against each other.
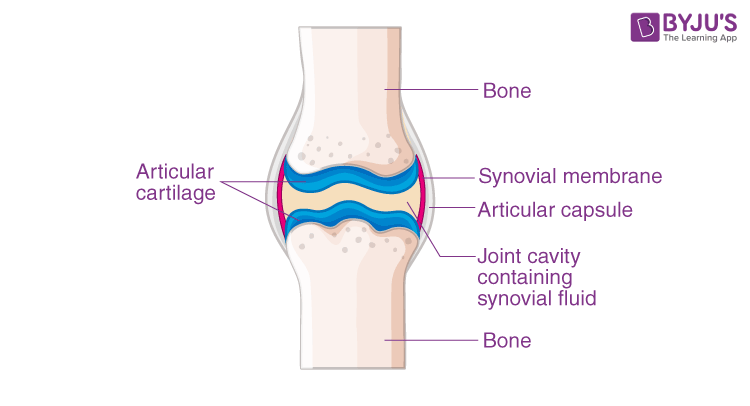
20. Match the following
|
Column 1 |
Column 2 |
||
|---|---|---|---|
|
A |
Inflammation of the joints |
1 |
Osteoporosis |
|
B |
Wild contraction of the muscles |
2 |
Tetany |
|
C |
Decreased bone mass and increased chances of fractures |
3 |
Arthritis |
- A-2, B-1, C-3
- A-1, B-2, C-3
- A-1, B-3, C-2
- A-3, B-2, C-1
Answer: d. A-3, B-2, C-1
Discussion:
- Tetany occurs due to the low calcium concentration in the body fluid. Here, wild contractions or spasms of the muscle take place. Voicebox, feet and hand are the common parts of the body which are affected by tetany.
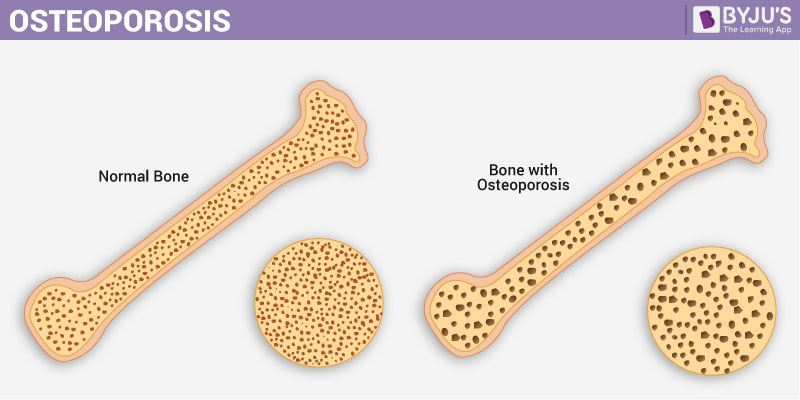
- Osteoporosis is an age-related disorder characterised by decreased bone mass, porous bones and increased chances of fracture. It is caused due to decreased levels of oestrogen and worsens with age.
- Arthritis is an inflammatory disease which causes the inflammation of the joints and causes joint pain and stiffness. It usually worsens with age.
Explore the next chapter’s important questions with regards to NEET, only at BYJU’S. Do check here for the important notes on Locomotion and Movement.
Recommended Video:

Related Concepts:
Comments